Statistics Dont Account For Late Recurrences
When comparing triple-negative breast cancer to positive tumors, its important to keep in mind late recurrences. Most statistics are presented as five-year survival rate, and in this setting, triple-negative breast cancer can look more ominous. But looking at longer periods of time, say 20 years following diagnosis, this may be different.
Can Tnbc Be Prevented
Researchers dont know all the factors that cause triple negative breast cancer. They have identified the BRAC1 gene mutation as one potential cause for triple negative breast cancer. Unfortunately, you cant prevent BRAC1 because you inherit this gene mutation from your parents.
But there are steps that help prevent breast cancers, including TNBC:
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Exercise on a regular basis.
- Know your family medical history.
- Monitor your breast health. Studies show 95% of women whose breast cancer was treated before it could spread were alive four years after diagnosis.
- Talk to your healthcare provider about genetic testing for the BRCA gene if you have a family history of breast cancer, ovarian cancer, pancreatic or prostate cancer. If you have the BRCA gene, there are steps you can take to prevent breast cancer.
Chemotherapy For Early Tnbc
Early TNBC is treated with chemotherapy. People with TNBC tend to get more treatment benefit from chemotherapy than people with hormone receptor-positive breast cancers do .
Some people get chemotherapy before breast surgery. This is called neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
For people with TNBC who have cancer remaining in their breast after neoadjuvant chemotherapy, treatment with the chemotherapy drug capecitabine may lower the risk of recurrence and improve survival .
Learn more about chemotherapy.
Also Check: How To Avoid Breast Cancer Naturally
Metastatic Breast Cancer: The Basics
Metastatic breast cancer , is breast cancer that has spread beyond the breast and the surrounding lymph nodes to other parts of the body, Nancy Lin, MD, an oncologist who specializes in breast cancer at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, told Health.
Approximately 30% of breast cancer patients will develop metastatic breast cancer following an initial earlier-stage diagnosis, according to a review in the Journal of Internal Medicine. Meanwhile, the American Society of Clinical Oncology reports that just 6% of women have metastatic breast cancer when they are first diagnosed.
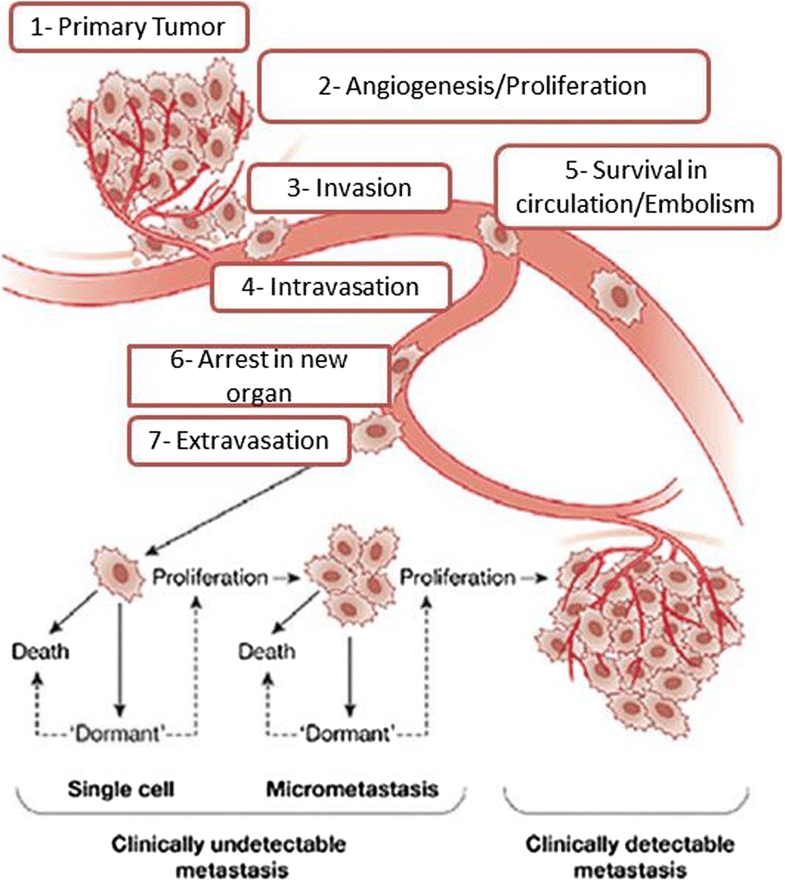
“Basically what’s happening is the cancer cells are growingthey get into the bloodstream which then allows them to travel to distant sites ,” Evelyn Toyin Taiwo, MD, hematologist and oncologist at Weill Cornell Medicine and NewYork-Presbyterian Brooklyn Methodist Hospital, told Health.
Metastatic breast cancer cells most often take up residence in the bones, liver, lungs, and brain, said Dr. Taiwo, but they can spread anywhere in the body.
It’s still unclear to science how or why certain cancers metastasize, and others don’t, said Dr. Lin, or why breast cancer cells seem to prefer spreading to those specific regions of the body. The type of cancer may play a role in where it metastasized.
Risk Factors For Triple
Doctors aren’t sure what makes you more likely to get triple-negative breast cancer. Not many women do — it only affects up to 20% of those who have breast cancer. You’re most at risk for triple-negative breast cancer if you:
- Are African-American or Latina
- Have what your doctor will call a BRCA mutation , especially the gene BRCA1
Recommended Reading: What Are The Symptoms Of Male Breast Cancer
A New Era Of Hope For Patients With Triple
Triple-negative breast cancer is a particularly devastating subtype of breast cancer, as it is often diagnosed in young women and is associated with an exceptionally poor prognosis. The triple-negative designation indicates that the three key features driving most breast cancers are lacking, but it provides no clues as to potential biologic drivers. In the absence of any biologic insights, tailored, targeted treatment decisions have historically not been possible.
Consequently, until as recently as 2018, we have relied exclusively on nonselective cytotoxic agents, with modest success. For example, conventional neoadjuvant chemotherapy confers a pathologic complete response in just 50% to 55% of patients with early-stage triple-negative breast cancer,1-4 and among those who do not achieve a pathologic complete response, approximately one-third will die within 3 years.5 Moreover, patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer treated with conventional chemotherapeutics have a median survival of 12 to 18 months and an estimated 5-year overall survival of 11%.6 Thus, therapeutic innovation for early and late triple-negative breast cancer has been desperately needed.
Biologic Insight Leads to Therapies
From biologic insight springs hope for therapeutic innovation. Heather L. McArthur, MD, MPHTweet this quote
Immune Modulation Via Checkpoint Blockade
Antibody-Drug Conjugates
Forecast Finally Changing in Triple-Negative Disease
REFERENCES
The Latest Progress In Research On Triple Negative Breast Cancer : Risk Factors Possible Therapeutic Targets And Prognostic Markers
Qingli Jiao1, Aiguo Wu1, Guoli Shao1, Haoyu Peng2, Mengchuan Wang1, Shufeng Ji1, Peng Liu3, Jian Zhang1
1 Department of General Surgery, Zhujiang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, China Department of Oncology, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, China Department of Breast Oncology, Cancer Center, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510275, China
Correspondence to:
Abstract: Triple negative breast cancer is one type of breast cancer , which is defined as negative for estrogen receptor , progesterone receptor and human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 . Its origins and development seem to be elusive. And for now, drugs like tamoxifen or trastuzumab which specifically apply to ER, PR or Her2 positive BC seem unforeseeable in TNBC clinical treatment. Due to its extreme malignancy, high recurrence rate and poor prognosis, a lot of work on the research of TNBC is needed. This review aims to summarize the latest findings in TNBC in risk factors, possible therapeutic targets and possible prognostic makers.
Keywords: Triple negative breast cancer risk factor therapeutic target prognostic marker
Submitted Apr 14, 2014. Accepted for publication Jul 28, 2014.
doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2014.08.13
Also Check: Estrogen And Progesterone Positive Breast Cancer Prognosis
Also Check: What Is Brca Testing For Breast Cancer
Survival Benefit Of Surgery And Systemic Therapy In Stratified Risk Groups
To further assess the survival benefit of surgery, Kaplan-Meier curves were generated in the stratified risk groups. The results showed that surgery could prolong overall survival in both the low- and intermediate-risk groups . However, surgery did not significantly improve prognosis in the high-risk group . In terms of systemic therapy, all stratified groups could prognostically benefit from chemotherapy .
Figure 6. Survival benefit of surgery in the low-risk , intermediate-risk , and high-risk groups.
Figure 7. Survival benefit of chemotherapy in the low-risk , intermediate-risk , and high-risk groups.
Er Pr Her2 And Ihc Subtypes
Information on ER, PR and HER2 status was obtained from pathology reports for the whole study period . From 2005 to January 2010, tumours were classified as ER negative if < 10% ER expression, and from February 2010 onwards if < 1% ER expression. PR-negative tumours were defined as < 10% PR expression throughout the study period. HER2 expression was routinely assessed with IHC and verified with in situ hybridization if the IHC results were borderline. We created six IHC subtypes: ER+PR+HER2, ER+PRHER2, ER+PR+HER2+, ER+PRHER2+, ERPRHER2+ and ERPRHER2 . Women with the rarer combinations ERPR+HER2 or ERPR+HER2+ were set to missing in the analysis . In total, n =21,786 women had known IHC subtype, while n =2351 women lacked information on ER, PR or HER2 status .
Table 1 Clinicopathologic characteristics by IHC subtype for women with invasive breast cancer, Norway 20052015 age 2074 years
Read Also: Does Red Wine Cause Breast Cancer
Prognosis For Metastatic Breast Cancer
Metastatic breast cancer isnt the same for everyone who has it. According to the National Breast Cancer Foundation, your symptoms at stage 4 will depend on the degree to which the cancer has spread in your body.
Although metastatic breast cancer has no current cure, it can be treated. Getting the right treatment can increase both your quality of life and longevity.
Life expectancy for breast cancer is based on studies of many people with the condition. These statistics cant predict your personal outcome each persons outlook is different.
The following factors can affect your life expectancy with metastatic breast cancer:
What Is The Staging Of Triple
Staging is the process of determining the extent of cancer and its spread in the body. Together with the type of cancer, staging helps determine the appropriate therapy and predict the chances for survival.
To determine if cancer has spread, medical professionals may use several different imaging techniques, including X-ray, CT scans, bone scans, and PET scans. Staging depends upon the size of a tumor and the extent to which it spread to lymph nodes or distant sites and organs in the body. Examination of lymph nodes removed at surgery and the results of ER, PR, and HER2 tests performed on the tumor tissue also help determine the stage of a tumor.
- The American Cancer Society defines 4 stages of breast cancer.
- Stage I is the lowest stage, while stage IV is the highest stage and refers to tumors that have metastasized, or spread to areas distant from the breast.
Most doctors specifically adjust breast cancer treatments to the type of cancer and the staging group.
Surgery
Many women with breast cancer will require surgery. Broadly, the surgical therapies for breast cancer consist of breast-conserving surgery and mastectomy .
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy destroys cancer cells with high-energy rays. Doctors commonly administer radiation therapy to patients after breast cancer surgery, most commonly after lumpectomy.
Chemotherapy
Types of chemotherapy include the following:
Other therapies for triple-negative breast cancer
Read Also: Stage 2 Breast Cancer Treatment
What Is The Treatment For Triple Negative Breast Cancer
Healthcare providers and researchers are making significant progress on TNBC treatments. Recent clinical trials are testing new combinations of drugs and new approaches to existing treatments. Some existing treatments are:
- Chemotherapy: Providers might combine chemotherapy and surgery, with chemotherapy being used to shrink your tumor before surgery or after surgery to kill cancer cells throughout your body.
- Surgery: This could be a lumpectomy to remove an individual lump, or a mastectomy to remove an entire breast. Providers then perform a sentinel node biopsy or axillary node surgery to look for signs your breast cancer has spread to your lymph nodes.
- Radiation therapy: Post-surgery radiation therapy helps reduce the chances your cancer will return or recur.
- Immunotherapy: This treatment stimulates your immune system to produce more cancer-fighting cells or help healthy cells identify and attack cancer cells. Immunotherapy can be added to chemotherapy to before surgery to shrink the tumor. You might also receive immunotherapy for about a year after your surgery and post-surgery radiation therapy.
Treatment And Outcome After Distant Metastasis

Treatments in patients diagnosed with distant metastasis are shown in Table Table3.3. Median distant disease-free interval among all patients who developed metastatic disease was 15 months: 24 among younger and 13 among older patients, although the difference between age groups did not reach statistical significance . Fifty six % in the whole group received palliative chemotherapy. Few patients received more than 1 line of palliative chemotherapy. Only 10% in the older group received palliative chemotherapy compared with 93% in the younger group . Fifty five % in the whole group received palliative radiotherapy and there was no significant difference between age groups .
You May Like: Which Bones Does Breast Cancer Spread To First
Brca And Homologous Recombination Deficiency
The prevalence of BRCA mutations is reported in up to 20%-30% of unselected TNBC patients. Poly polymerase inhibitors exploit this deficiency through synthetic lethality and have emerged as a therapeutic strategy in these patients. These agents have demonstrated efficacy in patients with BRCA-mutant metastatic breast cancer, prompting investigators to evaluate their role in the neoadjuvant setting. In unselected TNBC patients, the addition of veliparib to platinum-based chemotherapy failed to increase the pCR rate. In another study, the addition of olaparib to paclitaxel was not superior to carboplatin/paclitaxel in patients with HER2-negative breast cancer with a BRCA1/2 mutation. However, early phase II data using single-agent neoadjuvant talazoparib demonstrated an excellent pCR rate of 53% in patients with germline BRCA pathogenic variants. A single-arm pilot study with neoadjuvant Niraparib also demonstrated antitumor activity in patients with localized HER2-negative breast cancer with a BRCA1/2 mutation. The tumor response rate was 90.5% as assessed by MRI but pCR rates have not yet been reported. Survival outcomes from these studies are pending validation of these findings in larger cohorts and may represent an opportunity to de-escalate neoadjuvant treatment to a chemotherapy-free targeted regimen in carefully selected patients.
Triple Negative Breast Cancer
With this type of breast cancer, the breast cancer cells dont have ER+ or PR+ receptors. They dont overproduce the HER2 protein, so hormone therapy isnt very effective.
Instead, triple negative stage 4 breast cancer is usually treated with chemotherapy. Radiation therapy may also be an option, depending on the site of metastasis.
Don’t Miss: How To Test For Breast Cancer
Morbidity Financial And Social Burdens Of Therapy
Chemotherapy is often feared by patients due to the side effects associated with treatment however, the costs for administering therapy have also become a major burden for both the United States healthcare system as well as the patients it serves. Financial toxicity is not frequently disclosed, and can be materially and psychologically debilitating for patients. Financial hardships induced by the cost of cancer care worsen patient psychological stress and financial insolvency has been identified as a risk factor for early mortality in cancer patients.,
Is Triple Negative Breast Cancer An Aggressive Form Of Cancer
Its true that triple negative breast cancers can grow quickly. But your prognosis or expected outcome depends on more factors than your cancer subtype. Healthcare providers will also consider your tumors size and whether it has spread to your lymph nodes and other parts of your breast. Its also helpful to know researchers are focusing on ways to slow the spread of TNBC.
Read Also: What Is The History Of Breast Cancer
How Important Is Genetic Testing
Genetic testing can determine if you carry any of the gene mutations associated with TNBC. This can help assess your risk of recurrence. It can also help guide treatment decisions for advanced TNBC.
You can share this information with relatives who may be at increased risk. That gives them the opportunity to consider enhanced screening and cancer prevention strategies.
What Is The Recurrence Rate Of Triple
A 2019 study found that roughly 40% of people with stage 1 to stage 3 TNBC will see their cancer return after standard treatment. The remaining 60% will have long-term survival without recurrence.
The outcomes of treatment vary. About 42% of those with this form of cancer will have a rapid relapse after standard treatment. This recurrence typically occurs within the first 23 years following the initial diagnosis.
It is not currently possible to predict who will experience a relapse in their cancer, even if they have had intensive chemotherapy.
On average,
Triple-negative breast cancer can recur in various areas of the body and at local, regional, and distant levels:
- Local means that the cancer remains in the breast and has not spread.
- Regional is when the cancer spreads from the breast to lymph nodes and other structures located nearby.
- Distant refers to cancer that has spread far from the breast to other organs, such as the liver or lungs.
A 2017 study examined the patterns of recurrence among 1,930 people with TNBC. The researchers divided the patients into two age groups: 15% were younger than 40 years at the time of their diagnosis, and 85% were 40 years or older.
The researchers found only a small difference between the two groups in terms of recurrence of the cancer on the local level: 6% of those under 40 versus 5% of those aged 40 or above.
The same study found that the rate of regional recurrence was 2% for both groups.
Recommended Reading: Breast Cancer Screening Guidelines Uspstf
What Is The Survival Rate For Triple Negative Breast Cancer
Survival rates are a way to discuss the prognosis and outlook of a cancer diagnosis. The number most frequently mentioned is 5-year survival. Many patients live much longer, and some die earlier from causes other than breast cancer. With a constant change and improvement in therapies, these numbers also change. Current 5-year survival statistics are based on patients who were diagnosed at least 5 years ago and may have received different therapies than are available today.
Below are the statistics from the National Cancer Instituteâs SEER database for survival of all patients with breast cancer, by tumor stage:
| Stage |
|---|
Current Treatment Landscape And Emerging Therapies For Metastatic Triple
![[Full text] Understanding Patterns of Brain Metastasis in Triple ...](https://www.breastcancertalk.net/wp-content/uploads/full-text-understanding-patterns-of-brain-metastasis-in-triple.jpeg)
Supplements and Featured Publications
Abstract
Am J Manag Care. 2021 27:S87-S96.
Introduction
Worldwide, breast cancer is the most frequently diagnosed cancer in women. In the United States, it accounts for 30% of all cancers in women and is the second leading cause of cancer-related mortality, surpassed only by lung cancer. In 2021, an estimated 284,200 new cases of breast cancer and 44,130 deaths related to breast cancer will have occurred, representing 15% of all new cancer cases and 7.3% of all cancer deaths.1,2
TNBC
Epidemiology and Prevalence
TNBCs account for approximately 15% to 20% of all newly diagnosed breast cancers. Incidence rates in non-Hispanic Black women are almost double the rates compared with other racial/ethnic groups, which may account for the fact that they experience 40% higher breast cancer-associated death rates.6,7
Prognosis and Pathogenesis
Metastatic TNBC
Current Standard of Care
Second Line and Beyond
The Evolving Immunotherapy Landscape
Immunotherapy in Combination With Chemotherapy
A New Standard of Care: Atezolizumab plus nab-Paclitaxel
The combination of atezolizumab and nab-paclitaxel is included in the NCCN guidelines as a category 1 preferred treatment option for the initial treatment of mTNBC in patients with PD-L1positive disease, as determined by an FDA-approved companion diagnostic.25
Atezolizumab plus Paclitaxel
Pembrolizumab plus Chemotherapy
Nivolumab plus Chemotherapy
PD-L1 Expression
You May Like: What Is The Best Type Of Breast Cancer To Have