Treatments For Stage 2 Breast Cancer
The following are treatment options for ductal carcinoma and lobular carcinoma. Doctors consider stage 2A to be early stage breast cancer. Stage 2B is considered to be locally advanced breast cancer. Your healthcare team will suggest treatments based on your needs and work with you to develop a treatment plan.
Er And Her2 Receptor Status
Quality statement
Rationale
Quality measures
Structure
Data source:Data source:
Process
Data source:Data source:Data source:Data source:
Outcome
Data source:
What the quality statement means for different audiences
Service providersHealthcare professionalsCommissionersPeople with newly diagnosed invasive breast cancer or with breast cancer that has come back or spread
Definitions of terms used in this quality statement
Clinically appropriate
How Is Advanced Breast Cancer Diagnosed
There are various tests you can have to find out the reason for your symptoms. Your GP can refer you directly for these tests, or to your previous hospital specialist. If you are still having follow up care your hospital team will organise appropriate tests for you.
Most people will need some imaging or x-rays and the type you have depends on where your symptoms are. Some of the most common tests are:
- X-ray
- MRI scan
- Bone scan
Some people will also require a biopsy. If your x-ray or scan confirms that a tumour is causing your symptoms, sometimes this will be enough to allow a treatment plan to be confirmed. However, for some people a biopsy is needed to confirm the diagnosis again.
It can also be useful to have a new sample or biopsy from the secondary tumour, as occasionally the cancer cells biology can change . For instance hormone receptor status may change from negative to positive- allowing treatment with hormone blocking agents- or from positive to negative, meaning hormonal treatment is no longer appropriate. HER2 status can also change in some cases.
Also Check: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 3 Treatment
What Is Metastatic Breast Cancer
Metastasis is the process by which cancer cells spread. In the case of metastatic breast cancer, the cancer originated in breast tissue, then spread to other parts of the body.
Metastatic cancer is further described as local, regional or distant, depending on the location of the cancer cells in relation to the original tumor.
- Localized metastatic breast cancer often means the breast cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes.
- The more distant locations include the bones, lungs, skin, liver and brain, although its possible for other parts of the body to be affected.
Its important to remember that every cancer is unique and that your experience may not necessarily be the same as that of another breast cancer patient. With a personalized treatment plan, metastatic breast cancer is typically treatable. A recent National Cancer Institute study found that the number of U.S. women living longer with distant metastatic breast cancer is growing, thanks to advances in treatments.
Its also important to prepare yourself with information about the disease, its symptoms and how its detected and treated.
Advances In Breast Cancer Research
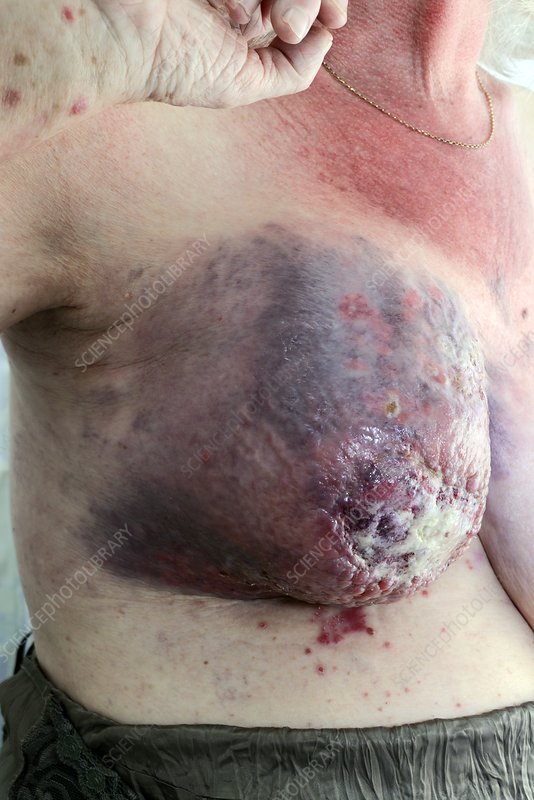
A polyploid giant cancer cell from triple-negative breast cancer.
NCI-funded researchers are working to advance our understanding of how to prevent, detect, and treat breast cancer. They are also looking at how to address disparities and improve quality of life for survivors of the disease.
This page highlights some of the latest research in breast cancer, including clinical advances that may soon translate into improved care, NCI-supported programs that are fueling progress, and research findings from recent studies.
Don’t Miss: Nipple Piercings And Breast Cancer
Additional Tools For Diagnosing Advanced Breast Cancer
The additional tools below are often used specifically for diagnosing advanced cancer:
Sentinel lymph node biopsy: This procedure removes sentinel lymph node cells during surgery for examination. When breast cancer spreads, it often heads first to the lymph nodes.
Chest X-ray: This detailed image of the chest may help doctors see whether cancer has spread to the bones.
Computed tomography scan: Also known as a CAT scan, this procedure takes detailed pictures of internal areas of the body using a computer linked to an X-ray machine. A dye may be used to help the organs show up more clearly in the images.
Bone scan: This procedure looks for bone metastasis, or cancer cells that have spread to the bone. A small amount of radioactive material is injected into the blood, then detected with a scanner.
Positron emission tomography scan: A PET scan is a detailed imaging tool that uses a radioactive drug, known as a tracer, to search for cancer cells within your body.
Can Metastatic Breast Cancer Go Into Remission
Metastatic breast cancer may never go away completely. But treatment can control its spread. Cancer may even go into remission at some points. This means you have fewer signs and symptoms of cancer.
A treatment break may be considered in certain situations, including if remission occurs or if someone is experiencing intolerable side effects. A pause in treatment can help you feel your best and improve your quality of life.
Don’t Miss: Stage 3 Cancer Definition
What Is Advanced Cancer
Advanced cancer is most often used to describe cancers that cannot be cured. This means cancers that wont totally go away and stay away completely with treatment. However, some types of advanced cancer can be controlled over a long period of time and are thought of as an ongoing illness.
Even if advanced cancer cant be cured, treatment can sometimes:
- Shrink the cancer
- Help relieve symptoms
- Help you live longer
For some people, the cancer may already be advanced when they first learn they have the disease. For others, the cancer may not become advanced until years after it was first diagnosed.
Advanced cancers can be locally advanced or metastatic.
Locally advanced means that cancer has grown outside the body part it started in but has not yet spread to other parts of the body. For example, some cancers that start in the brain may be considered advanced because of their large size or closeness to important organs or blood vessels. This can make them life-threatening even though they havent spread to other parts of the body. But other locally advanced cancers, such as some prostate cancers, may be cured.
Metastatic cancers have spread from where they started to other parts of the body. Cancers that have spread are often thought of as advanced when they cant be cured or controlled with treatment. Not all metastatic cancers are advanced cancers. Some cancers, such as testicular cancer, can spread to other parts of the body and still be very curable.
How You Might Feel
When breast cancer is advanced it can no longer be cured. But treatment can control it for some time and help to relieve symptoms.
Finding out that you cant be cured is distressing and can be a shock. Its common to feel uncertain and anxious. It’s normal to not be able to think about anything else.
Lots of information and support is available to you, your family, and friends. It can help to find out more about your cancer and the treatments you might have. Many people find that knowing more about their situation can make it easier to cope.
Talk to your doctor or nurse to understand:
- what your diagnosis means
- what is likely to happen
- what treatment is available
- how treatment can help you
You and your family will be looked after by a team of people who can provide you with support and information.
Don’t Miss: Estrogen Related Cancers
Complications With The Brain
The brain is another area in the body to which breast cancer cells can spread to rapidly. While this sounds to be an alarming condition, there are several treatments that are there for removing or shrinking the tumors that spread to the brain.
Brain metastases can affect many vital functions in the body, including your vision, your behavior, and your memory. Symptoms that indicate that the breast cancer cells have spread to the brain may include:
- Seizures
Some of the complications of brain metastases may include:
Seizures: You are likely familiar with the generalized tonic-clonic grand mal seizures in which a person shakes violently and becomes unconscious. These types of seizures are more likely to occur with brain metastases. Seizures can also cause different kinds of symptoms based on the type of seizure you experience. These can range from usual muscle stiffness to appearing dazed and confused, not being aware of your immediate surroundings. If you experience a seizure or develop a swelling in the brain, your doctor will prescribe an anti-seizure medication or a corticosteroid.
Falls: Brain metastases can cause weakness, numbness, and loss of balance, which are all symptoms that increase the risk of falls. Falls can result in serious disability and injury. If you have developed brain metastases, then it is essential to be extra careful about your movements and take preventive measures to ensure that you do not fall.
What Should A Person With Stage 3 Breast Cancer Expect From Treatment
Stage 3 treatment options vary widely and may consist of mastectomy and radiation for local treatment and hormone therapy or chemotherapy for systemic treatment. Nearly every person with a Stage 3 diagnosis will do best with a combination of two or more treatments.
Chemotherapy is always given first with the goal to shrink the breast cancer to be smaller within the breast and within the lymph nodes that are affected. This is known as neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
Other possible treatments include biologic targeted therapy and immunotherapy. There may be various clinical trial options for interested patients with Stage 3 breast cancer.
Also Check: 3rd Stage Breast Cancer
How Is Metastatic Breast Cancer Treated
The main treatment for metastatic breast cancer is systemic therapy. These therapies treat the entire body. Systemic treatments may include a combination of:
Your care team will plan your treatment based on:
- Body parts cancer has reached.
- Past breast cancer treatments.
- Tumor biology, or how the cancer cells look and behave.
Multidisciplinary Team Management Of Metastatic Breast Cancer
Quality statement
Rationale
Quality measures
Structure
Data source:
Process
Data source:
Outcome
Data source:Data source:Data source:
What the quality statement means for different audiences
Service providersHealthcare professionalsCommissionersPeople with breast cancer that has spread to other parts of the body
Also Check: Stage Four Breast Cancer Symptoms
When Do People Get A Metastatic Breast Cancer Diagnosis
Metastatic breast cancer can occur at different points:
- De novo metastatic breast cancer: About 6% of women and 9% of men have metastatic breast cancer when theyre first diagnosed with breast cancer.
- Distant recurrence: Most commonly, metastatic breast cancer is diagnosed after the original breast cancer treatment. A recurrence refers to the cancer coming back and spreading to a different part of the body, which can happen even years after the original diagnosis and treatment.
What Is The Treatment For Metastatic Breast Cancer
Treatments include many of the same treatments as other stages of breast cancer:
- Chemotherapy
- Radiation therapy
- Hormone therapy For patients diagnosed with Stage IV breast cancer that is hormone receptor positive, hormonal therapy may be the first line of defense against the disease. As long as the drugs are keeping the cancer from progressing, the patient may be kept on the medication for some time. If scans show the progression of the cancer, the medical oncologist may switch to another form of hormonal therapy or possibly stop this therapy and pursue a different line of systemic treatment, such as chemotherapy or biologic targeted therapy.
- Biologic targeted therapy
- Breast surgery It is controversial whether surgery should be done on the breast in the presence of known metastatic disease. In most cases, however, the knowledge of metastasis is discovered after the breast cancer surgery and other treatment has been performed. The cancer returns as a distant recurrence.
Recommended Reading: Invasive Ductal Breast Cancer Prognosis
Support When You Have Secondary Breast Cancer
Secondary breast cancer occurs when breast cancer cells spread from the first cancer in the breast through the lymphatic or blood system to other parts of the body. Read more about diagnosis, treatments and living with secondary breast cancer, and find support.
Secondary breast cancer is not the same as breast cancer recurrence. If you are concerned about your primary breast cancer returning, find information and support.
Stage 4 Breast Cancer
Advanced breast cancer refers to cancer that has spread beyond the breast to other parts of the body. This process of spreading from the original location to a new location is known as metastasis.
The most common places of breast cancer spread include the bones, liver, lung, and brain. However, breast cancer may also spread to other organs.
The majority of women who are diagnosed with metastatic breast cancer have been diagnosed with an earlier stage of breast cancer before. In this instance, the original cancer in the breast is called the primary cancer. However, for some women, a diagnosis of metastatic breast cancer may be their first diagnosis of cancer .
Don’t Miss: Cancer Dormancy
How Is Metastatic Breast Cancer Diagnosed
If you have symptoms of metastatic breast cancer, your provider may recommend tests including:
- Blood tests, including complete blood count and comprehensive metabolic panel.
- Imaging studies, including MRI, CT, bone scan and PET.
- Bronchoscopy, which uses a scope to look inside your lungs this can be done if there is a concerning spot in the lungs.
- Biopsy to remove tissue from a suspicious area and analyze it.
- A tap to remove fluid from an area with symptoms. For example, pleural tap removes fluid from the lung area. Spinal tap removes fluid from the spinal cord area.
Where Can Breast Cancer Spread
The most common places for breast cancer to spread to are the lymph nodes, bone, liver, lungs and brain. The symptoms you may experience will depend on where in the body the cancer has spread to. You might not have all of the symptoms mentioned here.
Remember other conditions can cause these symptoms. They don’t necessarily mean that you have cancer that has spread. But if you have symptoms that you are worried about, discuss them with your GP, cancer specialist, or breast care nurse so that you can be checked.
Also Check: Symptoms Of Stage 4 Breast Cancer
About Metastatic Breast Cancer
Cancer begins when healthy cells change and grow out of control, forming a mass or sheet of cells called a tumor. A tumor can be cancerous or benign. A cancerous tumor is malignant, meaning it can grow and spread to other parts of the body. A benign tumor means the tumor can grow but will not spread.When breast cancer is limited to the breast and/or nearby lymph node regions, it is called early stage or locally advanced. Read about these stages in a different guide on Cancer.Net. When breast cancer spreads to an area farther from where it started to another part of the body, doctors say that the cancer has metastasized. They call the area of spread a metastasis, or use the plural of metastases if the cancer has spread to more than 1 area. The disease is called metastatic breast cancer. Another name for metastatic breast cancer is “stage IV breast cancer if it has already spread beyond the breast and nearby lymph nodes at the time of diagnosis of the original cancer.
Doctors may also call metastatic breast cancer advanced breast cancer. However, this term should not be confused with locally advanced breast cancer, which is breast cancer that has spread to nearby tissues or lymph nodes but not to other parts of the body.
Stage 3 Diagnosed In 2016
When I was diagnosed, I told myself that having one of the most common types of cancer meant the best outlook for treatment and survival. Waiting for scan results was one of the hardest parts, but once I knew what I had, I could concentrate on getting through treatment. I looked for as much information and advice as possible. I started a blog to keep family and friends updated on my progress. It actually became cathartic and helped me keep my sense of humor. Looking back now, about a year after my diagnosis, I cant believe I went through it all. I discovered an inner strength I never knew existed. My advice to anyone with a recent diagnosis is dont panic, take everything one step at a time, and be as positive as possible. Listen to your body and be kind to yourself. It might all seem very daunting at first, but you canand willget through it.
Don’t Miss: Stage Iii Breast Cancer Prognosis
More Information About The Tnm Staging System
The T category describes the original tumor:
- TX means the tumor can’t be assessed.
- T0 means there isn’t any evidence of the primary tumor.
- Tis means the cancer is “in situ” .
- T1, T2, T3, T4: These numbers are based on the size of the tumor and the extent to which it has grown into neighboring breast tissue. The higher the T number, the larger the tumor and/or the more it may have grown into the breast tissue.
The N category describes whether or not the cancer has reached nearby lymph nodes:
- NX means the nearby lymph nodes can’t be assessed, for example, if they were previously removed.
- N0 means nearby lymph nodes do not contain cancer.
- N1, N2, N3: These numbers are based on the number of lymph nodes involved and how much cancer is found in them. The higher the N number, the greater the extent of the lymph node involvement.
The M category tells whether or not there is evidence that the cancer has traveled to other parts of the body:
- MX means metastasis can’t be assessed.
- M0 means there is no distant metastasis.
- M1 means that distant metastasis is present.
What Should I Ask My Healthcare Provider About Metastatic Breast Cancer
If youve been diagnosed with metastatic breast cancer, ask your provider:
- What are my treatment options?
- What is my prognosis?
- What side effects can I expect?
- Will complementary therapy help me feel better?
- What if I want to stop treatment?
- How can I feel my best during treatment?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Metastatic breast cancer is advanced breast cancer. Providers classify it as stage 4 breast cancer. It happens when cancer cells, often left behind after previous breast cancer treatment, start to spread to other parts of the body. While there is no cure for metastatic breast cancer, treatment can prolong your life and help you feel better. There are many medications available, so if one treatment isnt working, your care team can try a different approach. If you notice any symptoms or dont feel your best, especially if youve undergone breast cancer treatment in the past, talk to your healthcare provider.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 04/14/2021.
References
Don’t Miss: Signs Of Invasive Breast Cancer