Family History Of Breast Cancer
A positive family history of breast cancer is the most widely recognized risk factor for breast cancer. The lifetime risk is up to 4 times higher if a mother and sister are affected, and it is about 5 times greater in women who have two or more first-degree relatives with breast cancer. The risk is also greater among women with breast cancer in a single first-degree relative, particularly if the relative was diagnosed at an early age .
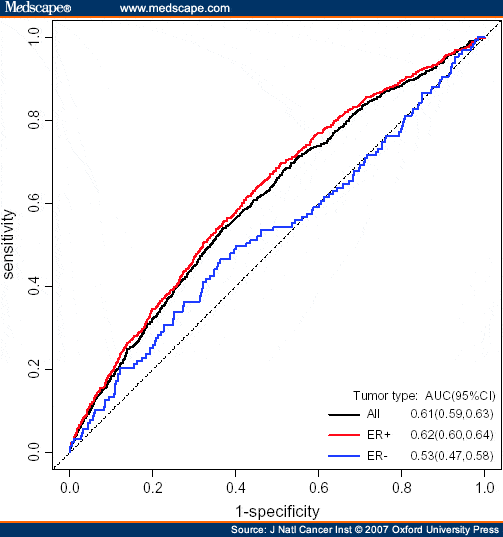
Despite a history indicating increased risk, many of these families have normal results on genetic testing. However, identification of additional genetic variants associated with increased risk may prove valuable. Michailidou et al conducted a controlled genome-wide association study of breast cancer that included 122,977 cases of European ancestry and 14,068 cases of East Asian ancestry, and identified 65 new loci associated with overall breast cancer risk. A GWAS by Milne et al identified 10 variants at 9 new loci that are associated with risk of estrogen receptornegative breast cancer.
A family history of ovarian cancer in a first-degree relative, especially if the disease occurred at an early age , has been associated with a doubling of breast cancer risk. This often reflects inheritance of a pathogenic mutation in the BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene.
The family history characteristics that suggest increased risk of cancer are summarized as follows:
- Ontario Family History Assessment Tool
Direct-to-consumer genetic testing
Core Needle Biopsy Of The Breast
If exams or imaging tests show you might have breast cancer, your doctor might refer you for a core needle biopsy to help find out for sure. This is often the preferred type of biopsy if breast cancer is suspected, because it removes more breast tissue than a fine needle aspiration , but it doesnât require surgery.
During this procedure, the doctor uses a hollow needle to take out pieces of breast tissue from the area of concern. This can be done with the doctor either feeling the area or while using an imaging test to guide the needle.
Biopsy Needle Diameters And Gauges
The outer diameter of the needle used for FNAB ranges from 0.5 to 0.7mm , whereas that of the needle used for CNB ranges from 1.25 to 3.00mm and may be even larger. The mean numbers of samples taken from each breast lesion were 3 for FNAB and 3 or 4 for CNB. Finally, damaged blood vessels will cause semi-static lesion pressure, which, for CNB, may include a volume up to approximately 1cm3 with a pressure of approximately 120mm Hg , potentially causing emissions of blood and cellular material during low-pressure phases until the pressure is again balanced.
You May Like: Triple-negative Breast Cancer Symptoms
Read Also: Is Estrogen Cream Safe For Breast Cancer Survivors
Can Radiologist Tell If It Is Cancer
While even the most advanced imaging technology doesnt allow radiologists to identify cancer with certainty, it does give them some strong clues about what deserves a closer look. Today well discuss a few things that radiologists are on the lookout for when examining mammography and breast ultrasound images.
What Should I Expect During A Breast Biopsy
Patients typically have an FNA or core needle biopsydone in the surgeons office and dont require a trip to the hospital. The medical provider will most likely use medicine to numb the area around where the needle will be inserted. However, this isnt always necessary, specifically with FNA biopsies, as the needle is so small.
The patient will lie on their back and have to remain still during the procedure. An ultrasound may be used to help guide the doctor so they can see where to place the needlethis doesnt hurt but can feel like pressure as they move the handpiece around.
FNA biopsies and core needle biopsies only take a few seconds to obtain, but the entire procedure start to finish typically takes 20-30 minutes to complete.
Since no incisions are needed, patients dont require stitches, but probably will have a small bandage placed over the biopsy site while it heals.
Surgical biopsies are usually done in an outpatient surgical setting. They are more invasive than FNA or core needle biopsies, but patients typically go home after the procedure. In addition to local anesthesia, patients are given intravenous medicationoften called twilight anesthesiato help them feel drowsy. In certain scenarios, patients need general anesthesia, which involves being put into a deep sleep during the procedure.
Read Also: Is Triple Negative Breast Cancer Curable
Read Also: Survival Rate Of Triple Negative Breast Cancer
What Causes Breast Cancer In Your 20s And 30s
Breast cancer happens when cells in the breast begin to grow and multiply abnormally. Changes in DNA can cause normal breast cells to become abnormal.
The exact reason why normal cells turn into cancerous cells is unclear, but researchers know that hormones, environmental factors, and genetics each play a role.
Roughly 5 to 10 percent of breast cancers are linked to inherited gene mutations. The most well known are breast cancer gene 1 and breast cancer gene 2 .
If you have a family history of breast or ovarian cancer, your doctor may suggest testing your blood for these specific mutations.
In some cases, breast cancer in your 20s and 30s has been found to differ biologically from the cancers found in older women.
For example, younger women are more likely to receive a diagnosis of triple-negative and HER2-positive breast cancers than older women.
more likely in adolescent and young women than in older women who have a diagnosis of early stage breast cancer.
Metastatic breast cancer means that the cancer has advanced to stage 4. It has moved beyond the breast tissue into other areas of the body, such as the bones or the brain.
Survival rates are lower for cancer that has metastasized to other parts of the body.
According to the American Cancer Society, the 5-year survival rate for women with breast cancer that has spread to other parts of the body is 28 percent for all ages.
However, some signs and symptoms of breast cancer may
- changes in the skin
Should I Be Worried About A Breast Biopsy
Some patients express concerns about whether a breast needle biopsy might cause cancer to spread. But theres no evidence of a negative long-term effect from a breast needle biopsy. And the benefits of a breast needle biopsy as opposed to a surgical biopsy or no biopsy at all outweigh the risks.
Read Also: What Is The Survival Rate For Stage 0 Breast Cancer
Breast Biopsy In Women 30 Years Old Or Less
Forty women 30 years of age or less underwent breast biopsy at Roswell Park Cancer Institute between January 1980 and January 1989. Thirty-eight of the 40 women had a palpable breast mass. Thirty-one of these young women had self-detected breast masses, and the median duration before presentation was 6 months.
Physical characteristics were described in 30 of the masses. Twenty-three were described as fibroadenomas or smooth, firm, and mobile. Seven masses were described as irregular. The median size of the breast mass was 1.5 cm . Mammography was performed in 20 patients, but results were reported as abnormal in only 6. Twenty of the masses were described histologically as fibroadenoma. Twelve were described histologically as fibrocystic disease or stromal fibrosis. One case was invasive adenocarcinoma.
Probability of serious underlying breast pathology in young women is low but not nil. Noninvasive and minimally invasive techniques are proposed by some authors as cost-efficient methods that may substitute for open biopsy in these patients. Unfortunately, false-negative results persist and are particularly unacceptable in these young women.
What If The Breast Biopsy Test Result Is Positive
Its important to understand that even if a breast biopsy result comes back positive for cancer, it doesnt necessarily mean the patient has advanced or stage IV breast cancer.
In fact, even if your doctor does diagnose you with cancer after a biopsy, it still may be at an early stage that can be treated with surgery, radiation therapy and/or hormonal therapy without chemotherapy being necessary.
Medical procedures have improved leaps and bounds over the years. Many diseases considered as fatal and beyond repair could now be cured with surgeries and medicines. So stay hopeful and know that everything has a solution. Your doctor and nurses will guide you through the way. It is important to inform your loved ones so they could provide emotional support to you as well.
Recommended Reading: What Are Signs Of Metastatic Breast Cancer
What Other Tests Are Involved In Detecting Breast Cancer
Apart from mammograms and ultrasounds, other diagnostic tests may be required to detect breast cancer along with clinical breast examination:
- Magnetic resonance imaging : Imaging of the breast is done using radio waves, magnetic fields, and computer imaging, offering a more detailed picture of the breast than a mammogram. This test is recommended for women with an above-average breast cancer risk due to certain factors such as family history or BRCA mutation.
- Nipple discharge exam: Fluid is collected from nipple discharge and then sent to the lab to look for cancer cells. Most nipple secretions are not cancerous and more likely to be caused by an injury, infection, or benign tumor.
- Genetic screening: Women with elevated risk factors may undergo genetic screening to see if they have mutations that put them at higher risk for developing the disease.
- Biopsy: Surgical removal of suspicious tissues for further examination. The type of biopsy done will depend on the location and size of the breast lump.
Currently, no diagnostic test other than a biopsy is 100% accurate. Since mammograms can cause false positive or false negative results, its important for women to be vigilant about regular self-examination, contact their doctors immediately if they notice anything unusual, and undergo annual testing to ensure early detection.
You May Like: How Can Breast Cancer Be Diagnosed
What Is A Biopsy Of Breast
A breast biopsy is a test that removes tissue or sometimes fluid from the suspicious area. The removed cells are examined under a microscope and further tested to check for the presence of breast cancer. A biopsy is the only diagnostic procedure that can definitely determine if the suspicious area is cancerous.
Read Also: What Is The Treatment For Stage 2 Breast Cancer
Breast Biopsy Questions Answered
Getting a breast biopsy? You might be wondering what it is and how it works.
A breast biopsy is a diagnostic procedure in which a doctor removes a small amount of breast tissue to examine under a microscope. If the tissue sample shows cancer, the physician can have it analyzed further to provide the most accurate diagnosis a critical first step in getting patients the best treatment possible for their particular type of breast cancer.
A biopsy may be ordered when a mammogram or other breast imaging reveals an abnormality or you feel a lump in your breast, or when a physician notices something suspicious during a clinical exam.
We spoke with , to learn more. Heres what she had to say.
What are the types of breast biopsies, and how are they different?
There are two basic types of breast biopsy: surgical and needle. A breast biopsy done surgically through an incision in the skin is called a surgical breast biopsy. A breast biopsy done by inserting a needle through the skin is called a breast needle biopsy.
There are two main types of breast needle biopsy:
- fine needle aspiration, which uses a thin, hollow needle attached to a syringe, and
- core needle biopsy, which uses a larger needle that removes a small, tube-shaped piece of tissue with a spring-loaded device or a vacuum-assisted device.
How painful is each kind of biopsy, and how long does it take to recover?
Do any breast biopsies require general anesthesia or an overnight stay in the hospital?
Clinical Considerations And Recommendations
How should individual breast cancer risk be assessed?
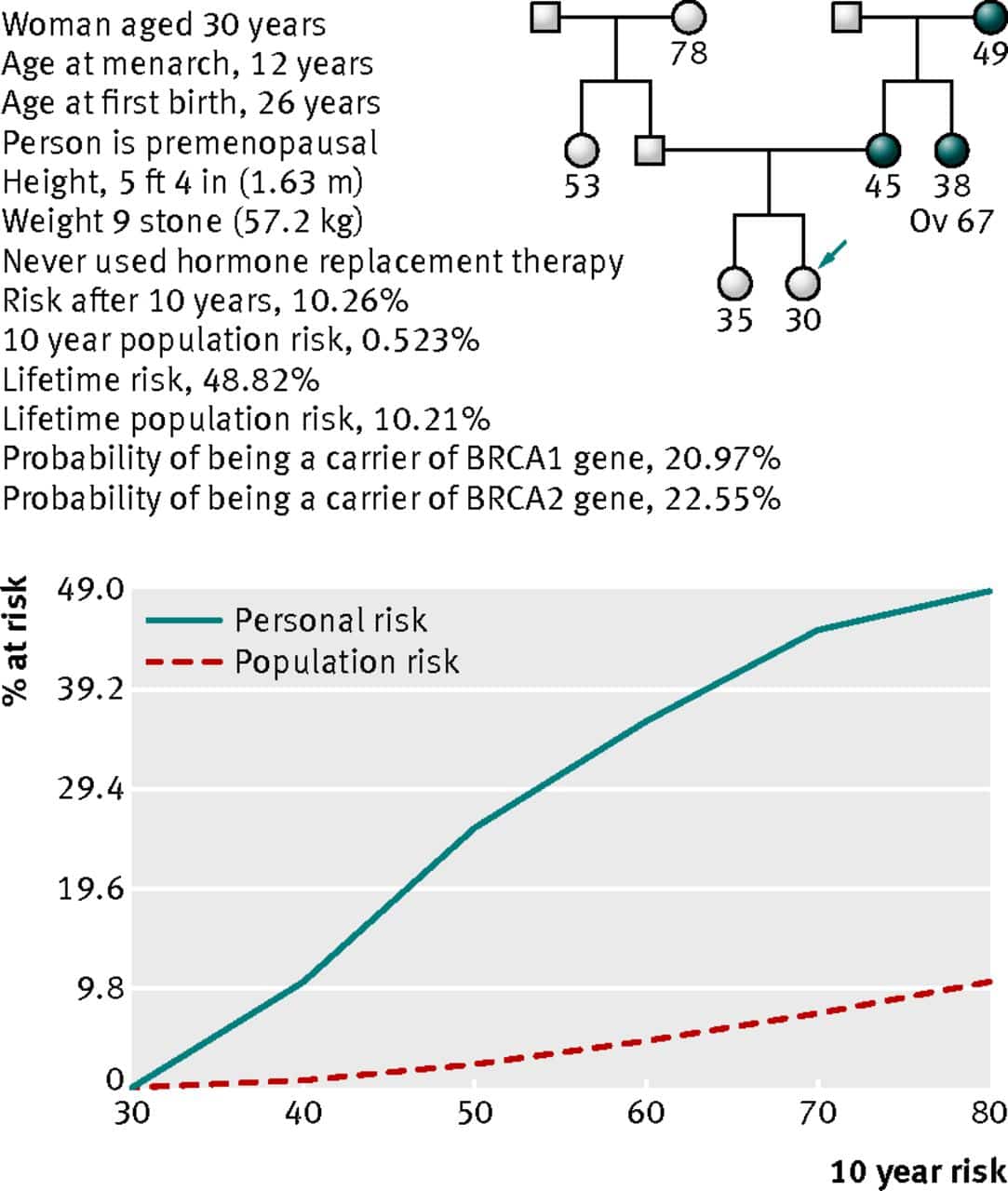
Health care providers periodically should assess breast cancer risk by reviewing the patients history. Breast cancer risk assessment is based on a combination of the various factors that can affect risk Box 1610111213. Initial assessment should elicit information about reproductive risk factors, results of prior biopsies, ionizing radiation exposure, and family history of cancer. Health care providers should identify cases of breast, ovarian, colon, prostate, pancreatic, and other types of germline mutation-associated cancer in first-degree, second-degree, and possibly third-degree relatives as well as the age of diagnosis. Women with a potentially increased risk of breast cancer based on initial history should have further risk assessment. Assessments can be conducted with one of the validated assessment tools available online, such as the Gail, BRCAPRO, Breast and Ovarian Analysis of Disease Incidence and Carrier Estimation Algorithm, International Breast Cancer Intervention Studies , or the Claus model 34.
Is screening breast self-examination recommended in women at average risk of breast cancer, and what should women do if they notice a change in one of their breasts?
Should practitioners perform routine screening clinical breast examinations in average-risk women?
When should screening mammography begin in average-risk women?
How frequently should screening mammography be performed in average-risk women?
Read Also: How To Check For Breast Cancer With Implants
Us Cancer Statistics Data Visualizations Tool
The Data Visualizations tool makes it easy for anyone to explore and use the latest official federal government cancer data from United States Cancer Statistics. It includes the latest cancer data covering the U.S. population.
See how the rates of new breast cancers or breast cancer deaths changed over time for the entire United States and individual states.Links with this icon indicate that you are leaving the CDC website.
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website’s privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance on other federal or private website.
CDC.gov Privacy Settings
We take your privacy seriously. You can review and change the way we collect information below.
These cookies allow us to count visits and traffic sources so we can measure and improve the performance of our site. They help us to know which pages are the most and least popular and see how visitors move around the site. All information these cookies collect is aggregated and therefore anonymous. If you do not allow these cookies we will not know when you have visited our site, and will not be able to monitor its performance.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Breast Cancer
There are many different signs and symptoms of breast cancer, so regularly checking your breasts for anything different or new is important.
The earlier breast cancer is diagnosed, the better the chance of successful treatment. Getting to know what your breasts look and feel like normally means its easier to spot any unusual changes and check them with your doctor. Common breast cancer signs and symptoms include:
- A lump or swelling in the breast, upper chest or armpit. You might feel the lump, but not see it.
- Changes in the size or shape of the breast
- A change in skin texture i.e. puckering or dimpling of the skin
- A change in the colour of the breast – the breast may look red or inflamed
- Rash, crusting or changes to the nipple
- Any unusual discharge from either nipple
Over a third of women in the UK do not check their breasts regularly for potential signs of breast cancer.
According to a YouGov survey commissioned by Breast Cancer Now, a third of those who do check their breasts for possible signs and symptoms dont feel confident that they would notice a change.
Asked what stops or prevents them from checking their breasts more regularly, over half forgetting to check, over a third not being in the habit of checking, a fifth not feeling confident in checking their breasts, not knowing how to check , not knowing what to look for and being worried about finding a new or unusual change .
Some factors are outside our control, including:
You May Like: Can Breast Cancer Lumps Be Visible
Analyzing Mammograms For False Positive Results
The researchers analyzed data collected by the Breast Cancer Surveillance Consortium on 3 million screening mammograms for 903,495 women aged 4079 years. The screenings were performed between 2005-2018 at 126 radiology facilities.
The study evaluated screening modality, screening interval, age and breast density. It estimated the cumulative risk that a woman would receive at least one false positive recall over 10 years of annual or biennial screening. It also assessed the risks of a false positive that resulted in a recommendation to repeat imaging within six months and separately, in a biopsy recommendation.
What Percentage Of Diagnostic Mammograms Is Cancer
The percentages are on a womans side when it comes to mammograms and breast cancer diagnosis. A small percentage of women, according to the American Cancer Society, are called back for additional tests following their initial mammogram. Ten percent of women return and of that percentage only 8 to 10 percent are biopsied. Eighty percent of biopsies come back benign.
In the majority of mammogram cases, women are diagnosed as cancer free. However, just because mammogram stats are on your side, this doesnt provide an excuse to skip your annual test, especially, as there are more statistics to consider.
Mammograms are the first defense against breast cancer, perhaps second to self-examination. In the United States, 12.4 percent of women will be diagnosed with invasive breast cancer and this year, 266,120 diagnosed cases are projected. Breast cancer is primarily a womens disease, but it does affect men. In 2018 it is projected that 2550 men will be diagnosed with the disease.
Risk Factors
The risks associated with breast cancer underscore the importance of scheduling a yearly mammogram.
There are really two primary risk factors associated with breast cancer: gender and age. If youre a woman, youre at risk. Growing older is also a risk.
Statistics are helpful, but not determinate. Dont avoid a diagnostic mammogram because your family history indicates that you may have less risk to developing breast cancer.
Early Detection is Crucial
You May Like: How Much Does It Cost To Check For Breast Cancer