Estrogen Receptors And Antiestrogen Resistance
Two ER genes have been identified: the classical ER on human chromosome 6q25.1 and ER on chromosome 14q2225. Each receptor acts as a nuclear transcription factor that binds responsive elements within the promoters of target genes or binds to other proteins and affects their abilities to regulate transcription . ER and ER homology is limited in the transcriptional regulatory domains, particularly in the N-terminal region. Both ER homodimers and heterodimers are formed and these may differ in their ability to affect transcription at some promoters . For example, the ER binds directly to EREs, which are broadly defined consensus sequences with some tolerance to variation in their sequence. ER also binds to, and regulates the transcriptional activation of, other transcription factors including AP-1, SP-1, and at cyclic AMP response elements .
Figure 1
Drugs That Lower Estrogen Levels
Some drugs, called aromatase inhibitors , stop the body from making estrogen in tissues such as fat and skin. But, these drugs do not work to make the ovaries stop making estrogen. For this reason, they are used mainly to lower estrogen levels in women who have been through menopause . Their ovaries no longer make estrogen.
Premenopausal women can take AIs if they are also taking drugs that stop their ovaries from making estrogen.
Aromatase inhibitors include:
- Exemestane
Ht After Breast Cancer
The relative risk for a breast cancer recurrence due to the use of HT wasexamined in a systematic review by Col et al. .Altogether 11 trials with 669 breast cancer patients who had received HT wereanalysed. Merely 4 of the 11 trials included a control group and in these nosignificantly increased recurrence rate could be detected. The yearly recurrencerate amounted to 4.2% after an observation period of 30 months. A recurrence ofbreast cancer was diagnosed in 17 patients under HT in comparison to 66patients without HT . Taken together, in a total of 11 analysedstudies on 669 breast cancer patients with HT there was nosignificant increase in the recurrence of breast cancer with an RR of 0.82 . The case numbers in these studies were, however, toosmall to enable an unambiguous conclusion to be drawn about the safety of HT in thispatient collective.
The effects of systemic HT after breast cancer disease were examined in 2independent, prospective randomised trials.
You May Like: What Is Stage Three Cancer
B Er Coregulators In Breast Cancer
Accumulating evidence shows that ER target gene expression results from the coordinated actions of ER and its coregulators, which include both coactivators and corepressors . Most of these coregulators contain a LXXLL motif that interacts with the ligand binding domain of ER. These coregulators more often are associated with various enzymatic properties, e.g., acetyltransferase, deacetylases, methyltransferase, phosphokinase, ubiquitin ligase, and ATPases, that regulate chromatin remodeling, thereby directly or indirectly regulating target gene expression . For instance, coactivator p300, a histone acetyl transferase , acetylates histones on ER’s target gene chromatin, which facilitates opening of ER target chromatin and recruitment of transcription initiation complex that activates E2-responsive gene transcription . SWI/SNF complex, an ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling complex, is also known to regulate ER transcriptional activity .
1. Coactivators in breast cancer
2. Corepressors in breast cancer
Breast Cancer Risk Before Menopause
A pooled analysis of data from 7 studies found higher blood estrogen levels is linked to an increased risk of breast cancer in premenopausal women .
Study selection criteria: Prospective nested case-control studies with at least 100 breast cancer cases, pooled analyses and meta-analyses.
Table note: Relative risks above 1 indicate increased risk. Relative risks below 1 indicate decreased risk.
This table shows breast cancer risk related to total estradiol levels.
|
Study |
Study Population |
Risk of Breast Cancer in Women with Higher Estradiol Levels Compared to Women with Lower Estradiol LevelsRelative Risk |
|
New York University Womens Health Study |
||
|
Nurses Health Study II |
||
|
UK Collaborative Trial of Ovarian Cancer Screening |
||
|
Melbourne Collaborative Cohort Study |
||
|
Study of Osteoporosis Fractures Research Group |
||
|
1.73 |
* Relative risk for estrogen receptor-positive and progesterone receptor-positive breast cancers was 2.8 . Relative risk for estrogen receptor-negative and progesterone receptor-negative breast cancers was 1.1 .
Relative risk for ER-positive cancers only. Relative risk for ER-negative breast cancers was 1.65 .
Results are for estradiol blood levels measured in the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle. Results for estradiol levels measured in the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle were not statistically significant.
|| Relative risk for women with higher levels of free estradiol compared to women with lower levels of free estradiol was 1.75 .
Also Check: Stage 3 Breast Cancer
An Overview Of Antiestrogen Resistance
Despite the relative safety and significant antineoplastic and chemopreventive activities of antiestrogens, most initially responsive breast tumors acquire resistance . It is unlikely that any single mechanism or single gene confers antiestrogen resistance. Rather, several mechanisms likely exist that encompass pharmacologic, immunological, and molecular events. These mechanisms, none of which are fully understood, likely vary within tumors. Intratumor variability in antiestrogen responsiveness will reflect the presence of multiple cell subpopulations . Since breast cancers appear highly plastic and adaptable to selective pressures, the intratumor diversity in antiestrogen responsive subpopulations also likely changes over time. Tumors appear capable of dynamically remodeling their cell populations in response to changes in host immunity or endocrinology, or the administration of local or systemic therapies. This plasticity is probably both cellular and molecular .
A different resistance phenotype has been described in human breast cancer xenografts that exhibit a switch to a TAM-stimulated phenotype. This mechanism of clinical but not pharmacologic resistance may not be the dominant antiestrogen resistance phenotype. If the prevalence of acquired resistance phenotypes in ER+ tumors broadly reflects what is seen in de novo resistance, then the dominant resistance phenotype is a loss of antiestrogen responsiveness.
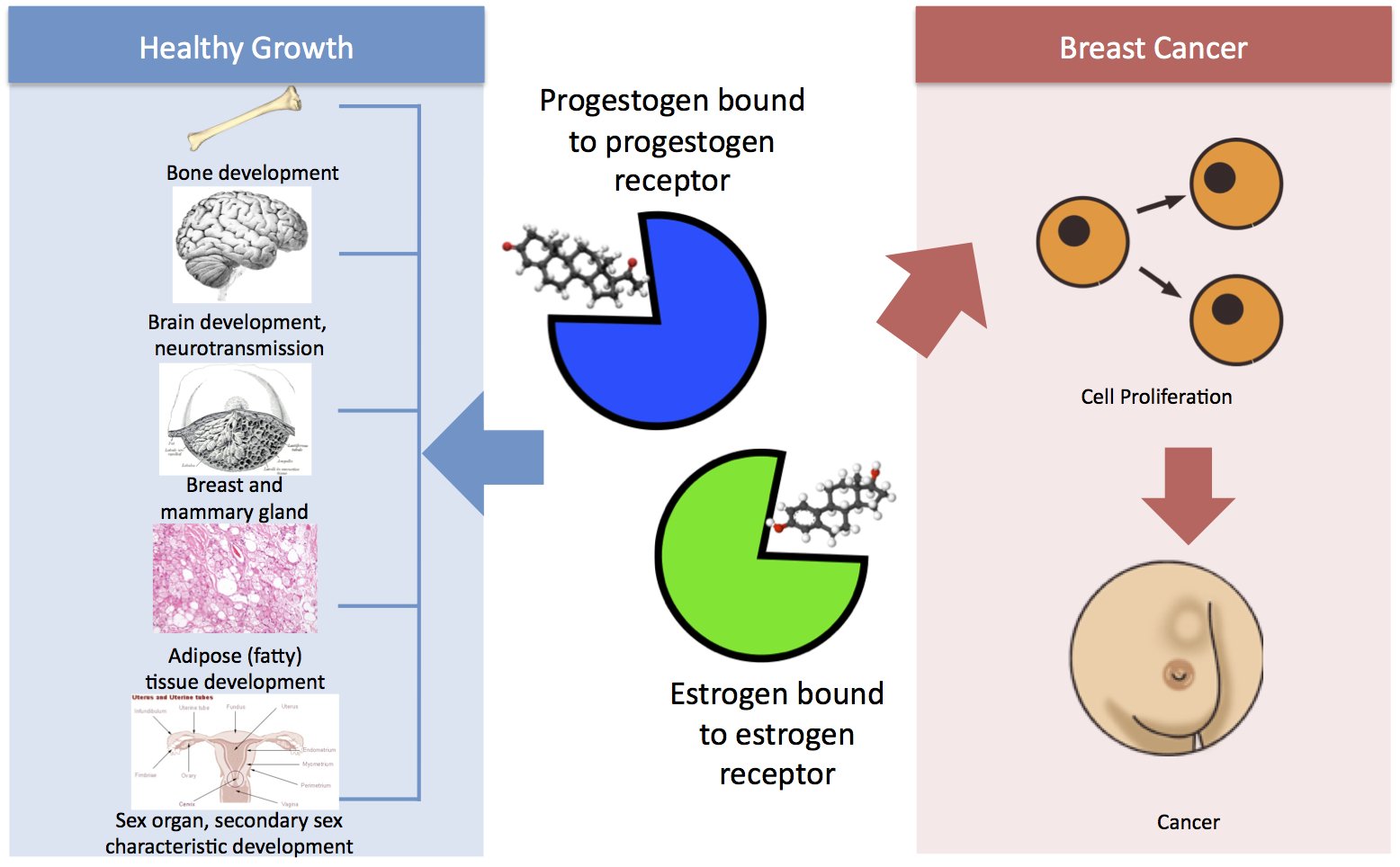
Combination Of Estradiol And Progesterone Had A Greater Effect On Cell Proliferation
Next, we treated MCF-7 cells with E2 alone, progesterone alone, or a combination of both. In the cell viability assay, treatment of MCF-7 cells with either E2 or progesterone had a continuous viability promotion effect, although progesterone appeared to have a relatively lower ability to promote viability than estradiol. Notably, after combined treatments with E2 and progesterone, MCF-7 cells showed the highest viability among all groups . Moreover, in the colony formation assay, a combination of E2 and progesterone resulted in greater colony numbers than single treatments in MCF-7 cells . These data indicated that E2 combined with progesterone promoted higher proliferation than either single treatment.
Figure 2.ABvs
Read Also: Symptoms Of Breast Cancer In Teenagers
Estrogen And Breast Cancer Risk
Estradiol, and possibly estrone, increase the risk of developing breast cancer. And a lower level of these estrogens throughout a woman’s lifetime is associated with a lower risk of developing breast cancer.
Factors such as pregnancy and breastfeeding alter estrogen levels in ways that are believed to have a protective effect. Having a first child before the age of 30, having more children, and breastfeeding are all associated with a lower risk of breast cancer. This is due to the reduced production of estrogens during pregnancy and lactation .
Because oral contraceptives and hormone replacement therapies contain estrogen, there is a small potential they may increase the risk of breast cancer for some women.
While we know that estrogen receptor-positive breast cancers are worsened by estrogen, other breast cancer types typically are also more common among women who have had a higher lifetime exposure to estrogen.
Minimize Exposure To Heavy Metals
Heavy metals including copper, cobalt, arsenic, cadmium, mercury and lead have been found to stimulate estrogen receptors. Sources of arsenic include some brands of rice, seafood, well water cadmium is high in cigarettes and can be found in some soils mercury is mainly prevalent in larger fish and old dental amalgams and lead contamination is a component of air pollution, paint and dyes, and ceramic glazes among other sources.
Essentially, heavy metal and toxin exposure is hard to completely avoid in our world, even with careful choices. Because of this, I advise my patients to use compounds that provide safe, gentle detoxification of heavy metals and other contaminants, on a daily or periodic basis.
Modified citrus pectin, is derived from the pith of citrus fruit and has been shown in human studies to remove harmful heavy metals and reduce toxic body burden over time. MCP is able to cross the intestinal barrier and circulate in the bloodstream, where it binds to toxins and heavy metals and helps safely excrete them, without removing essential minerals. I also recommend ingredients such alpha-lipoic acid, N-acetyl cysteine, garlic, cilantro and other herbs and nutrients that provide support for our bodys complex detoxification systems.
Also Check: Stage 3 Cancer Symptoms
Gene Networks In Estrogen Receptor
ER expression is both necessary and sufficient to predict responsiveness to antiestrogens in a high proportion of breast tumors. Thus, antiestrogen-induced effects on ER-mediated signaling are almost certainly of critical importance in effecting clinical responses in many tumors. Nonetheless, we still do not know the genes responsible for signaling to these effects, or whether the effects are primarily to induce cell death, repress cell survival, or a combination of both. As noted above, ER-independent events may also interact with ER-mediated signaling and this may be important in the broader context of a gene network that regulates antiestrogen responsiveness. Thus, estrogens and antiestrogens may differentially affect a gene network that contains some ER-regulated genes . More recently, this concept has been extended to incorporate the likely ability of integrated signals to induce apoptosis while concurrently blocking differentiation and proliferation . It is predicted that such a network would be affected by TAM in TAM-stimulated models by signaling through patterns similar to estradiol. In antiestrogen unresponsive cells, signaling through this network may use different signaling patterns and/or exhibit differential regulation/expression of some of the same genes affected by estradiol.
What Is The Link Between Estrogen And Breast Cancer
About 8 out of 10 breast cancers are hormone receptor-positive. These cancers need estrogen, progesterone or both hormones to grow. Excess exposure to estrogen raises cancer risk. Excess exposure can occur because of:
- Hormone replacement therapies for menopause.
- Naturally high estrogen levels.
- Klinefelter syndrome, a genetic condition affecting men.
In the past, some men took estrogen to treat prostate cancer. Healthcare providers rarely use this treatment now because it increases the risk of male breast cancer.
Read Also: Malignant Neoplasm Of Breast Meaning
Receptors For Breast Cancer
Some breast cancer cells have hormone or protein receptors that affect how the cancer grows.
On this page
Breast cancer cells may have receptors that hormones or a protein called HER2 can attach to and encourage the cells to grow. A pathologist tests the cancer cells that were taken during the biopsy or surgery for these receptors.
The results help you and your doctor decide on the most effective treatment for you.
What Are The Side Effects Of Hormone Therapy

The side effects of hormone therapy depend largely on the specific drug or the type of treatment . The benefits and harms of taking hormone therapy should be carefully weighed for each person. A common switching strategy used for adjuvant therapy, in which patients take tamoxifen for 2 or 3 years, followed by an aromatase inhibitor for 2 or 3 years, may yield the best balance of benefits and harms of these two types of hormone therapy .
Hot flashes, night sweats, and vaginal dryness are common side effects of all hormone therapies. Hormone therapy also may disrupt the menstrual cycle in premenopausal women.
Less common but serious side effects of hormone therapy drugs are listed below.
Tamoxifen
- Breathing problems, including painful breathing, shortness of breath, and cough
- Loss of appetite
Also Check: Stage Iv Breast Cancer Life Expectancy
Chemicals And Additives To Avoid
Many chemicals used in agriculture, body care products, food packaging and plastic water bottles are estrogenic, called xenoestrogens or estrogen mimics. In addition to binding with estrogen receptors, these toxins are fat soluble, so they tend to accumulate in fat cells. We know that breast tissue has a high concentration of fat, particularly after menopause. Studies have shown that breast milk often contains dangerous levels of these chemicals. Reduce exposure by avoiding plastic food and beverage containers, canned foods, and body products with these common chemicals. For a list of chemicals to avoid, visit the Environmental Working Group site.
Ix Estrogen Receptor Subtypes In Breast Cancer
In addition to the above-mentioned E2-related receptors, recently a number of ER splice variants have been reported to be important for breast cancer development. The ER variants such as ER36 and ER46 initiate their transcription from exon 2 of the ER gene. ER46 lacks the first coding exon of ER and acts as an inhibitor for ER functions, whereas ER36 lacks both transcriptional activation domains but retains the DNA binding domain and the ligand binding domain . ER36 is predominantly located in plasma membrane and in the cytoplasm and can be detected in both ER-positive and ER-negative breast cancers . Down-regulation of ER36 mRNA correlated with local progression, lymph node metastasis, and advanced cancer stages, indicating its involvement in breast cancer progression . It appears that ER36 mediates extranuclear and mitogenic E2 signaling in ER-negative breast cancer cells like MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-436 through the EGFR/Src/ERK signaling pathway, implying that ER36 may play an important role in the malignant growth of ER-negative breast cancers . ER36 is also known to be involved in tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer cells. For instance, rapid phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and AKT was detected in ER36-overexpressed MCF7 cells treated with tamoxifen . These subtypes of ER pose an additional layer of complexity to breast cancer development and require attention for further research.
Recommended Reading: Invasive Metastatic Breast Cancer
Signs Of Breast Cancer
Take time to get to know the normal look and feel of your breasts while showering, dressing or looking in the mirror so you can detect any changes that may indicate cancer such as:
- A lump, lumpiness or thickening.
- Changes to the nipple such as a change in shape, crusting, a sore or an ulcer, redness or a nipple that turns in when it used to stick out.
- Changes to the skin of the breast such as dimpling of the skin, unusual redness or other color changes.
- Change in the shape or size of the breast either an increase or decrease.
- Unusual discharge from the nipple without squeezing.
- Swelling or discomfort in the armpit.
- Persistent, unusual pain not related to your normal monthly cycle, which remains after a menstrual period and occurs in one breast only.
Though not necessarily cancer, these signs should be checked by your doctor without delay.
Other resources Ive put together for you:
Diagnosis Of Vaginal Atrophy
When serum estradiol level decreases below 73pmol/l postmenopausal patients candevelop a clinically relevant vaginal atrophy. An exact knowledge of the symptoms ofvaginal atrophy is necessary in order to make a rapid and targeted diagnosis. Thediagnosis of vaginal atrophy is generally made in the course of a gynaecologicalexamination. Here, attention should be paid first of all to dry vaginal mucousmembranes and possible petechial haemorrhages or, respectively, bleeding on contact.Patients often report on accompanying dyspareunia, itching and burning sensations.Furthermore, breakage of collagenous reinforcement fibres in the vaginal epitheliumcan lead to a loss of vaginal membranous folds, the so-called rugae of thevagina.
An increase of the vaginal pH value to a basic value > 5 can be an indication fora vaginal infection caused by reduced colonisation of the vagina by lactobacilli. Asummary of the clinical symptoms of vaginal atrophy is given in .
Table 1Symptoms of a vaginal atrophy .
| Symptoms of vaginal atrophy |
|---|
Due to the close embryological relationship of the female urinary bladder and urethrawith the vaginal system, they all have a high density of estrogen receptors. Thiscan lead to recurrent cystitis and prolapse complaints due to a postmenopausal ortherapy-induced decline of the serum estradiol level.
An algorithm for the clinical diagnosis of vaginal atrophy is presented in .
Table 2Algorithm for clinical diagnosis of vaginal atrophy.
| Vaginal atrophy |
|---|
Recommended Reading: What Does Stage 3b Cancer Mean
What Types Of Hormone Therapy Are Used For Breast Cancer
Several strategies are used to treat hormone-sensitive breast cancer:
Blocking ovarian function: Because the ovaries are the main source of estrogen in premenopausal women, estrogen levels in these women can be reduced by eliminating or suppressing ovarian function. Blocking ovarian function is called ovarian ablation.
Ovarian ablation can be done surgically in an operation to remove the ovaries or by treatment with radiation. This type of ovarian ablation is usually permanent.
Alternatively, ovarian function can be suppressed temporarily by treatment with drugs called gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, which are also known as luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone agonists. By mimicking GnRH, these medicines interfere with signals that stimulate the ovaries to produce estrogen.
Estrogen and progesterone production in premenopausal women. Drawing shows that in premenopausal women, estrogen and progesterone production by the ovaries is regulated by luteinizing hormone and luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone . The hypothalamus releases LHRH, which then causes the pituitary gland to make and secrete LH and follicle-stimulating hormone . LH and FSH cause the ovaries to make estrogen and progesterone, which act on the endometrium .
Examples of ovarian suppression drugs that have been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration are goserelin and leuprolide .