When Should I Go To The Emergency Room
You might also have unusually strong side effects from your cancer treatment. While your healthcare provider likely gave you medication to help control your side effects, you should go to the emergency room if your side effects continue despite medication.
Many cancer treatments affect your immune system, increasing the chance you will develop infections. Symptoms that might require an emergency room visit during treatment are:
- Fever of 100.5 and above.
- Persistent nausea and vomiting.
What Is The Chance I Could Die In The Next 5 Years
The average 5-year survival rate for all people with breast cancer is 89%. The 10-year rate is 83%, and the 15-year rate is 78%. If the cancer is located only in the breast , the 5-year survival rate is 99%. More than 70% of breast cancers are diagnosed at an Early Stage.
All survival statistics are primarily based on the stage of breast cancer when diagnosed. Some of the other important factors are also listed below that affect survival.
Stage 0 breast cancer can be also described as a pre-cancer. If you have DCIS you can be quite confident you will do well. DCIS does not spread to other organs. What can be concerning is when an invasive cancer grows back in the area of a prior lumpectomy for DCIS. This type of local recurrence does carry a risk to your life. Luckily, this does not happen frequently. Also, be aware that those who have had DCIS in the past are at a higher risk for developing an entirely new, invasive breast cancer. Take our video lesson on Non-Invasive DCIS to learn more.
Stage I invasive breast cancer has an excellent survival rate. The chance of dying of Stage I breast cancer within five years of diagnosis is 1 to 5% if you pursue recommended treatments.
Stage II breast cancer is also considered an early stage of breast cancer. There is a slightly increased risk to your life versus a Stage I breast cancer. Altogether, the risk of Stage II breast cancer threatening your life in the next 5 years is about 15%.
What Is Stage 3 Breast Cancer
Also called locally advanced breast cancer, stage 3 breast cancer is a more advanced form of invasive breast cancer. Cancer cells have spread from the milk ducts into the nearby lymph nodes, the skin of the breast, or the chest wall.
Stage 3 breast cancer may further be classified into substages stage 3A, 3B, and 3C depending on the size of the breast tumor and the extent of the cancer spread. Notably, breast cancer stages are sometimes referred to using Roman numerals, such as stage III instead of stage 3.
Recommended Reading: Metastatic Breast Cancer Treatment Drugs
What Is Stage 4 Breast Cancer
Also known as metastatic breast cancer, the cancer in this stage has spread beyond the breast, underarm and internal mammary lymph nodes to other parts of the body near to or distant from the breast. The cancer has spread elsewhere in the body. The affected areas may include the bones, brain, lungs or liver and more than one part of the body may be involved.
At stage 4, TNM designations help describe the extent of the disease. Higher numbers indicate more extensive disease. Most commonly, stage 4 breast cancer is described as:,
- T: T1, T2, T3 or T4 depends on the size and/or extent of the primary tumor.
- N1: Cancer has spread to the lymph nodes.
- M1: The disease has spread to other sites in the body.
Relative Survival Rate By Stage
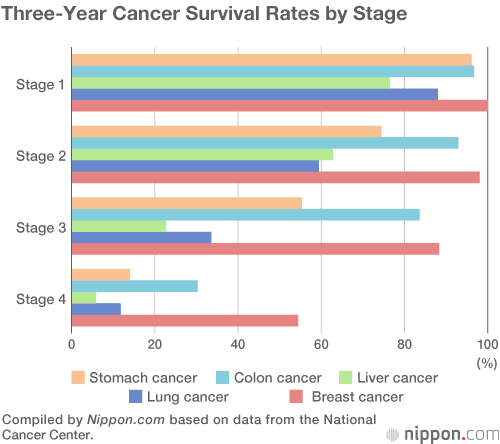
The survival rates by stage are based on the stage at the time of diagnosis. Youâve probably been given a number and letter for your cancer stage. Here, the terms localized, regional, and distant are used instead of numbers and letters. Hereâs what they mean and the 5-year relative survival rates for each:
- Localized breast cancer is only in the breast. This includes stage IA , some IIA , and some IIB . The 5-year relative survival rate is 99%.
- Regional breast cancer has spread to nearby tissue or lymph nodes. This includes stage IB , some IIA , some IIB , and all stage III . The 5-year relative survival rate is 86%.
- Distant breast cancer has spread to other parts of the body. This includes stage IV, pronounced âstage 4â). The 5-year relative survival rate is 28%.
Recommended Reading: Can Anyone Get Breast Cancer
What Tumor Factors Threaten My Life More
There are important tumor biology factors not well reflected in survival statistics by breast cancer stage. Below we list a few important factors that carry a higher risk to life beyond just the stage of cancer. You must ask your surgeon or medical oncologist to explain your receptor status and give you a copy of your biopsy pathology report.
Triple Negative Receptor breast cancer
Triple negative breast cancer is considered a more aggressive breast cancer. Invariably it does require chemotherapy. If you have triple negative breast cancer the risk of dying is higher than the standard statistics usually quoted for a particular stage of breast cancer . Learn more about Triple Negative Breast Cancer with our video lesson
HER2-Positive breast cancer
HER2-positive breast cancers are also more aggressive tumors. But the good news is that we now have incredibly effective, targeted chemotherapy and immunotherapy for HER2-positive cancers. Our video lesson covers HER2-Positive Breast Cancer in more detail .
Breast Cancer at a Young Age
Women younger than 40 have a higher chance of being diagnosed with a more advanced stage breast cancer. Also, the specific cancer type younger women develop has a higher chance of being more aggressive . As a result, age is a relative risk factor for survival.
Untreated breast cancer
Teaching everyone to be an expert in their own breast cancer care.
What Does It Mean When A Breast Is Inoperable
If your physician uses the word âinoperable,â it may simply mean that a simple surgery at this time would not be enough to get rid of all the breast cancer that is within the breast and the tissue around the breast. There must be healthy tissue at all of the margins of the breast when it is removed. Keep in mind that the breast tissue goes beyond the breast mound â it goes up to the clavicle and down to a few inches below the breast mound. There must also be tissue to close the chest wound after the surgery is performed.
Read Also: How Many Women Survive Breast Cancer
Breast Cancer Prognosis: Fear Hope And Understanding Survival Rates
Following a breast cancer diagnosis, its natural to wonder about your prognosis. Prognosis refers to the overall outlook of a disease how well it generally responds to treatment and how it may affect your life expectancy. A prognosis cant predict the future for any one individual. Its important to discuss your cancer prognosis with your doctor to better understand the road ahead.
Stage 3b Breast Cancer
Stage 3B breast cancer means a tumour of any size that has spread to other tissues near the breast such as skin, muscles, or ribs. At this stage, the tumour may or may not have spread to the lymph nodes. However, the cancer has not spread to other distant parts of the body.
Cancer that has spread to the skin of the breast might be inflammatory breast cancer, a rare form of cancer which can be aggressive and challenging to treat.
Recommended Reading: How To Cope With Breast Cancer
What Does Stage 3 Mean
Because stage 3 breast cancer has spread outside the breast, it can be harder to treat than earlier stage breast cancer, though that depends on a few factors.
With aggressive treatment, stage 3 breast cancer is curable however, the risk that the cancer will grow back after treatment is high.
Doctors further divide stage 3 cancer into the following stages:
What Questions Should I Ask My Doctor
You will have lots of questions about your cancer, starting with your diagnosis. Here are some basic questions you might ask:
- What is triple negative breast cancer?
- How do you know my cancer is triple negative breast cancer?
- Why did I get this cancer?
- Do I need genetic testing?
- Has my breast cancer spread, and if so, how far has it spread?
- What is the stage of my cancer?
- What is my prognosis or expected outcome?
- What treatments do you recommend?
- Why do you recommend those treatments?
- What are those treatment side effects?
- Will I need surgery? If so, what surgery do you recommend and why?
- Im interested in participating in clinical trials. Are you able to help me find one?
- Do you know if there are any local support groups?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Triple negative breast cancer is one of the more challenging breast cancers to treat. You might be discouraged by what you have read about triple negative breast cancer. But there are a number of very effective treatments for triple negative breast cancer, including immunotherapy, chemotherapy, surgery and radiation. And every day researchers learn more about this rare cancer. Their knowledge is your power. If youre concerned you arent getting the straight story about your cancer, ask your healthcare provider to walk you through your diagnosis and treatment options.
Don’t Miss: What Is Radiation Therapy For Breast Cancer
What Is Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Before discussing how invasive ductal carcinoma is staged and what those stages mean, it may be helpful to explain exactly what this malignancy is.Invasive ductal carcinoma involves the ducts that carry milk from the lobules to the nipples. The malignancy develops when cancerous cells form in one of these ducts and then spread to the surrounding tissues or lymph nodes. Invasive ductal carcinoma is the most common type of breast cancer, accounting for approximately 80% of the total number of cases.
Invasive ductal carcinoma can cause the following symptoms:
- A lump within the breast or the underarm area
- Pain or swelling in one breast
- Redness or a rash on a breast
- Dimpling around a nipple
- Inward turning of a nipple
- Discharge from a nipple
- Other changes in the size, shape or feel of a breast
These symptoms can be difficult to notice, especially when invasive ductal carcinoma hasnt yet progressed past its early stages, so its important to perform monthly breast examinations and consult with a physician about any noticeable changes, even if they appear minor.
Notably, many individuals with invasive ductal carcinoma also have ductal carcinoma in situ , a type of noninvasive breast cancer that occurs when cancerous cells remain confined to the milk duct rather than spreading to nearby tissues. Although DCIS is often considered to be precancerous and preinvasive, it can become invasive and begin spreading to surrounding tissues if left untreated.
Factors That Influence Breast Cancer Prognosis
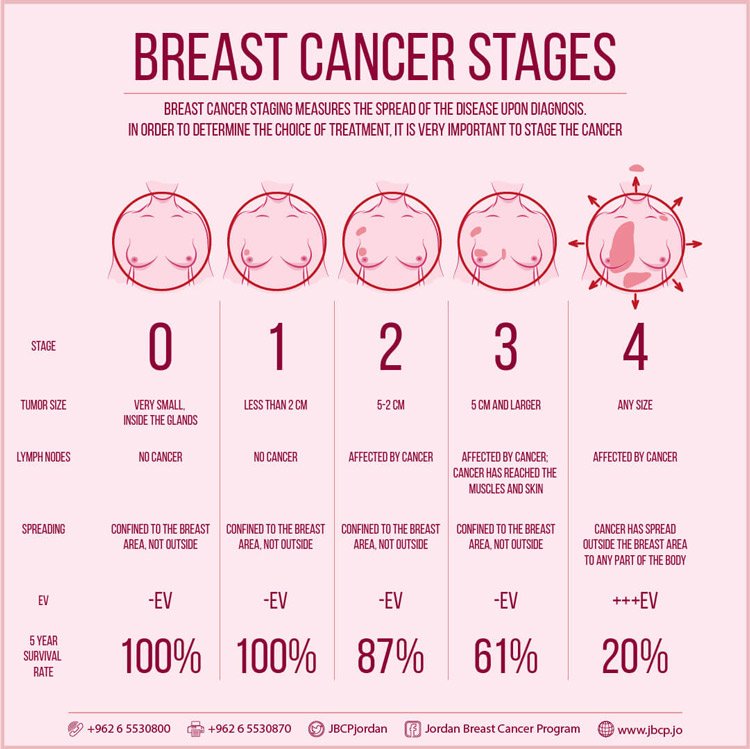
The stage of a persons breast cancer is an important predictor of their prognosis. The stages of the disease range from 0 to 4 . Stages can also have substages, denoted by a letter . These are based on factors such as tumor size and types of cancer cells. A doctor will determine a persons stage at diagnosis, based on how far the cancer has spread throughout the body.
For early-stage and locally advanced breast cancer , a doctor will consider the following variables when estimating a persons prognosis:
- Tumor grade, which pertains to how abnormal the cancer cells look under a microscope compared to normal cells
- How many lymph nodes contain cancer cells
Additionally, there are important genetic features present in some breast cancers that also factor into treatment options and prognosis:
- HER2 status Whether or not the cancer cells contain high levels of a protein called human epidermal growth factor receptor 2
- Hormone receptor status Whether the cancer cells contain the estrogen receptor or progesterone receptor
- The genetic profile of the tumor, as determined by a diagnostic test such as Oncotype Dx
Early detection of breast cancer leads to a better prognosis. If the breast cancer has spread to other parts of the body, then it is known as metastatic breast cancer or stage 4 breast cancer. The presence of metastases has a negative impact on breast cancer survival.
You May Like: What Does Breast Cancer Lumps Look Like
What Causes Breast Cancer Recurrence
The goal of cancer treatments is to kill cancer cells. But, cancer cells are tricky. Treatments can reduce tumors so much that tests dont detect their presence. These weakened cells can remain in the body after treatment. Over time, the cells get stronger. They start to grow and multiply again.
Even surgery to remove a cancerous tumor isnt always 100% effective. Cancer cells can move into nearby tissue, lymph nodes or the bloodstream before surgery takes place.
Dcis Breast Cancer Survival Rate
The DCIS breast cancer treatment prognosis is very good as it is non-invasive. The survival rate usually not depends upon selected treatment option, as treatment is totally depended upon patient condition, means the size of the tumor. The usual finding shows that the general mortality rate from breast cancer after at 20 years of diagnosis is 3.3% 5,6.
Read Also: What Are The Symptoms Of Breast Cancer With Pictures
Prognosis For Stage 2 Breast Cancer
In stage 2 breast cancer, cancer cells have continued to multiply in the breast tissue and possibly nearby lymph nodes. The standard treatment is still surgery, although chemotherapy and drug therapy may be used in some cases. The five-year survival rate for stage 2 breast cancer is usually greater than 90 percent.
What Is The Survival Rate For Triple
What is the survival rate for triple-positive breast cancer? The relative 5-year survival rate for stage 3 breast cancer is 86 percent, according to the American Cancer Society . This means that out of 100 people with stage 3 breast cancer, 86 will survive for 5 years.
Is triple-positive breast cancer worse? Triple-Positive vs.
At first glance, it would seem triple-positive breast cancer would offer the best prognosis, followed by tumors that are ER-positive or HER2-positive, with triple-negative tumors having the worst outcomes. However, that doesnt appear to be the case.
Is triple-positive breast cancer treatable? See Triple-negative Breast Cancer to learn more. Triple-positive breast tumors are HER2-positive, ER-positive, and PR-positive. These cancers are treated with hormone drugs as well as drugs that target HER2.
What does it mean to have triple-positive breast cancer? Triple-positive refers to breast tumors that are ER-, PR- and HER2-positive. It means the cancer cells grow in response to estrogen , progesterone and a growth-promoting protein thats on the outside of all breast cells known as HER2.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Best Treatment For Stage 1 Breast Cancer
Talk With Others Who Understand
MyBCTeam is the social network for people with breast cancer and their loved ones. On MyBCTeam, over 57,000 members come together to ask questions, give advice, and share their stories with others who understand life with breast cancer.
Have you or a loved one been diagnosed with breast cancer? Did your doctor give you a detailed prognosis? Share your experiences in the comments below, or start a conversation by posting on MyBCTeam.
The Tnm Staging System
The breast cancer staging system, called the TNM system, is overseen by the American Joint Committee on Cancer . The AJCC is a group of cancer experts who oversee how cancer is classified and communicated. This is to ensure that all doctors and treatment facilities are describing cancer in a uniform way so that the treatment results of all people can be compared and understood.
In the past, stage number was calculated based on just three clinical characteristics, T, N, and M.
The T category describes the original tumor:
-
HER2 status: are the cancer cells making too much of the HER2 protein?
- Advertisement
Oncotype DX score, if the cancer is estrogen-receptor-positive, HER2-negative, and there is no cancer in the lymph nodes
Adding information about tumor grade, hormone-receptor status, HER2 status, and possibly Oncotype DX test results has made determining the stage of a breast cancer more complex, but also more accurate.
In general, according to experts, the new staging system classifies triple-negative breast cancer at a higher stage and classifies most hormone receptor-positive breast cancer at a lower stage.
You also may see or hear certain words used to describe the stage of the breast cancer:
-
Distant: The cancer is found in other parts of the body as well.
The updated AJCC breast cancer staging guidelines have made determining the stage of a cancer a more complicated but accurate process. So, the characteristics of each stage below are somewhat generalized.
Recommended Reading: Can You Get Breast Cancer At Any Age
Screening For Breast Cancer
Women aged between 50 and 74 are invited to access free screening mammograms every two years via the BreastScreen Australia Program.
Women aged 40-49 and 75 and over are also eligible to receive free mammograms, however they do not receive an invitation to attend.
It is recommended that women with a strong family history of breast or ovarian cancer, aged between 40 and 49 or over 75 discuss options with their GP, or contact BreastScreen Australia on 13 20 50.
Survival Statistics For Breast Cancer
Survival statistics for breast cancer are very general estimates and must be interpreted very carefully. Because these statistics are based on the experience of groups of people, they cannot be used to predict a particular persons chances of survival.
There are many different ways to measure and report cancer survival statistics. Your doctor can explain the statistics for breast cancer and what they mean to you.
Recommended Reading: How Many Stages Are There To Breast Cancer
Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
Ductal carcinoma in situ is breast cancer of the milk ducts. The milk ducts are canals that take milk from the milk glands to the nipple.
Without treatment, DCIS can spread and become more aggressive. In about half of all cases, DCIS may become invasive cancer.
A doctor may recommend an MRI scans or a mammogram and a biopsy to diagnose breast cancer and determine its stage.
They will stage a cancer from 0 to 4. A higher stage indicates more advanced disease.
To determine the stage of breast cancer, doctors look at three factors:
- T, or the size of the breast tumor.
- N, or the spread of the cancer to lymph nodes, and how many it has affected.
- M, or the cancer has spread to other areas of the body, which is known as metastasis.
There are four stages of breast cancer after stage 0:
- Stage 1: The tumors are small and have spread very little, if at all.
- Stage 2: At this stage, the tumors are slightly larger and have spread to nearby tissue but not other organs. They may infect a small number of lymph nodes or a limited section of nearby tissue.
- Stage 3: These cancers are larger and have spread further than stage 2 tumors. They may infect wider areas of breast tissue or several nearby lymph nodes but not other organs.
- Stage 4: The cancer cells have spread to other organs in the body.
Doctors may divide each stage into A and B categories.
Donât Miss: Secondaries Breast Cancer