Inflammatory Breast Cancer Pictures And Symptoms
The symptoms of IBC include a breast that:
- Quickly changes appearance
- Looks larger, thicker or heavier
- Feels very warm
- Has skin that looks dimpled or ridged like an orange
- Is tender, aches or feels painful
- Has larger lymph nodes under the arm or around the collarbone
- Has a flatter nipple or one that is turned inward
Unlike other forms of breast cancer, there is no lump formation with IBC.
Inflammatory Breast Cancer Pictures of Different Symptoms
Below are some of the pictures of IBC for reference only, you may not experience them at all. If you find anything abnormal with your breast and are concerned, do not hesitate to visit your doctor.
As these inflammatory breast cancer picture shows, the texture of the breast may change and appear to look dimpled or ridged, like an orange peel. This is referred to as peau dorange, which is French for orange skin and it is caused by cancer cells blocking the lymph vessels beneath the skin, which have formed into ridges or tiny lumps.
One of the first symptoms women experience is the breast appearing to be red, pink or purple. The discoloration may look like bruising that covers one-third or more of the breast. It may also feel warm or be tender.
With IBC, the skin may appear to be splotchy or irritated and there may be bumps present.
Inflammatory breast cancer pictures show the discoloration that can appear.
Who Is Mainly Affected By Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers among women, second only to skin cancer. Its most likely to affect women over the age of 50.
Though rare, men can also develop breast cancer. Approximately 2,600 men develop male breast cancer every year in the United States, making up less than 1% of all cases.
Transgender women are more likely to develop breast cancer compared to cisgender men. Additionally, transgender men are less likely to develop breast cancer compared to cisgender women.
What age does breast cancer occur?
Breast cancer is most often diagnosed in adults over the age of 50, but it can occur at any age.
What race is most affected by breast cancer?
Overall, women who are non-Hispanic white have a slightly higher chance of developing breast cancer than women of any other race or ethnicity. Women who are non-Hispanic Black are almost as likely as non-Hispanic white women to develop the disease. Statistically, women who are Asian, Hispanic or Native American are the least likely to develop breast cancer.
What Questions Should I Ask My Healthcare Provider
Learning everything you can about your diagnosis can help you make informed decisions about your health. Here are some questions you may want to ask your healthcare provider:
- Where is the tumor located?
- Has the tumor spread?
- What stage breast cancer do I have?
- What do the estrogen receptor , progesterone receptor and HER2 tests show and what do the results mean for me?
- What are my treatment options?
- Is breast cancer surgery an option for me?
- Will I be able to work while I undergo treatment?
- How long will my treatment last?
- What other resources are available to me?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Being diagnosed with breast cancer can feel scary, frustrating and even hopeless. If you or a loved one is facing this disease, its important to take advantage of the many resources available to you. Talk to your healthcare provider about your treatment options. You may even want to get a second opinion before making a decision. You should feel satisfied and optimistic about your treatment plan. Finally, joining a local support group can help with feelings of isolation and allow you to talk with other people who are going through the same thing.
You May Like: What Is Basal Breast Cancer
How To Determine Your Grade Of Nipple Inversion
Many people know that they have inverted nipples, but arent clear on how inverted their nipples are.
Heres how to figure it out:
You may only experience inversion in one nipple, or even different grades of inversion in each nipple.
For some women, inverted nipples can make breastfeeding more difficult. Some women find that their baby has a hard time latching onto the nipple to feed. This may be because, due to inversion, the nipple doesnt become erect.
If you plan to become pregnant or are already breastfeeding, talk with your doctor.
There are some techniques that you can use to help bring the nipple out, including:
- nipple shields to help the baby latch on
- breast shields to apply pressure to the nipple, helping it protrude
- manual nipple stimulation with your hands
You may also find that milk flows better when using a breast pump.
Where Did Your Breast Cancer Begin
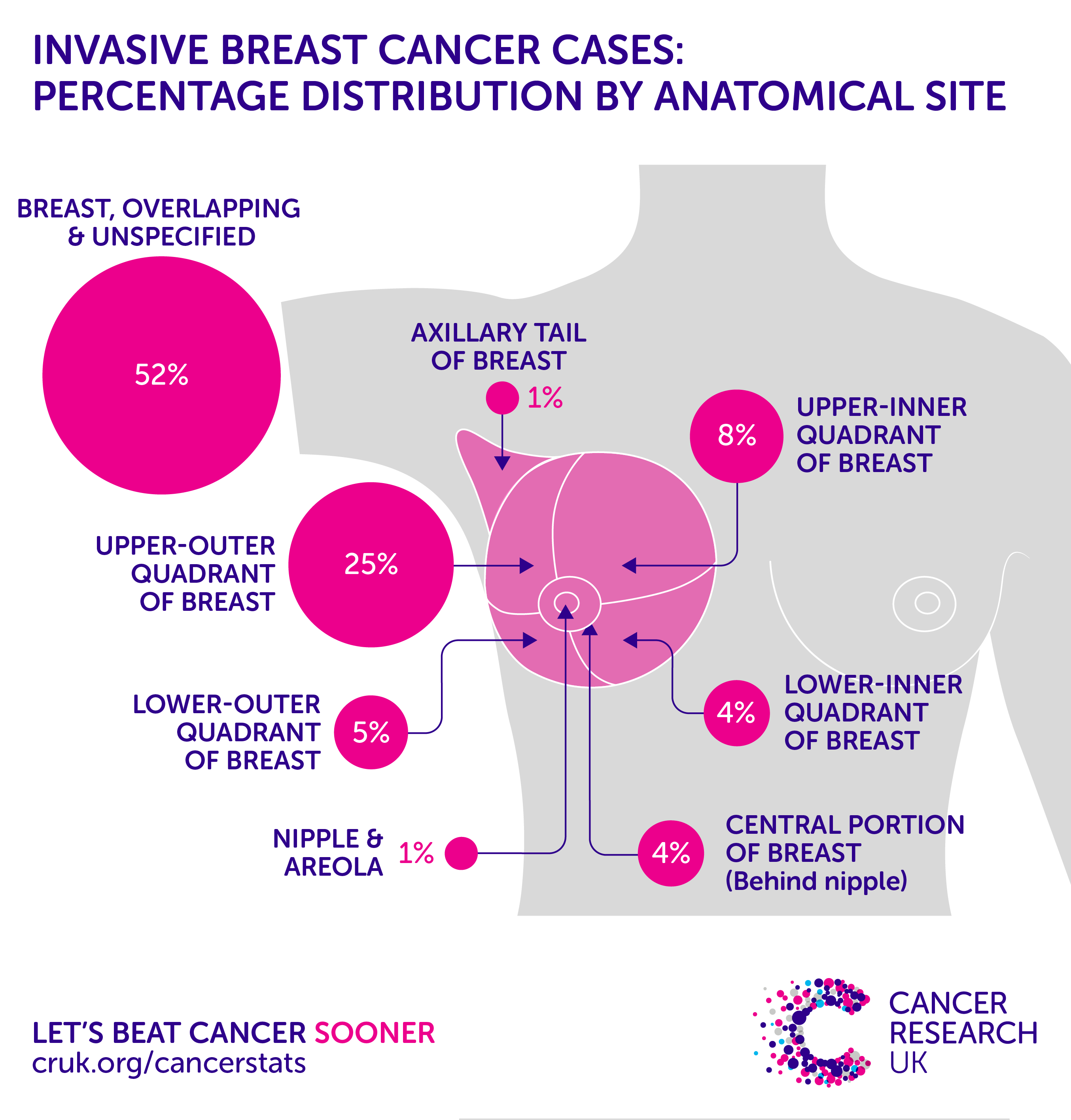
The type of tissue where your breast cancer begins determines how the cancer behaves and what treatments are most effective.
Parts of the breast where cancer begins include:
Milk ducts: Ductal carcinoma is the most common type of breast cancer. This type of cancer forms in the lining of a milk duct within your breast. The ducts carry breast milk from the lobules, where its made, to the nipple. Ductal carcinoma can remain within the ducts as a noninvasive cancer, which is called ductal carcinoma in situ, or it can break out of the ducts, which is called invasive ductal carcinoma.
Milk-producing lobules: Lobular carcinoma starts in the lobules of the breast, where breast milk is produced. When it breaks out of the lobules, its considered invasive lobular carcinoma. The lobules are connected to the ducts, which carry breast milk to the nipple.
Connective tissues: Rarely breast cancer can begin in the connective tissue thats made up of muscles, fat and blood vessels. Cancer that begins in the connective tissue is called sarcoma. Examples of sarcomas that can occur in the breast include phyllodes tumor and angiosarcoma.
Also Check: Does Underwire Cause Breast Cancer
What Are The Types Of Breast Cancer
There are several different types of breast cancer, including:
Can cancer form in other parts of the breast?
When we say breast cancer, we usually mean cancers that form in milk ducts or lobules. Cancers can also form in other parts of your breast, but these types of cancer are less common. These can include:
- Angiosarcoma. This rare type of cancer begins in the cells that make up the lining of blood or lymph vessels.
- Phyllodes tumors. Starting in the connective tissue, phyllodes tumors are rare. Theyre usually benign , but they can be malignant in some cases.
Breast Reconstruction After A Mastectomy
After cancerous breast tissue is removed, you may be thinking about restoring your breasts shape. People who have had a mastectomy often want to restore the breast mound, but its also not uncommon to skip the restoration and go flat instead.
If you decide to go with reconstruction, know that you dont have to do so right away. You can put off reconstruction for days, months, or even years. In fact, if youre undergoing any other breast cancer treatments, like radiation or chemotherapy, you may decide to postpone reconstruction until those treatments are done.
Reconstruction has several forms. Some people may opt for a full silicone implant for their breast reconstruction. In other cases, a plastic surgeon may be able to use body fat, muscle, and tissue from another part of your body to rebuild a breast. Nipple reconstruction is also possible for some people.
Don’t Miss: How I Cured My Breast Cancer
Mucinous Carcinoma Of The Breast
Mucinous carcinoma, also known as colloid carcinoma, is a rare form of invasive ductal carcinoma . About 2 percent of breast cancers are pure mucinous carcinoma, while up to 7 percent of breast cancers have some component of mucinous carcinoma cells.
With this type of cancer, the tumor consists of abnormal cells that appear to float in pools of mucus when looked at under a microscope.
Its typically a less aggressive type of cancer that has a lower probability of spreading to the axillary lymph nodes than some other types of IDC.
Mucinous carcinoma tends to be more common in post-menopausal women, with the average age at diagnosis being around 60 to 70 years of age.
Skin Rash On The Breasts
You may not associate breast cancer with redness or a skin rash, but in the case of inflammatory breast cancer , a rash is an early symptom. This is an aggressive form of breast cancer that affects the skin and lymph vessels of the breast.
Unlike other types of breast cancer, IBC doesnt usually cause lumps. However, your breasts may become swollen, warm, and appear red. The rash may resemble clusters of insect bites, and its not unusual to have itchiness.
Also Check: What Is The Worst Type Of Breast Cancer To Have
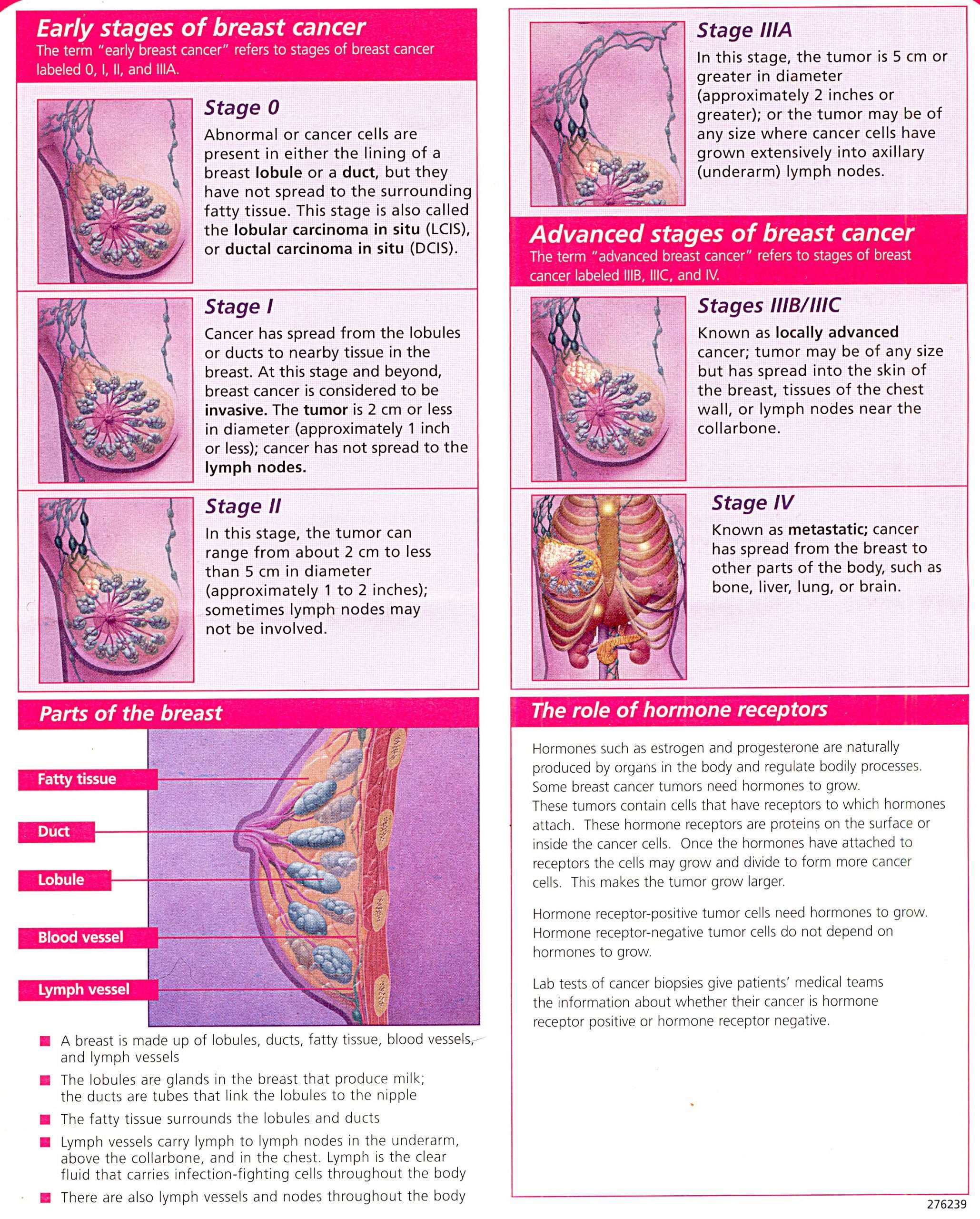
In Situ Vs Invasive Breast Cancers
The type of breast cancer can also refer to whether the cancer has spread or not. In situ breast cancer is a pre-cancer that starts in a milk duct and has not grown into the rest of the breast tissue. The term invasive breast cancer is used to describe any type of breast cancer that has spread into the surrounding breast tissue.
Invasive breast cancer has spread into surrounding breast tissue. The most common types are invasive ductal carcinoma and invasive lobular carcinoma. Invasive ductal carcinoma makes up about 70-80% of all breast cancers.
Diagnosing Inflammatory Breast Cancer
If you are being treated for swelling or redness of the breast and it doesnt seem to be getting better after taking antibiotics for a week, your healthcare provider may order imaging tests to check for IBC. These tests may include an ultrasound and the following:
- Mammogram This test will be done to check the thickness of the skin and the density of the treated breast in comparison to the healthy breast.
- MRI It takes images of the breast and structures of your body using radio waves and magnets.
- CT This scan provides detailed images of your bodys insides.
- PET This scan, along with a CT, can find cancer in any area of the body, including the lymph nodes.
- Biopsy This test is done by removing a small piece of the skin or tissue of the breast to help diagnose cancer. A biopsy can sometimes be done with a needle or a surgical incision may be needed to remove tissue for testing. The type of biopsy performed with depends on whether a mass is discernible on imaging tests. The test will look for unusual cell growth and check for the presence of proteins found in some cancers.
Stages of Inflammatory Breast Cancer
Recommended Reading: What Is Hormonal Breast Cancer
Looking For More On How To Track Side Effects
Cancer.Net offers several resources to help you keep track of your symptoms and side effects. Please note that these links will take you to other sections of Cancer.Net:
- Cancer.Net Mobile: The free Cancer.Net mobile app allows you to securely record the time and severity of symptoms and side effects.
- ASCO Answers Managing Pain: Get this 32-page booklet about the importance of pain relief that includes a pain tracking sheet to help patients record how pain affects them. The free booklet is available as a PDF, so it is easy to print.
- ASCO Answers Fact Sheets: Read 1-page fact sheets on anxiety and depression, constipation, diarrhea, and rash that provide a tracking sheet to record details about the side effect. These free fact sheets are available as a PDF, so they are easy to print, fill out, and give to your health care team.
The next section in this guide is Follow-up Care and Monitoring. It explains the importance of checkups after you finish cancer treatment. Use the menu to choose a different section to read in this guide.
Learn more about the importance of follow-up care.
What Increases Your Risk Of Breast Cancer
Factors that can elevate risk breast cancer risk include:
- A personal or family history of breast cancer, including DCIS and LCIS
- Inherited genetic predispositions, most commonly with BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene mutations
- Elevated lifetime estrogen exposure, including:
- Early onset of menstruation
- Late-onset of menopause
- Older age of first childbirth or never having given birth
- Taking estrogen and progesterone after menopause
Recommended Reading: When Can Breast Cancer Occur
Are Your Cancer Cells Fueled By Hormones
Some breast cancers are sensitive to your bodys naturally occurring female hormones estrogen and progesterone. The breast cancer cells have receptors on the outside of their walls that can catch specific hormones that circulate through your body. Knowing that your breast cancer is sensitive to hormones gives your health care team a better idea of how best to treat the cancer or prevent cancer from recurring.
Hormone status of breast cancers includes:
Estrogen receptor positive: The cells of this type of breast cancer have receptors that allow them to use the hormone estrogen to grow. Treatment with anti-estrogen hormone therapy can block the growth of the cancer cells.
Progesterone receptor positive: This type of breast cancer is sensitive to progesterone, and the cells have receptors that allow them to use this hormone to grow. Treatment with endocrine therapy blocks the growth of the cancer cells.
Hormone receptor negative: This type of cancer doesnt have hormone receptors, so it wont be affected by endocrine treatments aimed at blocking hormones in the body.
Physical Emotional And Social Effects Of Cancer
Cancer and its treatment cause physical symptoms and side effects, as well as emotional, social, and financial effects. Managing all of these effects is called palliative care or supportive care. It is an important part of your care that is included along with treatments intended to slow, stop, or eliminate the cancer.
Palliative care focuses on improving how you feel during treatment by managing symptoms and supporting patients and their families with other, non-medical needs. Any person, regardless of age or type and stage of cancer, may receive this type of care. And it often works best when it is started right after a cancer diagnosis. People who receive palliative care along with treatment for the cancer often have less severe symptoms, better quality of life, and report that they are more satisfied with treatment.
Palliative treatments vary widely and often include medication, nutritional changes, relaxation techniques, emotional and spiritual support, and other therapies. You may also receive palliative treatments similar to those meant to get rid of the cancer, such as chemotherapy, surgery, or radiation therapy.
Learn more about the importance of tracking side effects in another part of this guide. Learn more about palliative care in a separate section of this website.
Also Check: What’s The Worst Stage Of Breast Cancer
How To Reduce Risk
There is no guaranteed way to prevent breast cancer, but there are certain steps a person can take to lower their risk.
Actions that may lower the risk of breast cancer include:
- Get to a healthy weight: High body weight and weight gain as an adult increase the risk of breast cancer after menopause. The
Several benign breast conditions can cause symptoms that resemble those of cancer. Some of these issues require treatment, while others go away on their own.
Though these conditions are benign, they can cause:
- discomfort or pain
Some common benign breast conditions include:
If a person is unsure what is causing any breast-related symptom, they should talk with a doctor as soon as possible.
As with most cancers, early breast cancer detection and treatment leads to a better outcome. People should attend regular breast examinations and tell a doctor about any breast-related symptoms or changes.
According to the ACS , when a doctor diagnoses breast cancer before it has spread beyond the breast, the relative 5-year survival rate is 99%.
Relative survival rates can help people understand the likelihood of treatment being successful. A relative 5-year survival rate indicates the percentage of people living 5 years after their diagnosis compared to people without the disease.
When breast cancer has spread beyond the breast to the lymph nodes, the 5-year survival rate is 86%. The same survival rate for cancer that has spread to other organs is 29%.
Surgery With Partial Preservation Of Milk Ducts
This is also known as the parachute flap technique. Women undergoing this procedure should still be able to breastfeed because some of the milk duct system remains attached. You shouldnt experience a change in nipple sensation.
Heres how it works:
- After applying local anesthesia, your doctor will make an incision around the base of your nipple.
- While still attached, the nipple and areola are both lifted from the breast and sewn into a protruding shape.
- Your doctor will then close the incision and apply medicated gauze.
You May Like: Can Stage 0 Breast Cancer Come Back
How Inflammatory Breast Cancer Is Treated
In cancer care, doctors specializing in different areas of cancer treatment work together to create a patients overall treatment plan that combines different types of treatments. This is called a multidisciplinary team. Cancer care teams include a variety of other health care professionals, such as physician assistants, nurse practitioners, oncology nurses, social workers, pharmacists, genetic counselors, nutritionists, and others.
Inflammatory breast cancer is considered a locally-advanced breast cancer and is typically treated with several types of treatment, including chemotherapy, surgery, radiation therapy, HER2 targeted therapy, and/or hormone therapy, as appropriate.
Inflammatory breast cancer treatment usually starts with chemotherapy. Chemotherapy before surgery is called neoadjuvant therapy or preoperative therapy. After chemotherapy, people with inflammatory breast cancer usually have surgery to remove the breast. Then, they receive radiation therapy to the chest wall and the nearby lymph nodes. If a patient has metastatic breast cancer when first diagnosed, the main treatment options are systemic therapies, such as chemotherapy. Surgery and/or radiation therapy are less commonly used.
The common types of treatments used for inflammatory breast cancer are described below. Your care plan may also include treatment for symptoms and side effects, an important part of cancer care.