What Causes Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Researchers know that invasive ductal carcinoma occurs when cells in a duct undergo changes that trigger rapid and abnormal cell division, or when cells exceed their normal lifespan. The exact causes of these unusual cellular behaviors are not yet fully understood by scientists.
Anyoneincluding mencan develop breast cancer. However, clinical data shows that IDC and other types of breast cancer are more likely to affect women who:
- Previously received radiation treatment to the chest
- Have a family history of breast cancer
- Have certain inherited gene mutations, such as BRCA1 or BRCA2
- Have a personal history of breast conditions, such as lobular carcinoma in situ
- Are overweight or obese
- Breast skin that is dimpled, similar to an orange peel
- Redness, dryness or a rash on the breast skin
- Unusual pain in one breast
- Nipple pain and/or discharge
Many breast changes are unrelated to cancer and are not a cause for concern. However, diagnostic testing is necessary to rule out IDC and other breast malignancies. Women who notice an unusual lump or changes in their breast skin should promptly consult with a medical professional who can identify the cause of their symptoms and recommend appropriate treatment.
Management Of Breast Cancer
Surgery and radiation therapy, along with adjuvant hormone or chemotherapy when indicated, are considered primary treatment. Surgical therapy may consist of lumpectomy or total mastectomy. Radiation therapy may follow surgery in an effort to eradicate residual disease while reducing recurrence rates. There are 2 general approaches for delivering radiation therapy:
- External-beam radiotherapy
Surgical resection with or without radiation is the standard treatment for ductal carcinoma in situ.
Pharmacologic agents
Pharmacologic treatment for metastatic breast cancer is typically selected according to the molecular characteristics of the tumor. Agents used include the following :
- Hormone therapy
- HER2-targeted therapy
- CDK4/6 inhibitors
- mTOR inhibitors
- PIK3CA inhibitors
In patients receiving adjuvant aromatase inhibitor therapy for breast cancer who are at high risk for fracture, the monoclonal antibody denosumab or either of the bisphosphonates zoledronic acid and pamidronate may be added to the treatment regimen to increase bone mass. These agents are given along with calcium and vitamin D supplementation.
See Treatment and Medication for more detail.
Prevention
Two selective estrogen receptor modulators , tamoxifen and raloxifene, are approved for reduction of breast cancer risk in high-risk women. Prophylactic mastectomy is an option for women found to be at extremely elevated risk.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Most individuals with early are asymptomatic. However, when the size of the carcinoma is larger than 2 cm, individuals or their partner may discover a lump while palpating the breast or their underarm area. It is therefore recommended to regularly perform a breast self-exam for screening purposes. The appearance of the breast or the nipple may also indicate possible malignancy, including swelling of one breast, thickening of the breast skin, nipple discharge, or nipple . Pain in one particular location of the breast or the nipple, is an unusual symptom that occurs in about 5% of affected individuals. In more severe local yet advanced carcinomas, individuals may present clinically with peau d’orange , redness or ulceration of the skin in the breast, or fixation of the breast and lump to the chest wall.
Don’t Miss: Can Guys Get Breast Cancer
Diagnosis Of Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is often first detected as an abnormality on a mammogram before it is felt by the patient or health care provider.
Evaluation of breast cancer includes the following:
- Clinical examination
The following physical findings should raise concern:
- Lump or contour change
- Edema or peau dorange
If a palpable lump is found and possesses any of the following features, breast cancer may be present:
- Fixation to skin or muscle
Screening
Early detection remains the primary defense in preventing breast cancer. Screening modalities include the following:
- Breast self-examination
- Ultrasonography
- Magnetic resonance imaging
Ultrasonography and MRI are more sensitive than mammography for invasive cancer in nonfatty breasts. Combined mammography, clinical examination, and MRI are more sensitive than any other individual test or combination of tests.
Biopsy
Core biopsy with image guidance is the recommended diagnostic approach for newly diagnosed breast cancers. This is a method for obtaining breast tissue without surgery and can eliminate the need for additional surgeries. Open excisional biopsy is the surgical removal of the entire lump.
See Workup for more detail.
What Are The Causes Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
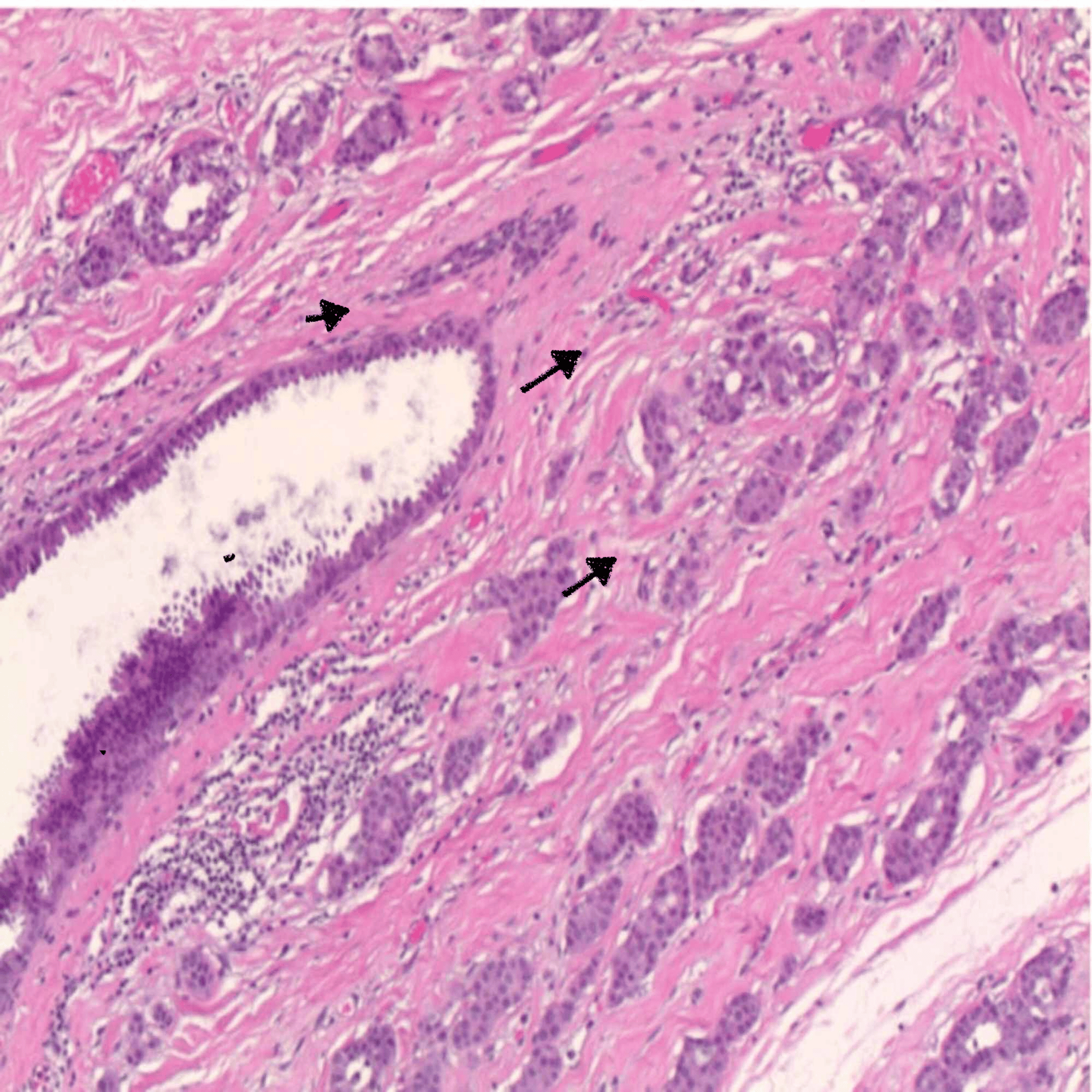
The most common cause of is and genetic mutations of the breast tissue cells. Damage to DNA can cause changes in various genes, like and , that usually control cell growth, prolong cell survival, manage cell division, and prevent unwanted cell death. If such changes occur, they can progressively result in uncontrolled cell growth and become cancerous and potentially penetrate into the stroma.
A wide variety of genetic and environmental risk factors can lead to DNA damage and the consequent development of invasive ductal carcinoma. An individuals sex assigned at birth is a very important risk factor, as most occur in those who have been assigned female at birth. Additionally, advanced age increases the possibility of any malignancy, including IDC, to form. Having a personal and/or family history of breast or increases the likelihood of developing IDC. In addition, a history of invasive ductal carcinoma in one breast poses a greater risk for developing a second cancerous lesion in the other breast.
Finally, increased exposure to hormones such as also increases the risk for developing malignancies originating from the breasts, such as IDC. Factors which increase estrogen include having menarche before 12 years of age, having the first after 30 years of age, never experiencing pregnancy, and experiencing after the age of 55. Similarly, exposure to administered , for instance through various contraceptive methods or through poses an additional risk.
Also Check: How Treatable Is Breast Cancer
Prognosis By Cancer Type
DCIS is divided into comedo and noncomedo subtypes, a division that provides additional prognostic information on the likelihood of progression or local recurrence. Generally, the prognosis is worse for comedo DCIS than for noncomedo DCIS .
Approximately 10-20% of women with LCIS develop invasive breast cancer within 15 years after their LCIS diagnosis. Thus, LCIS is considered a biomarker of increased breast cancer risk.
Infiltrating ductal carcinoma is the most commonly diagnosed breast tumor and has a tendency to metastasize via lymphatic vessels. Like ductal carcinoma, infiltrating lobular carcinoma typically metastasizes to axillary lymph nodes first. However, it also has a tendency to be more multifocal. Nevertheless, its prognosis is comparable to that of ductal carcinoma.
Typical or classic medullary carcinomas are often associated with a good prognosis despite the unfavorable prognostic features associated with this type of breast cancer, including ER negativity, high tumor grade, and high proliferative rates. However, an analysis of 609 medullary breast cancer specimens from various stage I and II National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project protocols indicates that overall survival and prognosis are not as good as previously reported. Atypical medullary carcinomas also carry a poorer prognosis.
Additionally, lymph node metastasis is frequently seen in this subtype , and the number of lymph nodes involved appears to correlate with survival.
What Does It Mean If My Carcinoma Is Called Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Invasive Lobular Carcinoma Or Carcinoma With Ductal And Lobular Features
Breast carcinomas are often divided into 2 main types: invasive ductal carcinoma and invasive lobular carcinoma, based on how they look under the microscope. In some cases, the tumor can have features of both and is called a mixed ductal and lobular carcinoma. Another term for invasive ductal carcinoma is invasive mammary carcinoma of no special type, because it is the most common type of breast carcinoma.
Both invasive ductal carcinomas and invasive lobular carcinomas arise from the cells lining the ducts and lobules in the breast. In general, invasive lobular and invasive ductal carcinomas of the breast arent treated differently.
Also Check: Collagen Supplements And Estrogen Positive Breast Cancer
Treatment For Invasive Breast Cancer
As with all types of breast cancer, the treatments youre offered will depend on the features of invasive breast cancer seen under the microscope. This includes the size, grade, hormone receptor status and HER2 status.
Treatment aims to remove the cancer and reduce the risk of it coming back or spreading to other parts of the body.
Stage Groups For Breast Cancer
Doctors assign the stage of the cancer by combining the T, N, and M classifications , the tumor grade, and the results of ER/PR and HER2 testing. This information is used to help determine your prognosis . The simpler approach to explaining the stage of breast cancer is to use the T, N, and M classifications alone. This is the approach used below to describe the different stages.
Most patients are anxious to learn the exact stage of the cancer. If you have surgery as the first treatment for your cancer, your doctor will generally confirm the stage of the cancer when the testing after surgery is finalized, usually about 5 to 7 days after surgery. When systemic treatment is given before surgery, which is typically with medications and is called neoadjuvant therapy, the stage of the cancer is primarily determined clinically. Doctors may refer to stage I to stage IIA cancer as “early stage” and stage IIB to stage III as “locally advanced.” Stage 0: Stage zero describes disease that is only in the ducts of the breast tissue and has not spread to the surrounding tissue of the breast. It is also called non-invasive or in situ cancer . Stage IA: The tumor is small, invasive, and has not spread to the lymph nodes . Stage IB: Cancer has spread to the lymph nodes and the cancer in the lymph node is larger than 0.2 mm but less than 2 mm in size. There is either no evidence of a tumor in the breast or the tumor in the breast is 20 mm or smaller .
Stage IIA: Any 1 of these conditions:
Also Check: What Is Hormone Positive Breast Cancer
What If My Report Mentions Micrometastases In A Lymph Node
This means that there are cancer cells in the lymph nodes that are bigger than isolated tumor cells but smaller than regular cancer deposits. If micrometastases are present, the N category is described as pN1mi. This can affect the stage of your cancer, so it might change what treatments you may need. Talk to your doctor about what this finding may mean to you.
Diagnosing Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Some women may feel a lump in their breast and seek evaluation, while others may learn they have breast cancer during their mammogram screening or breast X-ray. Other imaging tests and a biopsy may also be ordered to help the doctor assess the patients condition.
During a biopsy, the doctor removes some tissue or fluid from the breast for analysis under a microscope. The sample is sent off to a lab, where a pathologist checks for the presence of cancer cells, and it may take a few days to get the results.
If the diagnosis is breast cancer, the doctor then needs to determine its stage, including whether or not its started to spread inside or outside the breast. The specifics guide any treatment decisions.
Read Also: Stage 3 Breast Cancer Survival Rates
What Is Vascular Lymphovascular Or Angiolymphatic Invasion What If My Report Mentions D2
If cancer cells are seen in small blood vessels or lymph vessels under the microscope, it is called vascular, angiolymphatic, or lymphovascular invasion. When cancer is growing in these vessels, there is an increased risk that it has spread outside the breast. If your report does not mention this type of invasion, it means it is not there. Even if it is there, it does not always mean that your cancer has spread. How this finding affects your treatment is best discussed with your doctor.
D2-40 and CD34 are special tests that the pathologist may use to help identify these types of vascular invasion. These tests are not needed in every case.
Kinds Of Breast Cancer
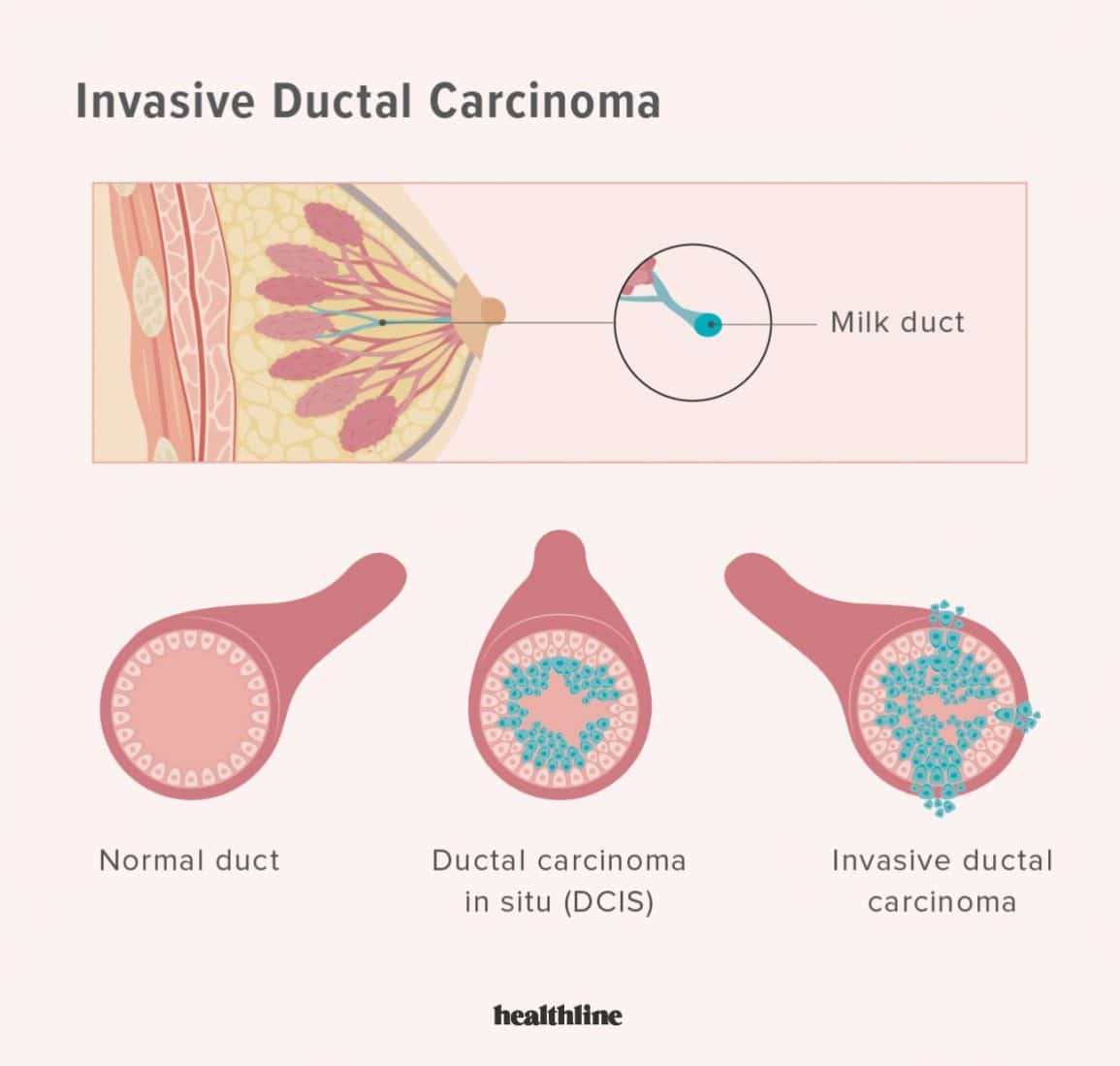
The most common kinds of breast cancer are
- Invasive ductal carcinoma. The cancer cells begin in the ducts and then grow outside the ducts into other parts of the breast tissue. Invasive cancer cells can also spread, or metastasize, to other parts of the body.
- Invasive lobular carcinoma. Cancer cells begin in the lobules and then spread from the lobules to the breast tissues that are close by. These invasive cancer cells can also spread to other parts of the body.
Recommended Reading: Long-term Side Effects Of Radiation Therapy For Breast Cancer
What If My Report Mentions Sentinel Lymph Node
In a sentinel lymph node biopsy, the surgeon finds and removes the first lymph node to which a tumor drains. This lymph node, known as the sentinel node, is the one most likely to contain cancer cells if they have started to spread. This procedure may be done during surgery to remove a breast cancer. It is a way to check for the spread of cancer to underarm lymph nodes without removing as many of them.
The sentinel lymph node is then checked to see if it contains cancer cells. If there is no cancer in the sentinel node, it’s very unlikely that the cancer has spread to other lymph nodes, so no further lymph node surgery is needed.
If a sentinel lymph node does contain cancer, your report will say that cancer was present in the lymph node. It may also say how large the deposit of cancer cells is. In some cases, if cancer is found in a sentinel lymph node, you may then also need additional treatment such as surgery to remove more underarm lymph nodes or radiation therapy to the underarm region. You should discuss this with your doctor.
What Are The Symptoms Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Like other breast cancers, IDC may present as a lump that you or your doctor can feel on a breast exam. But in many cases, at first, there may be no symptoms, Wright says.
That is why it is important to have screening mammograms to detect breast cancers such as invasive ductal carcinoma. A mammogram may detect a lump that is too small for you to feel, or suspicious calcifications in the breast, either of which will lead to further testing.
According to Wright, the following are possible signs of invasive ductal carcinoma and other breast cancers. If you notice any of these, you should contact your doctor right away for further evaluation:
- Lump in the breast
- Nipple discharge, other than breast milk
- Scaly or flaky skin on the nipple or an ulceration on the skin of the breast or nipple. These can be signs of Pagets disease, a different kind of breast cancer that can occur along with IDC.
- Lumps in the underarm area
- Changes in the appearance of the nipple or breast that are different from your normal monthly changes
Read Also: Is There Financial Help For Breast Cancer Patients
When Should I See My Healthcare Provider Regarding Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
If you notice any unusual changes in your breast tissue, schedule an appointment with your healthcare provider. If youre currently undergoing treatment for invasive ductal carcinoma, call your healthcare provider if you develop any concerning symptoms, such as high fever, chills, confusion, chest pain, shortness of breath , bone pain or abdominal pain.
What Does Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Treatment Involve
Treatment for invasive ductal carcinoma will vary based on factors like the patients age, overall health and care preferences as well as the cancers stage and biological makeup. Generally speaking, many IDC treatment plans include a combination of one or more of the following:
- Surgery to remove tumors, cancerous breast tissue or surrounding lymph nodes
- Radiation therapy to damage cancer cells with high-powered, precisely delivered X-ray beams
- Chemotherapy to attack cancer cells throughout the body with potent medication
- Targeted therapy to disturb various processes that facilitate cancer growth
- Hormonal therapy to address IDC that tests positive for hormone receptors
- Immunotherapy to help the immune system recognize cancer and disrupt its growth
Advancements in breast cancer treatment have improved the outlook for patients with IDC. When diagnosed in an early stage, IDC is considered highly treatable.
You May Like: What Are The Chances Of Breast Cancer Returning
Invasive Carcinoma Of No Special Type
| Invasive carcinoma of no special type | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Invasive ductal carcinoma |
| Histopathologic types of breast cancer, with relative incidences and prognoses, with “invasive ductal carcinoma” at bottom left | |
| Oncology, Dermatology, Breast surgery |
Invasive carcinoma of no special type also known as invasive ductal carcinoma or ductal NOS and previously known as invasive ductal carcinoma, not otherwise specified is a group of breast cancers that do not have the “specific differentiating features”. Those that have these features belong to other types. While breast cancer is extremely rare in men, invasive carcinoma of no special type is the most commonly diagnosed form of male breast cancer.
In this group are: pleomorphic carcinoma, carcinoma with osteoclast-like stromal giant cells, carcinoma with choriocarcinomatous features, and carcinoma with melanotic features. It is a diagnosis of exclusion, which means that for the diagnosis to be made all the other specific types must be ruled out.
Rare Types Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Medullary ductal carcinoma accounts for only 3%5% of breast cancers. It may appear on a mammogram, and it does not always feel like a lump rather, it can feel like an abnormally spongy area in the breast tissue.
Mucinous ductal carcinoma is also called colloid breast cancer. It occurs when cancer cells within the milk duct of the breast produce mucous, which also contains breast cancer cells. The cells and mucous combine to form a tumor. Pure mucinous ductal carcinoma tends to grow slowly, and has a better prognosis than some other types of IDCs.
Papillary carcinoma forms finger-like projections that can be seen under a microscope. Many papillary tumors are benign, but even those that become cancerous are usually very treatable with a good prognosis. Papillary carcinoma most commonly occurs in people older than 60.
Tubular ductal carcinoma is a rare diagnosis of IDC, comprising only 2% of breast cancer diagnoses. The name comes from how the cancer looks under the microscope like hundreds of tiny tubes. Tubular breast cancer has an excellent prognosis.
You May Like: Does Breast Cancer Stop Your Period