Diagnosing Inflammatory Breast Cancer
If you are being treated for swelling or redness of the breast and it doesnt seem to be getting better after taking antibiotics for a week, your healthcare provider may order imaging tests to check for IBC. These tests may include an ultrasound and the following:
- Mammogram This test will be done to check the thickness of the skin and the density of the treated breast in comparison to the healthy breast.
- MRI It takes images of the breast and structures of your body using radio waves and magnets.
- CT This scan provides detailed images of your bodys insides.
- PET This scan, along with a CT, can find cancer in any area of the body, including the lymph nodes.
- Biopsy This test is done by removing a small piece of the skin or tissue of the breast to help diagnose cancer. A biopsy can sometimes be done with a needle or a surgical incision may be needed to remove tissue for testing. The type of biopsy performed with depends on whether a mass is discernible on imaging tests. The test will look for unusual cell growth and check for the presence of proteins found in some cancers.
Stages of Inflammatory Breast Cancer
What Increases Your Risk Of Breast Cancer
Factors that can elevate risk breast cancer risk include:
- A personal or family history of breast cancer, including DCIS and LCIS
- Inherited genetic predispositions, most commonly with BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene mutations
- Elevated lifetime estrogen exposure, including:
- Early onset of menstruation
- Late-onset of menopause
- Older age of first childbirth or never having given birth
- Taking estrogen and progesterone after menopause
Signs And Symptoms Of Inflammatory Breast Cancer
Inflammatory breast cancer causes a number of signs and symptoms, most of which develop quickly , including:
- Swelling of the skin of the breast
- Redness involving more than one-third of the breast
- Pitting or thickening of the skin of the breast so that it may look and feel like an orange peel
- A retracted or inverted nipple
- One breast looking larger than the other because of swelling
- One breast feeling warmer and heavier than the other
- A breast that may be tender, painful or itchy
- Swelling of the lymph nodes under the arms or near the collarbone
If you have any of these symptoms, it does not mean that you have IBC, but you should see a doctor right away. Tenderness, redness, warmth, and itching are also common symptoms of a breast infection or inflammation, such as mastitis if youre pregnant or breastfeeding. Because these problems are much more common than IBC, your doctor might suspect infection at first as a cause and treat you with antibiotics.
Treatment with antibiotics may be a good first step, but if your symptoms dont get better in 7 to 10 days, more tests need to be done to look for cancer. Let your doctor know if it doesn’t help, especially if the symptoms get worse or the affected area gets larger. The possibility of IBC should be considered more strongly if you have these symptoms and are not pregnant or breastfeeding, or have been through menopause. Ask to see a specialist if youre concerned.
Don’t Miss: Signs Of Breast Cancer Metastasis
What Clinical Trials Are Available For Women With Inflammatory Breast Cancer
NCI sponsors clinical trials of new treatments for all types of cancer, as well as trials that test better ways to use existing treatments. Participation in clinical trials is an option for many patients with inflammatory breast cancer, and all patients with this disease are encouraged to consider treatment in a clinical trial.
Descriptions of ongoing clinical trials for individuals with inflammatory breast cancer can be accessed by searching NCIs list of cancer clinical trials. NCIs list of cancer clinical trials includes all NCI-supported clinical trials that are taking place across the United States and Canada, including the NIH Clinical Center in Bethesda, MD. For information about how to search the list, see Help Finding NCI-Supported Clinical Trials.
People interested in taking part in a clinical trial should talk with their doctor. Information about clinical trials is available from NCIs Cancer Information Service at 18004CANCER and in the NCI booklet Taking Part in Cancer Treatment Research Studies. Additional information about clinical trials is available online.
Selected References
Anderson WF, Schairer C, Chen BE, Hance KW, Levine PH. Epidemiology of inflammatory breast cancer . Breast Diseases 2005 22:9-23.
Other Symptoms Of Inflammatory Breast Cancer
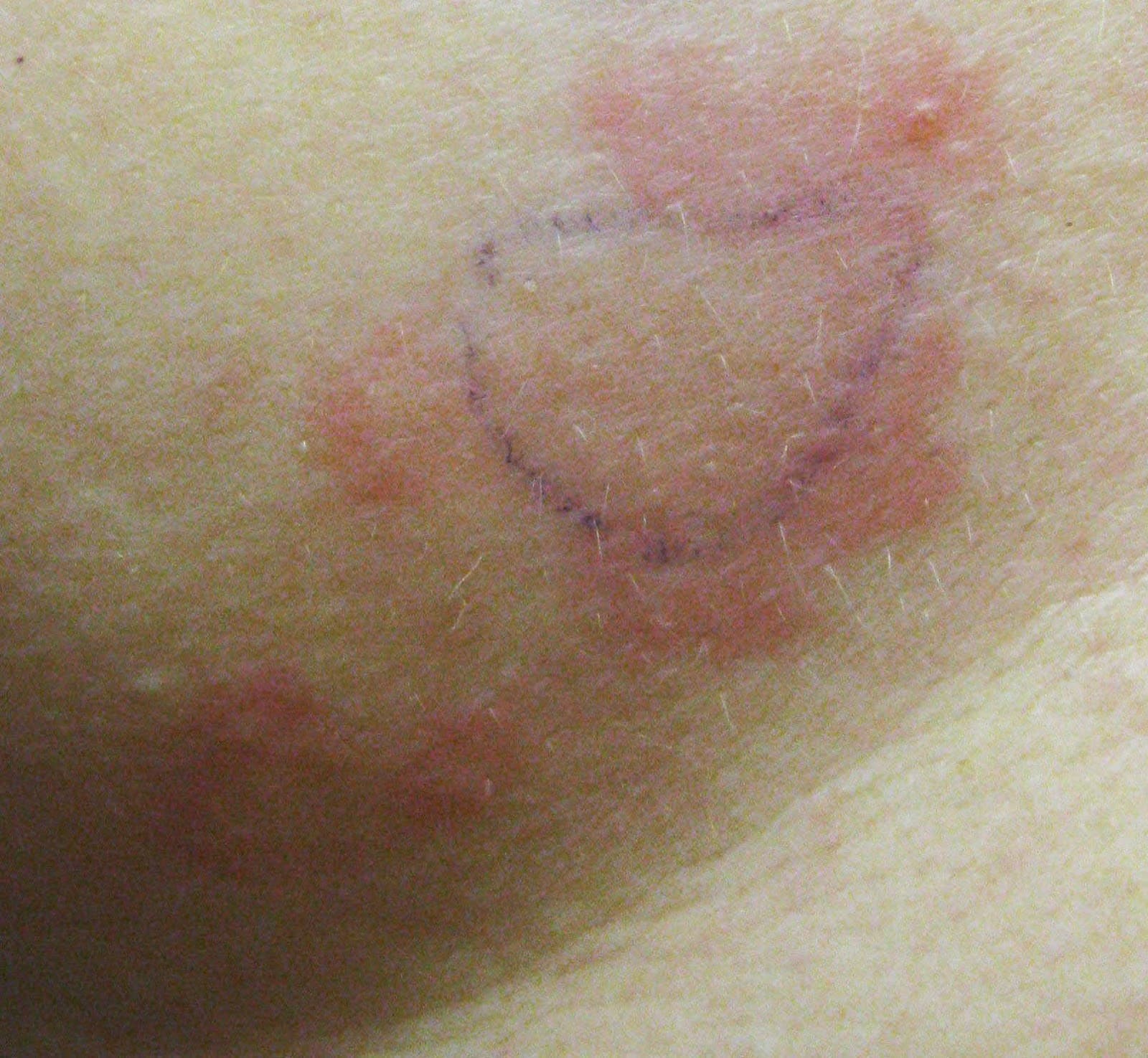
In addition to a breast rash, other possible signs and symptoms of inflammatory breast cancer include:
- A flattened, retracted or inverted nipple
- Swollen lymph nodes around the collarbone or under the arms
- A solid, hard lump in breast tissue
Most inflammatory breast cancer symptoms develop relatively quickly over three to six weeks. If you notice any unusual changes in the size, appearance, or texture of your breasts, promptly speak with a general physician or obstetrician/gynecologist who can evaluate your symptoms and refer you to a cancer specialist, if necessary.
Read Also: How To Know If You Have Breast Cancer Female
Moffitts Approach To Inflammatory Breast Cancer
Moffitt Cancer Centers Don & Erika Wallace Comprehensive Breast Program is home to multispecialty team that focuses exclusively on breast malignancies. As a high-volume cancer center, our experts have an unparalleled level of experience treating uncommon and complex diseases like inflammatory breast cancer. Moffitt also works diligently to discover breakthroughs in treatment through our trailblazing clinical trial program, which gives eligible patients access to promising new therapies before theyre made widely available.
We invite you to visit MoffittFloridas No. 1 cancer hospitalif youd like to have a breast rash evaluated by a specialist or receive a second or third opinion regarding inflammatory breast cancer treatment. No referrals are necessary to visit Moffitt, and youll be connected with a professional in less than 24 hours after you contact us. To get started, call or complete a new patient registration form online.
Hives Of Unknown Cause
While hives can often be traced to a certain trigger, many cases can also be idiopathic, meaning that the cause is unknown. As the AAD explains, millions of Americans experience hives during their lifetime with no definitive explanation.
When hives of unknown cause come and go for longer than 6 weeks, this is called chronic spontaneous urticaria . Treatment for CSU includes antihistamines and other medications, and dietary changes.
You May Like: How Many Chemo Sessions For Breast Cancer
How Does It Work
Electrical impulses change the outer layer of the cancer cells in the treated area causing gaps, called pores, to open up on the cells surface for a short time. This allows the chemotherapy drug to enter the cancer cells more easily. Once the pores close, the chemotherapy is sealed inside the cells.
The dose of chemotherapy drug is much lower than when its given to treat the whole body.
How To Tell The Difference Between A Bug Bite And Cancer
According to the United Kingdoms National Health Service , bug bites usually cause a lump on the skin that can be small, inflamed, painful, and itchy. They usually resolve within a few hours or days.
However, in some cases, people may develop a mild allergic reaction. This can cause a larger area of skin around the bite to become swollen, inflamed, and painful. This usually resolves within a week.
People should contact a doctor if they develop any symptoms of breast cancer or their current symptoms do not resolve and occur alongside other symptoms of breast cancer.
Learn more
- Whiteheads: These produce a white bump.
- Blackheads: These appear black on the skin surface.
- Papules: These are inflamed lesions that appear as small, inflamed bumps. They may also be tender to touch.
- Pustules: These are inflamed at the base and have pus-filled lesions at the top. The lesions may be white or yellow.
- Nodules: These are large lesions that can be solid and painful. They are usually deep within the skin.
- Cystic acne: These are painful lesions filled with pus. They are also deep within the skin.
Bug bites are usually itchy, whereas pimples are not. A bug bite may also appear similar to a pimple if it becomes infected. Infected bug bites may lead to a buildup of pus.
An infected bug bite may also cause symptoms that appear similar to those of breast cancer. These symptoms can include:
- warmth around the bite
There are many other possible causes of spots or rashes on the breast, including:
Read Also: Anti Estrogen Pills For Breast Cancer
Stage 3 Inflammatory Breast Cancer Treatment
Treatment for stage 3 IBC typically includes a method called a multimodal approach, which involves a combination of three treatments:
- Systemic therapies. Systemic therapies impact organs and tissues throughout your body and can help to shrink the cancer before surgery. Some examples of systemic therapies include:
- chemotherapy, which uses strong drugs to kill cancer cells or slow their growth
- targeted therapy, which can specifically target cells that are HER2-positive
- hormone therapy, which can block the activity of hormone receptors on cancer cells
Tests For Inflammatory Breast Cancer
Doctors determine a diagnosis based not just on the breast’s appearance, but on the results further testing, which may include:
- A biopsy that removes a small sample of affected tissue in your breast to be examined in a lab
- Biopsy results that show whether you have the HER2 protein, which is present in about 20 percent of breast cancer cases
- The determination of hormone receptor status, or whether you have more hormone receptors than usual within the cancer cells
Knowing whether your cancer has any of these characteristics will help you and your care team make informed treatment decisions.
If the biopsy results in an inflammatory breast cancer diagnosis, your doctor will likely order a breast magnetic resonance imaging to detect how much of the breast tissue and lymph nodes are affected, and whether the other breast has been affected . You may have other tests performed, including positron emission tomography scan, computed tomography scan and bone scan, to also see whether the cancer has spread to any other parts of the body.
You May Like: Why Do I Have Breast Cancer
Who Is At Risk For Inflammatory Breast Cancer
Inflammatory breast cancer is rare but can occur in women and men of any age. Its one of the few breast cancers thats known to affect people younger than 40, although the average age at diagnosis is 52. Additionally:
- People who are overweight have an increased risk of inflammatory breast cancer.
- Black women appear to have a higher risk of inflammatory breast cancer than white women.
- There may be a genetic link to inflammatory breast cancer risk, such as the BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene mutations that increase the likelihood of other breast cancers, although more research is needed.
Support For Living With Secondary Breast Cancer

Everyones experience of being diagnosed with secondary breast cancer is different. For many people, uncertainty can be the hardest part of living with secondary breast cancer.
You may find it helpful to talk to someone else whos had a diagnosis of secondary breast cancer.
Chat to other people living with secondary breast cancer on our online Forum.
Meet other people with a secondary diagnosis and get information and support at a Living with Secondary Breast Cancer group.
You can also call Breast Cancer Nows Helpline free on 0808 800 6000.
Image credit: graphic adapted from: Sersa et al.Electrochemotherapy in treatment of tumours. European Journal of Surgical Oncology. 2008. 34: 232240. Adapted by permission under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 license:creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0.
Also Check: What Treatments Are Available For Breast Cancer
Pagets Disease Of The Breast
Pagets disease of the breast is a type of cancer that affects the skin on the nipple and usually the skin around the nipple, known as the areola.
A diagnosis of Pagets disease can mean there is a tumor inside the breast. Often, people with Pagets disease have invasive breast cancer.
Symptoms of Pagets disease include:
- itching or tingling of the nipple or areola
- skin changes on or around the nipple, such as inflammation, crusting, flaking, or thickening
- flattening of the nipple
Treatment for Pagets disease depends upon the location of tumors in the breast. Possible treatments include:
- surgery to remove the breast and possibly lymph nodes
- surgery to remove the nipple and areola only
- chemotherapy or hormonal treatments
- radiation to treat any other tumors
Like IBC, Pagets disease is rare. According to the National Cancer Institute, it occurs in of all breast cancer cases.
Survival For Inflammatory Breast Cancer
Many factors can influence life expectancy for women with inflammatory breast cancer. These include:
- the exact position of the cancer
- how big the cancer is and whether it has spread only to the lymph nodes or to other organs
- how abnormal the cancer cells look under the microscope
- whether the cancer cells have receptors for hormone therapies
- how well the cancer responds to treatment
Inflammatory breast cancer can develop quickly and may spread to other parts of the body. So, in general, the outlook with this type is not as good as for women diagnosed with other types of breast cancer. But doctors think that the outlook is improving as breast cancer treatment improves.
Also Check: Most Common Site Of Breast Cancer Metastasis
What Is Metastatic Breast Cancer
Breast cancer usually begins in the ducts that carry milk to the nipple, and can metastasize reach other parts of the body when the cancer cells get into the blood or lymph systems. Most of the time, cancer cells die at some point in the process of trying to spread. But, if conditions are favorable for the cancer cells, some of them are able to form new tumors in other parts of the body. Metastatic cancer cells can also remain inactive at a distant site for many years before they begin to grow again, if at all.
What Is Male Breast Cancer
Breast cancer in men is very rare, with less than 1 percent of all breast cancers found in men. The risk increases for older men and those with high estrogen levels, low male-hormone levels or a family history of breast cancer. Increased risk is also associated with those who have been exposed to radiation, heavy drinkers, and those with liver disease or who are obese. Treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, hormone therapy and drugs that target genetic changes in cells that cause cancer.
Don’t Miss: What Are The Main Symptoms Of Breast Cancer
Warmth Pain And Tenderness
You may feel pain, burning, tenderness, or abnormal warmth in the breast affected by IBC, per the NCI. That breast may also feel itchy or heavy, per the ACS. These signs are also common in breast infections such as mastitis or cellulitis.
Healthcare providers may confuse IBC with an infection and try to treat it with antibiotics, according to an August 2018 paper published in the journal Surgical Clinics of North America. This can result in a delayed diagnosis. If your symptoms don’t get better within 710 days of antibiotic treatment, follow up with a healthcare provider for more tests, the ACS recommends.
Providers can also misdiagnose IBC as a breastfeeding-related change, allergic reaction, insect bite, or cyst , per the September 2018 paper. If your symptoms don’t go away with prescribed treatment, make sure to follow up with your provider.
An IBC diagnosis can be difficult to process, but know that treatments are advancing, per the ACS. There are already multiple treatment options available, such as chemotherapy, surgery, and radiation therapy. Some people can get drug-based immunotherapy and targeted therapy. Often, you may receive multiple treatments together.
Watch out for symptoms, and never hesitate to contact a healthcare provider if something feels off. IBC is easier to treat if diagnosed early.
Peeling Scaling Or Flaking Skin
Dont immediately be alarmed if you notice peeling, scaling, or flaking on your breasts or the skin around your nipples. This is a symptom of breast cancer, but it can also be a symptom of atopic dermatitis, eczema, or another skin condition.
After an exam, your doctor may run tests to rule out Pagets disease, which is a type of breast cancer affecting the nipples. It can also cause these symptoms.
Don’t Miss: Can Metastatic Breast Cancer Go Into Remission
Treatment For Inflammatory Breast Cancer
The treatment for inflammatory breast cancer can be slightly different to other types of breast cancer.
Chemotherapy
You usually have chemotherapy as your first treatment. This is called neo adjuvant chemotherapy. It helps to control the cancer cells in the breast and reduces the swelling. It also aims to destroy any cancer cells that might have spread elsewhere in the body.
Surgery
After chemotherapy you have surgery unless there is a reason why this isn’t suitable for you. You are most likely to have your whole breast removed .
Some women might be able to have breast conserving surgery. For this type of surgery, the surgeon removes the area of cancer and a surrounding area of healthy tissue. But for most women, mastectomy is the best option.
The surgeon usually removes the lymph nodes under your armpit.
Radiotherapy
After surgery you have radiotherapy to the remaining breast tissue. This is to help stop the cancer coming back.
Other drug treatment you may have
You have hormone therapy tablets for some years if your breast cancer has hormone receptors. Your doctor might recommend that you also have targeted cancer therapy, such as trastuzumab and pertuzumab, if your cancer has receptors for those drugs.
Breast reconstruction
You may be able to have breast reconstruction after you have finished your treatment . Do ask your surgeon, they can tell you whether this is suitable for you.