Are There Any Side Effects
Radiation therapy is usually well tolerated and many patients are able to continue their normal routines. However, some patients may eventually develop painful side effects. Be sure to talk to a member of your radiation oncology treatment team about any problems or discomfort you may have. Many of the side effects of radiation therapy are only in the area being treated. For example, a breast cancer patient may notice skin irritation, like a mild to moderate sunburn, while a patient with cancer in the mouth may have soreness when swallowing. Some patients who are having their midsection treated may report feeling sick to their stomach. These side effects are usually temporary and can be treated by your doctor or other members of the treatment team.
Side effects usually begin by the second or third week of treatment, and they may last for several weeks after the final radiation treatment. In rare instances, serious side effects develop after radiation therapy is finished. Your radiation oncologist and radiation oncology nurse are the best people to advise you about the side effects you may experience. Talk with them about any side effects you are having. They can give you information about how to manage them and may prescribe medicines or changes in your eating habits to help relieve your discomfort.
Dealing With Feelings Of Sadness
If you have continued feelings of sadness, have trouble getting up in the morning or have lost motivation to do things that previously gave you pleasure, you may be experiencing depression. This is quite common among people who have had cancer.
Talk to your GP, as counselling or medication even for a short time may help. Some people can get a Medicare rebate for sessions with a psychologist. Ask your doctor if you are eligible. Cancer Council may also run a counselling program in your area.
For information about coping with depression and anxiety, call beyondblue on 1300 22 46 36. For 24-hour crisis support, call Lifeline on 13 11 14.
What Are The Different Kinds Of Radiation Therapy
Most radiation therapy is administered by a radiation oncologist at a radiation center and usually begins three to four weeks after surgery. The radiation is used to destroy undetectable cancer cells and reduce the risk of cancer recurring in the affected breast.
There are two main kinds of radiation therapy that may be considered, and some people have both.
- External Beam Breast Cancer Radiation
- Internal Breast Cancer Radiation
Keep in mind that the course of treatment you decide is something you should discuss with your radiation oncologist in order to ensure that it is as effective as possible.
Don’t Miss: Can I Have Breast Cancer At 14
Keeping Health Insurance And Copies Of Your Medical Records
Even after treatment, its very important to keep health insurance. Tests and doctor visits cost a lot, and even though no one wants to think of their cancer coming back, this could happen.
At some point after your treatment, you might find yourself seeing a new doctor who doesnt know about your medical history. Its important to keep copies of your medical records to give your new doctor the details of your diagnosis and treatment. Learn more in Keeping Copies of Important Medical Records.
Nerve Damage Around The Treatment Area
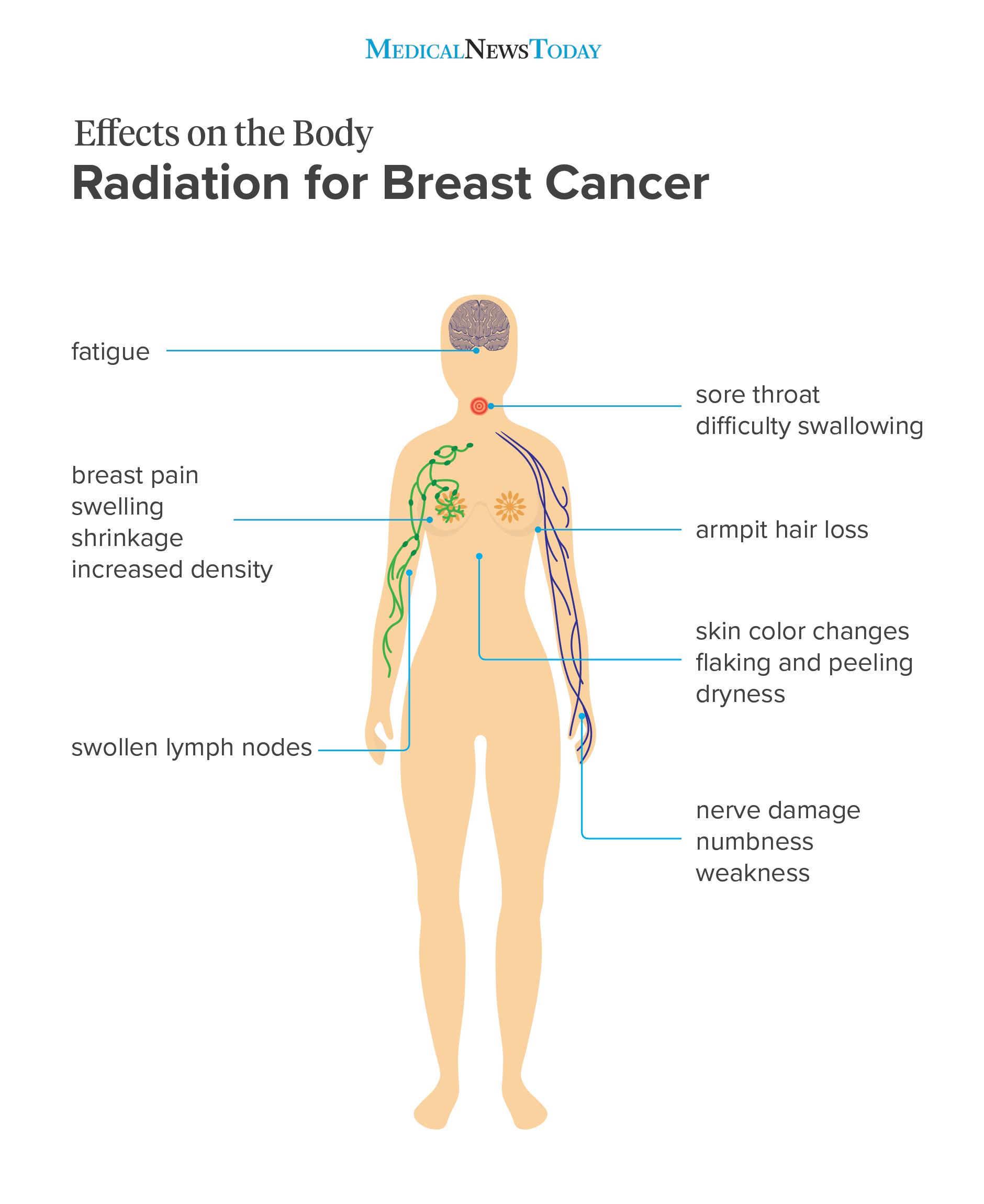
Scaring from radiotherapy may cause nerve damage in the arm on the treated side. This can develop many years after your treatment. Symptoms include tingling, numbness, pain, and weakness. In some people, it may cause some loss of movement in the arm and shoulder.
Speak to your doctor if you notice any of these symptoms.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Treatment For Triple Negative Breast Cancer
External Beam Radiation Therapy
The most common way of delivering radiation to the breast is with a treatment machine called a linear accelerator, which delivers radiation beams from outside the body, targeting the whole breast or chest wall.
The patient is positioned on a bed and the head of the linear accelerator is lined up to focus the radiation to the targeted area. At each treatment appointment additional time is taken to ensure the correct positioning of the patient prior to treatment delivery. Once correctly positioned, the treatment takes only a few minutes to deliver. The head of the linear accelerator moves around the patient, delivering the beams. Patients do not feel the treatment being delivered.
Although the radiation therapists leave the room while the treatment is being given, they monitor the patients on closed circuit television and through microphones in the treatment room.
What Happens After Radiation Therapy Treatment Ends
Once treatment ends, you will have follow-up appointments with the radiation oncologist. It’s important to continue your follow-up care, which includes:
-
Checking on your recovery
-
Watching for treatment side effects, which may not happen right away
As your body heals, you will need fewer follow-up visits. Ask your doctor for a written record of your treatment. This is a helpful resource as you manage your long-term health care.
Recommended Reading: Where Can Breast Cancer Lumps Appear
How Does Radiation Therapy Work
Radiation therapy uses special high-energy X-rays or particles to damage a cancer cells DNA. When a cancer cells DNA is damaged, it cant divide successfully and it dies.
Radiation therapy damages both healthy cells and cancer cells in the treatment area. Still, radiation affects cancer cells more than normal cells. Cancer cells grow and divide faster than healthy cells and also are less organized. Because of this, it’s harder for cancer cells to repair the damage done by radiation. So cancer cells are more easily destroyed by radiation, while healthy cells are better able to repair themselves and survive the treatment.
The treatment area may include the breast area, the lymph nodes, or another part of the body if the cancer has spread.
Radiation treatments are carefully planned to make sure you receive the greatest benefits and the fewest side effects possible.
- Brachytherapy/Internal Radiation
- Internal radiation, called brachytherapy by doctors, uses a radioactive substance sealed in seeds or tiny tubes that are placed inside your body directly into the cancer or the place where the cancer was. Read about brachytherapy.
Another type of radiation therapy, called intraoperative radiation therapy, is a type of partial-breast radiation. With intraoperative radiation therapy, the entire course of radiation is delivered at one time during breast cancer surgery. Read more about intraoperative radiation therapy.
Radioprotective Drugs For Reducing Side Effects
One way to reduce side effects is by using radioprotective drugs, but these are only used for certain types of radiation given to certain parts of the body. These drugs are given before radiation treatment to protect certain normal tissues in the treatment area. The one most commonly used today is amifostine. This drug may be used in people with head and neck cancer to reduce the mouth problems caused by radiation therapy.
Not all doctors agree on how these drugs should be used in radiation therapy. These drugs have their own side effects, too, so be sure you understand what to look for.
Don’t Miss: What Happens After Radiation Treatment For Breast Cancer
Pain And Skin Changes
During and just after treatment, your treated breast may be sore. Talk with your health care provider about using mild pain relievers such as ibuprofen, naproxen or acetaminophen to ease breast tenderness.
The treated breast may also be rough to the touch, red , swollen and itchy. Sometimes the skin may peel, as if sunburned. Your provider may suggest special creams to ease this discomfort.
Sometimes the skin peels further and the area becomes tender and sensitive. This is called a moist reaction. Its most common in the skin folds and the underside of the breast.
If a moist reaction occurs, let your radiation team know. They can give you creams and pads to make the area more comfortable until it heals.
Fatigue is common during radiation therapy and may last for several weeks after treatment ends.
Fatigue is mainly a short-term problem, but for some, it can persist .
You may feel like you dont have any energy and may feel tired all of the time. Resting may not help.
Regular exercise, even just walking for 20 minutes every day, may help reduce fatigue . Getting a good nights sleep is also important.
Talk with your health care provider if you are fatigued or have problems sleeping .
Learn more about fatigue and insomnia.
Why Do Some Women Refuse Treatments For Their Breast Cancer
Adjuvant therapy after surgery, such as chemotherapy, hormonal therapy, and radiation therapy, has contributed to a 39% decrease in breast cancer mortality since 1989. Unfortunately, a significant number of women decline evidence-based adjuvant therapy. A recent study suggests that distrust of the medical system plays a significant role in such refusal.
I write about alternative cancer treatments a lot, in particular the lack of evidence for such practices, many of which are at best pseudoscientific and at worst pure mystical nonsense. The reason, of course, is simple. Im a breast cancer surgeon, and I hate seeing people who might be saved from death due to cancer falling prey to treatments that demonstrably lessen their chances of survival, either by leading patients to reject effective treatment in favor of ineffective or even harmful treatments or, at the very least, to delay effective treatment until the patient realizes that the quackery chosen isnt preventing the growth and spread of his or her tumor. This can sometimes take a long time. Ive seen women with breast cancer whose breasts were basically eaten away until there was nothing left but an ulcerated mass on their chestmore than that, a bleeding, rotting, malodorous ulcerated mass. Yes, its an ugly picture, but Ive seen it all too many times.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Percentage Of Getting Breast Cancer
What Is Radiation Therapy And How Does It Work
Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells. It affects cells only in the part of the body that is treated with the radiation. Breast cancer radiation therapy may be used to destroy any remaining mutated cells that remain in the breast or armpit area after surgery.
Note: There are special situations in which radiation is used for women with metastatic breast cancer experiencing painful bone metastasis. This section however focused on the use of radiation for adjuvant therapy .
Who should expect to be prescribed radiation therapy and what is involved?Some people with Stage 0 and most people with Stage 1 invasive cancer and higher, who have had a lumpectomy, can expect radiation therapy to be a part of their treatment regimen.
Vitamins To Avoid During Radiation Therapy
Your radiation oncologist may tell you to avoid taking certain antioxidant vitamin supplements, such as vitamins C, A, D, and E, while you’re having radiation therapy. These vitamins might interfere with radiation’s ability to destroy cancer cells.This is because radiation works in part by creating free radicals highly energized molecules that damage cancer cells. Free radicals in the environment can damage all cells, but in the case of radiation treatment they are focused on the cancer cells. Antioxidants help keep free radicals from forming or neutralize them if they do form.
Because of the potential conflict between the goal of radiation therapy and the goal of antioxidants , it makes sense to stop taking any antioxidant supplements during radiation therapy. When radiation is finished, you can resume taking your supplements.
Throughout your treatment, do your best to eat a well-balanced diet that contains all of the vitamins you need. Vitamins that come naturally from food are unlikely to interfere with treatment.
Read Also: How Successful Is Chemotherapy For Breast Cancer
What Are The Types Of Radiation Therapy
- External radiation therapy
- External radiation therapy is given from a special machine . The patient never becomes radioactive.
- Internal radiation therapy
- Internal radiation therapy is when the source of radiation is placed inside the body near the cancer cells. The length of time the implant is in place depends upon the type of implant received.
Radiation Therapy Uses High Energy X
Its a localised treatment affecting only the area which is specifically targeted. Although some healthy tissue may be in the treatment area, it generally has the ability to repair itself, unlike cancer cells.
In early breast cancer, radiation therapy is used with the aim of getting rid of any malignant or pre-cancerous cells remaining in the breast following partial mastectomy or lumpectomy. This reduces the risk of developing a local recurrence of cancer in the breast in the future. Radiation therapy is also used to treat the chest wall after mastectomy if the cancer has high-risk features.
The regional lymph nodes in the axilla , supraclavicular fossa or internal mammary chain may also be treated in some cases.
In these settings, large international trials have demonstrated that radiation therapy reduces the incidence of local breast cancer recurrence.
Radiation therapy is usually given after surgery, once the wounds have healed. For people needing chemotherapy, radiation is given after that treatment has been completed.
Read Also: What Is The Prognosis For Metastatic Breast Cancer
Radiation Therapy Side Effects
The side effects of radiation therapy depend on the type of radiation therapy youre having. In general, the side effects tend to develop as treatment goes on and may be more troubling toward the end of treatment. Overall, the most common side effects are redness, swelling, and skin peeling in the area being treated. Read more about radiation therapy side effects.
Change In Breast Shape Size And Colour
If youve had radiotherapy after breast-conserving surgery, the breast tissue on the treated side may feel firmer than before, or the breast may be smaller and look different.
Although this is normal, you may be concerned about differences in the size of your breasts, or worry that the difference is noticeable when youre dressed.
You can discuss this with your breast surgeon to see if anything can be done to make the difference less noticeable.
Also Check: What To Say To Someone Diagnosed With Breast Cancer
What Happens To My Job If I Get Cancer
Ultimately, its going to depend on where you work, what kind of job you have, and who you work for. If you work in a position that requires a modest amount of physical labor, for example, you may have a hard time performing the required duties once you start treatment. If, on the other hand, you have a remote, work-from-home position, you may be able to keep working without too much interruption.
While employers are not supposed to discriminate based on medical conditions, unfortunately, it does happen from time to time. In these cases, you can submit complaints with the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission.
Physician Trust Versus A More Generalized Distrust
How could these results be? The authors note that attempts to increase physician trust as a strategy to reduce mistrust in the healthcare system have had results ranging from zero to very modest, which makes sense if patients view the two issues as separate. I like to make an analogy to Congress. Voters routinely express extreme distrust of Congress, but most voters actually like their own representative. Similarly, its not hard to envision how most patients might actually like and trust their own doctors, while simultaneously having a great deal of mistrust for the health care system as a whole.
As the authors note:
So what to do?
The authors note that improving trust in the healthcare system will require more than just trying to build trust in patients physicians, noting:
If ordinary businesses can learn to increase trust in their brands, why not the same with health care institutions? Dean says.
Read Also: What Does Breast Cancer Cause
What Happens Before Radiation Therapy Treatment
Each treatment plan is created to meet a patient’s individual needs, but there are some general steps. You can expect these steps before beginning treatment:
Meeting with your radiation oncologist. The doctor will review your medical records, perform a physical exam, and recommend tests. You will also learn about the potential risks and benefits of radiation therapy. This is a great time to ask any questions or share concerns you may have.
Giving permission for radiation therapy. If you choose to receive radiation therapy, your health care team will ask you to sign an “informed consent” form. Signing the document means:
-
Your team gave you information about your treatment options.
-
You choose to have radiation therapy.
-
You give permission for the health care professionals to deliver the treatment.
-
You understand the treatment is not guaranteed to give the intended results.
Simulating and planning treatment. Your first radiation therapy session is a simulation. This means it is a practice run without giving radiation therapy. Your team will use imaging scans to identify the tumor location. These may include:
-
An x-ray
Depending on the area being treated, you may receive a small mark on your skin. This will help your team aim the radiation beam at the tumor.
You may also be fitted for an immobilization device. This could include using:
-
Tape
-
Plaster casts
These items help you stay in the same position throughout treatment.
Do I Need Genetic Counseling And Testing
Your doctor may recommend that you see a genetic counselor. Thats someone who talks to you about any history of cancer in your family to find out if you have a higher risk for getting breast cancer. For example, people of Ashkenazi Jewish heritage have a higher risk of inherited genetic changes that may cause breast cancers, including triple-negative breast cancer. The counselor may recommend that you get a genetic test.
If you have a higher risk of getting breast cancer, your doctor may talk about ways to manage your risk. You may also have a higher risk of getting other cancers such as ovarian cancer, and your family may have a higher risk. Thats something you would talk with the genetic counselor about.
Links with this icon indicate that you are leaving the CDC website.
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website’s privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance on other federal or private website.
Recommended Reading: What Are Signs Of Breast Cancer In Males