What Is The Treatment For Her2
Specialized breast cancer treatments, known as targeted therapies, have been developed to treat breast cancers that express the HER2 protein. Targeted therapies are newer forms of cancer treatment that specifically attack cancer cells and do less damage to normal cells than traditional chemotherapy. Targeted therapies for HER2-positive breast cancer include the following:
- Trastuzumab is an antibody against the HER2 protein Adding treatment with trastuzumab to chemotherapy given after surgery has been shown to lower the recurrence rate and death rate in women with HER2-positive early breast cancers. Using trastuzumab along with chemotherapy has become a standard adjuvant treatment for these women.
- Pertuzumab also works against HER2-positive breast cancers by blocking the cancer cellâs ability to receive growth signals from HER2.
- Lapatinib is another drug that targets the HER2 protein and maybe given combined with chemotherapy. It is used in women with HER2-positive breast cancer that is no longer helped by chemotherapy and trastuzumab.
- T-DM1 or ado-trastuzumab emtansine is a combination of Herceptin and the chemotherapy medication emtansine. Kadcyla was designed to deliver emtansine to cancer cells by attaching it to Herceptin.
Read Also: What Chemo Drugs Are Used For Triple Negative Breast Cancer
Stage 3 Lung Cancer Symptoms
Early stage lung cancer may produce no visible symptoms. There may be noticeable symptoms, such as a new, persistent, lingering cough, or a change in a smokers cough . These symptoms may indicate that the cancer has progressed to stage 3.
Other symptoms may include:
- trouble breathing, being winded or short of breath
- pain in chest area
- bone pain
- headache
What Hormones Does Suzanne Somers Use
I use an estrogen cream every day and progesterone cream two weeks a month. Thats why, at 62, I dont require any pharmaceutical drugs. Fugh-Berman: Menopausal hormone therapy DOUBLES the risk of dementia, according to data from the Womens Health Initiative, and increases age-related memory problems, too.
Also Check: Is Er Positive Breast Cancer Hereditary
Where Do These Numbers Come From
The American Cancer Society relies on information from the SEER* database, maintained by the National Cancer Institute , to provide survival statistics for different types of cancer.
The SEER database tracks 5-year relative survival rates for breast cancer in the United States, based on how far the cancer has spread. The SEER database, however, does not group cancers by AJCC TNM stages . Instead, it groups cancers into localized, regional, and distant stages:
- Localized: There is no sign that the cancer has spread outside of the breast.
- Regional: The cancer has spread outside the breast to nearby structures or lymph nodes.
- Distant: The cancer has spread to distant parts of the body such as the lungs, liver or bones.
What Is Stage Iii
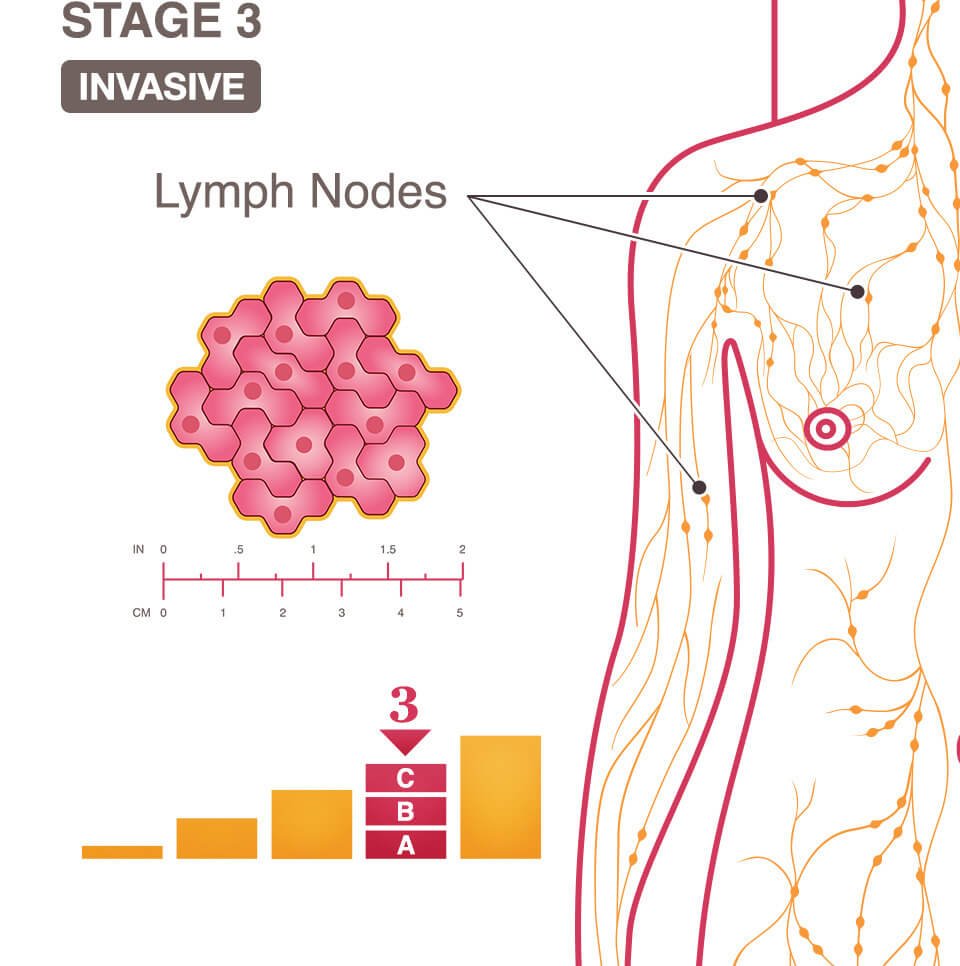
In this stage, I tell my patients the real war against the cancer begins, Cruz said. Spreading is much more advanced.
According to Cruz, stage III is unique in that it has three subcategories: IIIA, IIIB and IIIC.
IIIA has tumors all larger than five millimeters and has spread to lymph nodes. Cruz said the higher number of lymph nodes with cancer cells, the more advanced it is.
In stage IIIB, the tumor has spread to the chest wall and skin of the breast. In many cases, this spreading can result in swelling or ulcers. The cancer cells have also spread to nine lymph nodes.
There is advanced spreading in stage IIIC: the cancer has spread to the chest wall, skin of the breast, 10 or more lymph nodes and the collarbone.
In stage III, yes there is advanced spreading. Yes it is harder to treat, but not untreatable, Cruz said. Thats what we tell our patients, although the spreading is scary, we can still fight it.
Read Also: Breast Cancer Recurrence After 10 Years
Don’t Miss: Breast Cancer Stage 3
Breast Examination After Treatment For Breast Cancer
After surgery
The incision line may be thick, raised, red and possibly tender for several months after surgery. Remember to examine the entire incision line.
If there is redness in areas away from the scar, contact your physician. It is not unusual to experience brief discomforts and sensations in the breast or nipple area .
At first, you may not know how to interpret what you feel, but soon you will become familiar with what is now normal for you.
After breast reconstruction
Following breast reconstruction, breast examination for the reconstructed breast is done exactly the same way as for the natural breast. If an implant was used for the reconstruction, press firmly inward at the edges of the implant to feel the ribs beneath. If your own tissue was used for the reconstruction, understand that you may feel some numbness and tightness in your breast. In time, some feeling in your breasts may return.
After radiation therapy
After radiation therapy, you may notice some changes in the breast tissue. The breast may look red or sunburned and may become irritated or inflamed. Once therapy is stopped, the redness will disappear and the breast will become less inflamed or irritated. At times, the skin can become more inflamed for a few days after treatment and then gradually improve after a few weeks. The pores in the skin over the breast also may become larger than usual.
What to do
What Does A Breast Cancer Diagnosis Mean
You may have received a diagnosis for breast cancer, or maybe you know someone who has received a diagnosis. What does that mean, exactly? Are there any similar threads that run through a breast cancer diagnosis? Some, but each breast cancer is unique to the person, as is each specific treatment protocol. Breast cancer is not a one-size-fits-all disease.
Before diagnosis, I thought all breast cancers were the same. I have since learned otherwise.
Breast cancer. When you hear those words, either by your own diagnosis or by the diagnosis of someone you know or love, its devastating. Thats it.
Your initial reactions run through you, knocking over any amount of sense you thought you had, with no regard for your sanity. You tell yourself to calm down, to try and think, damnit! Yet, the moment swallows you and from that moment on, you know that youll never forget where you were or what you were doing.
I. Have. Breast. Cancer.
What the hell does that mean? Do I have early stage? Late stage? Has it spread? Is it encapsulated? Is it common? Is it aggressive? Do my breasts have to be cut off? Do I need chemotherapy? How about radiation? Do I get to keep most of my lymph nodes? Will I lose my hair? Will I be sick? Will I get to live after I endure the medical community and their science? What is my prognosis? Will it come back? If it does come back, does that effect my survival rate?
What the hell does my particular diagnosis mean?!
This much I know for sure.
Also Check: Breast Cancer Spread To Lungs Prognosis
Early Stage Clinical Trials
In a proof of concept study published in the Lancet, authors investigated olaparib in patients with advanced metastatic breast cancer with germline BRCA1/BRCA2 mutations. They investigated two doses of olaparib at 400 mg BD and 100 mg BD. Approximately half of patients in this study had TNBC with the remainder having other histological subtypes. Patients were heavily pretreated with a median of 3 prior chemotherapy regimens and platinum sensitivity was not needed for trial enrolment. Overall response rates were impressive in this heavily pre-treated population at 41% in the group receiving the higher dose and 22% in the group receiving the lower dose.
Kaufman et al investigated olaparib further in a large phase 2 basket trial with 298 patients in a single-arm study. Patients with any advanced solid-organ malignancy were included if they harboured a gBRCA mutation. In the breast cohort, patients may have received multiple lines of treatment and there was no requirement for platinum sensitivity. Response rates were modest with only 8 of 62 patients responding in this unselected population.
Treatment Of Breast Cancer Stages I
The stage of your breast cancer is an important factor in making decisions about your treatment.
Most women with breast cancer in stages I, II, or III are treated with surgery, often followed by radiation therapy. Many women also get some kind of systemic drug therapy . In general, the more the breast cancer has spread, the more treatment you will likely need. But your treatment options are affected by your personal preferences and other information about your breast cancer, such as:
- If the cancer cells have hormone receptors. That is, if the cancer is estrogen receptor -positive or progesterone receptor -positive.
- If the cancer cells have large amounts of the HER2 protein
- How fast the cancer is growing
- Your overall health
- If you have gone through menopause or not
Talk with your doctor about how these factors can affect your treatment options.
Don’t Miss: Tubular Cancer Of The Breast
What Is Stage 3 Triple Negative Breast Cancer
Typically, triple-negative breast cancer patients will receive a combination of surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy.
Research shows that survival rates are higher when chemotherapy is used to shrink the tumor before surgery. Doing chemotherapy before surgery usually means fewer cancer cells in the body at the time time of surgery. This makes it less likely for cancer cells to spread to other areas of the body during the surgery.
Another option to treat triple-negative breast cancer is using drugs that inhibit the poly ADP-ribose polymerase enzyme. Particularly in patients that also test positive for BRCA mutation, PARP inhibitors make it harder for the cancer cells to survive.
Finally, a combination of immunotherapy and chemotherapy may treat advanced triple-negative breast cancer that tested positive for the PD-L1 protein. Immunotherapy helps the patients immune system work harder to fight the cancer cells, in this case also fighting the PD-L1 protein.
If you or someone you know has been diagnosed with triple-negative breast cancer, request an appointment to meet with one of our breast cancer specialists located in the Denver area, Colorado Springs, Boulder, and other areas throughout the Colorado Front Range. We are also happy to quickly schedule a second opinion to help you with making the cancer treatment decision youre confident in.
What Is Stage Iv Breast Cancer
Stage IV is the most advanced stage of breast cancer. It has spread to nearby lymph nodes and to distant parts of the body beyond the breast. This means it possibly involves your organs such as the lungs, liver, or brain or your bones.
Breast cancer may be stage IV when it is first diagnosed, or it can be a recurrence of a previous breast cancer that has spread.
Also Check: What Does Stage 3 Cancer Mean
Stage Iiia Iiib & Iiic Treatment Options
Stage III is divided into subcategories known as IIIA, IIIB, and IIIC.
In general, stage IIIA describes invasive breast cancer in which either:
- no tumor is found in the breast or the tumor may be any size cancer is found in 4 to 9 axillary lymph nodes or in the lymph nodes near the breastbone or
- the tumor is larger than 5 centimeters small groups of breast cancer cells are found in the lymph nodes or
- the tumor is larger than 5 cm cancer has spread to 1 to 3 axillary lymph nodes or to the lymph nodes near the breastbone
Still, if the cancer tumor measures more than 5 cm across and:
it will likely be classified as stage IB.
In general, stage IIIB describes invasive breast cancer in which:
- the tumor may be any size and has spread to the chest wall and/or skin of the breast and caused swelling or an ulcer
- may have spread to up to 9 axillary lymph nodes or
- may have spread to lymph nodes near the breastbone
Still, if the cancer tumor measures more than 5 cm across and:
it will likely be classified as stage IIA.
Inflammatory breast cancer is considered at least stage IIIB. Typical features of inflammatory breast cancer include:
- reddening of a large portion of the breast skin
- the breast feels warm and may be swollen
- cancer cells have spread to the lymph nodes and may be found in the skin
In general, stage IIIC describes invasive breast cancer in which:
Still, if the cancer tumor measures any size and:
it will likely be classified as stage IIIA.
What Does It Mean To Have Stage 4 Breast Cancer

Stage 4 breast cancer means that the cancer has spread to other areas of the body, such as the brain, bones, lung and liver.
Although Stage 4 breast cancer is not curable, it is usually treatable and current advances in research and medical technology mean that more and more women are living longer by managing the disease as a chronic illness with a focus on quality of life as a primary goal. With excellent care and support, as well as personal motivation, Stage 4 breast cancer may respond to a number of treatment options that can extend your life for several years.
Recommended Reading: Is Invasive Breast Cancer Curable
What Does The Pain Feel Like When You Have Breast Cancer
Breast cancer can cause changes in skin cells that lead to feelings of pain, tenderness, and discomfort in the breast. Although breast cancer is often painless, it is important not to ignore any signs or symptoms that could be due to breast cancer. Some people may describe the pain as a burning sensation.
Survival Rates For Triple
Triple-negative breast cancer is considered an aggressive cancer because it grows quickly, is more likely to have spread at the time its found, and is more likely to come back after treatment than other types of breast cancer. The outlook is generally not as good as it is for other types of breast cancer.
Survival rates can give you an idea of what percentage of people with the same type and stage of cancer are still alive a certain amount of time after they were diagnosed. They cant tell you how long you will live, but they may help give you a better understanding of how likely it is that your treatment will be successful.
Keep in mind that survival rates are estimates and are often based on previous outcomes of large numbers of people who had a specific cancer, but they cant predict what will happen in any particular persons case. These statistics can be confusing and may lead you to have more questions. Talk with your doctor about how these numbers may apply to you, as he or she is familiar with your situation.
Also Check: Stage 1 Breast Cancer Prognosis
What Is The Staging Of Triple
Staging is the process of determining the extent of the cancer and its spread in the body. Together with the type of cancer, staging helps determine the appropriate therapy and predict the chances for survival.
To determine if the cancer has spread, medical professionals may use several different imaging techniques, including X-ray, CT scans, bone scans, and PET scans. Staging depends upon the size of a tumor and the extent to which it spread to lymph nodes or distant sites and organs in the body. Examination of lymph nodes removed at surgery and the results of ER, PR, and HER2 tests performed on the tumor tissue also help determine the stage of a tumor. Stage I is the lowest stage, while stage IV is the highest stage and refers to tumors that have metastasized, or spread to areas distant from the breast.
Most doctors specifically adjust breast cancer treatments to the type of cancer and the staging group.
Surgery
Many women with breast cancer will require surgery. Broadly, the surgical therapies for breast cancer consist of breast-conserving surgery and mastectomy .
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy destroys cancer cells with high-energy rays. Doctors commonly administer radiation therapy to patients after breast cancer surgery, most commonly after lumpectomy.
Chemotherapy
Types of chemotherapy include the following:
Other therapies for triple-negative breast cancer
Read Also: Anne Hathaway Breast Cancer
Nac Regimens And Surgical Methods
Three different NAC regimens were used: ED , FEC and EC . For the pts who underwent EC and most of the pts who underwent FEC, a further four cycles of D were then administered. Each chemotherapy regimen was administered every three weeks for four cycles however, this interval was prolonged by at least one week if the pt did not recover from the adverse effects. Subsequent to the completion of the four cycles of NAC, we evaluated the clinical responses and performed surgery within 23 weeks. The surgical methods included Pateys procedure in three pts, mastectomy in 16 pts and lumpectomy in three pts. All pts underwent level I+II ALN dissection. In addition, the three pts who received Pateys procedure underwent level III lymph node dissection.
You May Like: Signs Of Stage 3 Breast Cancer
Is Triple Negative Breast Cancer An Aggressive Form Of Cancer
Its true that triple negative breast cancers can grow quickly. But your prognosis or expected outcome depends on more factors than your cancer subtype. Healthcare providers will also consider your tumors size and whether it has spread to your lymph nodes and other parts of your breast. Its also helpful to know researchers are focusing on ways to slow the spread of TNBC.
Stages Of Breast Cancer
The stages of breast cancer range from 0 to IV .
The highest stage is any cancer with metastases , no matter the size of the tumor, the lymph node status or other factors. This is known as metastatic breast cancer and is the most advanced stage of breast cancer.
Most often, the higher the stage of the cancer, the poorer the prognosis will be.
The table below lists the TNM classifications for each stage of breast cancer for people who have surgery as their first treatment.
| When TNM is |
| IV |
|
*T1 includes T1mi. **N1 does not include N1mi. T1 N1mi M0 and T0 N1mi M0 cancers are included for prognostic staging with T1 N0 M0 cancers of the same prognostic factor status. ***N1 includes N1mi. T2, T3 and T4 cancers with N1mi are included for prognostic staging with T2 N1, T3 N1 and T4 N1, respectively. |
|
Used with permission of the American College of Surgeons, Chicago, Illinois. The original source for this information is the AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, Eighth Edition published by Springer International Publishing. |
Don’t Miss: Youngest Age To Have Breast Cancer