How Many Images Are In A Mammogram
A routine or screening mammogram is composed of 4 images. Each image is obtained by passing a very small amount of radiation through the breast. This radiation forms a picture on the detector on the other side of the breast. There is a mediolateral oblique view which is looking through your breast from the side.
Fat Necrosis And Dystrophic Calcifications
Fat necrosis and dystrophic calcifications can be seen on the sonogram as a hypoechoic or hyperechoic irregular mass with acoustic shadowing. Correlation with mammographic images, surgical history, pathology findings, and clinical breast examination are important for accurate assessment. Serial ultrasounds and/or mammograms or biopsy may be needed.
What Is Digital Tomosynthesis
Digital tomosynthesis, also known as 3-D mammography, is a relatively new application of technology that can be used for breast cancer screening. Digital tomosynthesis images are obtained by passing a small amount of radiation through the breast at different angles. A series of images are reconstructed that allow the radiologist to scroll
Read Also: When Is Breast Cancer Staged
Breast Density After Menopause
Breast density may decrease after menopause in both women who go through natural menopause and younger women who are in menopause after surgery to remove the ovaries .
For women who use menopausal hormone therapy , breast density may not decrease until they stop using MHT. MHT is also called postmenopausal hormone therapy and hormone replacement therapy .
Breast Reduction Augmentation Or Reconstruction
Mammographic appearances of postsurgical changes after breast reduction, breast reconstruction, and breast augmentation commonly are encountered. A variety of surgical techniques are used in breast reduction surgery. One of the most common is the keyhole incision technique. In this procedure, an incision is made around the areola and extended vertically in the 6-o’clock position to the inferior mammary fold. Typical mammographic findings may include alteration of the parenchymal architecture, cranial displacement of the nipple, patchy densities due to tissue removal and scarring, and the development of fat necrosis. Approximately 6 months after surgery, a new baseline mammogram should be obtained. Any new findings from the baseline examination, such as a developing density, mass, or calcifications, require a thorough evaluation, including possible tissue sampling.
Breast reconstruction may be performed after a mastectomy by means of reconstruction with autogenous tissue transfer and/or implants. The most common autogenous tissue transfer site is from the panniculus or from a free myocutaneous flap. The most frequent location of the donor tissue is from a flap harvested from the latissimus dorsi muscle or the transverse rectus abdominis muscle flap.
Simple cysts have 4 criteria:
-
They are usually well defined and round or ovoid.
-
They have thin smooth walls.
-
They contain no internal echoes.
-
They have posterior acoustic enhancement .
Recommended Reading: How Often Is Chemo Given For Breast Cancer
Classification Based On Human Perceptual Features
One way to obtain features is to ask radiologists to read a set of mammograms and to describe the appearance of the lesions . Radiologists are specialists who are trained to recognize the normal or abnormal appearance of radiographs. Therefore, it is only reasonable to classify breast lesions based on their perceptual descriptions. The advantage of this approach is that it makes direct use of radiologists’ expertise. However, a standard language must be developed for a computer technique to interpret radiologists’ description. Radiologists may often use somewhat differing terminology when describing breast lesions. Occasionally, they may also use the same words to convey slightly different meanings. This ambiguity in terminology is generally not a problem for a radiologist, since he or she can make good use of his or her own description in making the malignant versus benign diagnosis. However, it is problematic for computer classification because it is not possible for an automated technique to interpret a particular radiologist’s language unless a standard set of terms is used.
TABLE 24.1. Examples of human perceptual features and computer-extracted features that can be used to classify malignant and benign breast lesionsa
| Feature type or number |
|---|
Xiaozheng Xie, … Shui Yu, in, 2021
She Was Screened With A 3d Mammogram
Couric received a 3D mammogram, also called digital breast tomosynthesis , which is considered a major advancement in breast cancer detection. DBT doesnt exactly produce a 3D image of the breast, but it captures multiple images from various angles to provide a more complete image.
Digital tomosynthesis excels at whats most important in mammography, CTCA Atlanta Radiologist Henry Krebs, MD, wrote in a CancerCenter360® blog. Its sensitive enough to find an abnormality and specific enough to separate the abnormality from the overlying tissues, allowing us to see subtle masses and architectural distortion often found with early-stage cancer.
Dr. Krebs strongly recommends women undergo regular screenings for breast cancer and talk to their doctor about the benefits of DBT mammograms.
Wherever you decide to get your mammography screenings, the most important takeaway is to get them regularly, and to pay attention to abnormal changes in your breast, he wrote. Weve come a long way in the diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer, and early detectionthanks in large part to advances in mammographyhas been key.
Also Check: Her2-negative Breast Cancer Hereditary
Why Do Radiologists Call Back For More Images
Occasionally, a patient will be called back for more images simply because of one of these technical reasons.Sub sequently, the radiologist will inspect the images looking for abnormalities in the form of masses, calcifications, asymmetries, and architectural distortion. These will be explained in further detail.
A Call For Multidisciplinary Medicine And Shared Decision
In accompanying commentary, Amie Lee, MD, of UC-San Francisco remarks that the Villa-Camacho and Bahl study:
highlights that the long-established approach of uniformly recommending surgical excision for all radial scars no longer applies in the era of DBT. Ultimately, the decision to excise requires a multidisciplinary approach and shared decision-making with patients.
Lee cites recent literature showing a very low upgrade risk for these lesions, leading to wide practice variation regarding whether these lesions require routine excision.
She further points to current guidelines from the American Society of Breast Surgeons stating that most radial scars should be excised, although imaging follow-up is reasonable in certain scenarios .
All three researchers comment that, given the studys retrospective and single-center design, large and prospective studies are needed to validate or challenge the present reviews findings and observations.
Don’t Miss: Is Estrogen Cream Safe For Breast Cancer Survivors
How Does Architectural Distortion Affect Our Body
The expert explained that ADC can cause many negative health effects such as heart disease, lung cancer, and asthma. Furthermore, the long-term effects of ADC may not be revealed until years down the line. This is why it is important to consider both short and long-term effects before making any decisions.
The Diagnostic Value Of Mri For Architectural Distortion Categorized As Bi
Haibing Mei1, Jian Xu1, Gang Yao2^, Ying Wang1
1Department of Radiology, Ningbo Women & Childrens Hospital , 2Department of Radiology, Sir Run Run Hospital, Nanjing Medical University , China
Contributions: Conception and design: H Mei, J Xu, G Yao Administrative support: H Mei, G Yao Provision of study materials or patients: J Xu, Y Wang Collection and assembly of data: H Mei, J Xu, Y Wang Data analysis and interpretation: J Xu, G Yao, Y Wang Manuscript writing: All authors Final approval of manuscript: All authors.
^ORCID: 0000-0001-5890-2056.
Correspondence to:
Background: Architectural distortion is a common mammographic sign that can be benign or malignant. This study investigated the diagnostic value of magnetic resonance imaging for architectural distortions that were category 34 under the breast imaging reporting and data system by mammography.
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed 219 pathologically confirmed lesions in 208 patients who had BI-RADS category 34 architectural distortion in mammography images. Two radiologists described and categorized the architectural distortion and assigned the BI-RADS categories to the corresponding lesions on MRI images. Using the postoperative pathological diagnosis as the gold standard, we performed receiver operating characteristic analysis for the efficacy of mammography and MRI in differentiating patients with benign or malignant lesions.
Keywords: Mammography magnetic resonance imaging architectural distortion
Don’t Miss: Does Zantac Cause Breast Cancer
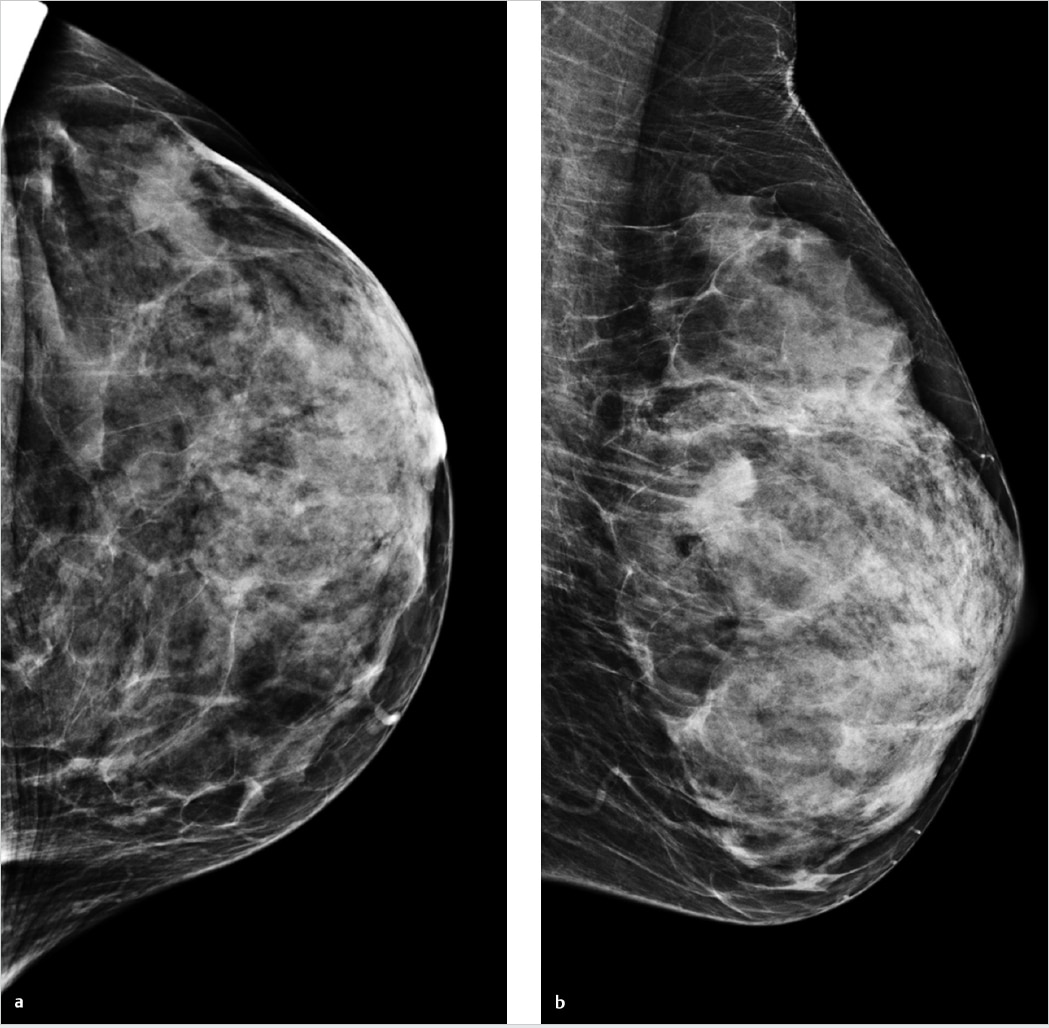
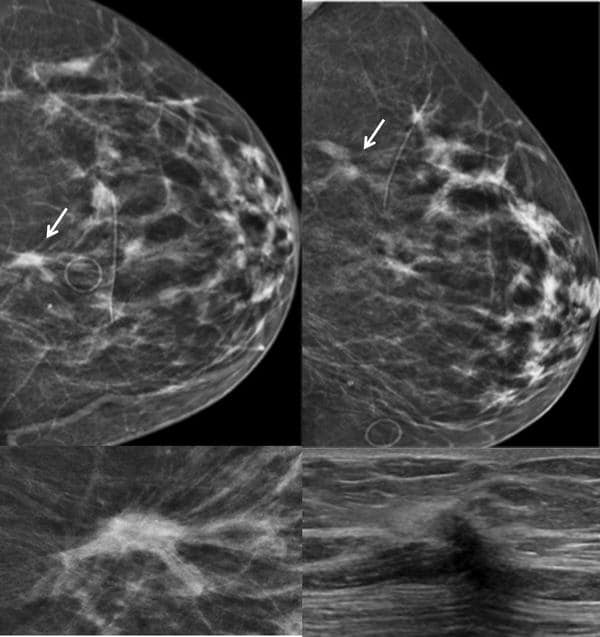
Architectural Distortion Is Among The Most Common Presentations For Breast Cancer
An architectural distortion may be caused by sclerosing adenosis, or a thing called radial scar, both of which are benign and both quite rare.
Breast cancer commonly causes architectural distortion.
Architectural distortion uncommonly indicates cancer. More common is for architectural distortion to be imaginary in the perception of the radiologist.
So in the future, someone will probably classify these into real and imaginary. Just kidding.
Although it is a subtle finding on mammography, architectural distortion is actually the third most common way that breast cancer appears. Mass or Cluster of suspicious microcalcifications are the other major ways that cancer is detected.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Breast Cancer
Knowing the signs and symptoms of breast cancer may help save your life. When the disease is discovered early, there are more treatment options and a better chance for a cure.
Most painful breast lumps are not cancerous. Any discrete breast lump whether painful or not should be evaluated because breast cancer often presents as a lump or thickening.
Recommended Reading: How Severe Is Stage 3 Breast Cancer
When To Expect Mammography Results
Some centers give you the results of your mammogram at the time of your screening. With others, it may take up to 2 weeks to get your results.
If you dont get your results within 2 weeks, contact your health care provider or the mammography center.
Dont assume the results were normal because you didnt get a report. Follow up to get your results.
What Causes Architectural Distortion In Breast
Architectural distortion can also be an associated finding. Benign causes of architectural distortion include radial scars complex sclerosing lesions sclerosing adenosis fat necrosis postprocedural change and rare spiculated benign lesions, such as granular cell tumor and breast fibromatosis. Malignant causes include breast cancer and ductal carcinoma in situ .
Also Check: Can You Have Breast Cancer Without Symptoms
The Diagnostic Efficiency Of Mri For Bi
DCE-MRI combined with DWI has high sensitivity and specificity for the diagnosis of breast cancer, but the diagnostic value of MRI for architectural distortions seen on mammography is not clear . Our study showed that architectural distortions were manifested as dot-like enhancements, mass-like enhancements, non-mass-like enhancements, and no enhancements, among which the seven cases with no enhancements and 26 cases with spot-like enhancements were benign lesions. We found that the DCE-MRI enhancement types and TIC types differed significantly between breast benign and malignant lesions, which is consistent with previous studies. Additionally, DWI had a high diagnostic efficiency in differentiating breast benign vs. malignant lesions, and the diagnostic threshold of the ADC value was 1.1×103 to 1.6×103 mm2/s . We found that the sensitivity and specificity were 79.8% and 95.6%, respectively, when differentiating benign and malignant lesions with the ADC value of 1.02×103 mm2/s, which is consistent with previous studies. The sensitivity of DCE-MRI combined with ADC in diagnosing breast benign and malignant lesions was higher than that of DCE-MRI alone. Our study showed that the specificity of DCE-MRI + ADC in differentiating breast benign vs. malignant lesions was higher than that of DCE-MRI + FFDM, which is consistent with the study by Ei Khouli et al. .
Patients Characteristics And Bi
A total of 175 malignant and 123 benign cases were identified. The age and distribution of BI-RADS scores are listed in Table 1. The mean age was 52.3 ± 8.7 in the malignant group, and 48.2 ± 8.9 in the benign group. The majority of malignant lesions had BI-RADS scores of 4B, 4C, and 5 . In the benign group, a substantial number of patients also had high BI-RADS 4B , but significantly lower than in the malignant groups . If including 4A, had BI-RADS 4A, and these patients would be recommended for biopsy and led to the false-positive diagnosis. In the present study, all benign lesions had histological confirmation. The pathological types are listed in Table 2. Lobular carcinoma in situ is a high-risk pathology and is classified into the malignant group. Figure 2 shows 2 cases presenting the typical features, and Figure 3 shows 4 cases presenting the atypical features of architectural distortion. The ROI was drawn to cover the entire area noted as suspicious.
Table 1 Age and BI-RADS of lesions determined on DBT in the study cohort.
Table 2 Pathological types of lesions in the study cohort.
Recommended Reading: What Treatments Are There For Breast Cancer
Feature Selection And Model Building
The feature selection was performed using a sequential method, by constructing multiple SVM classifiers. In this process, SVM with Gaussian kernel was used as the objective function to test the performance of a subset of features using 5-fold cross-validation. In the beginning, an empty candidate set was presented, and features were sequentially added. In each iteration, the training process was repeated 5,000 times to explore the robustness of each feature. After each iteration, the feature that led to the best performance was added to the candidate set. The process stopped when the addition of features no longer met the criterion, i.e., 106 as the termination tolerance for the objective function value. The algorithm was designed to explore all possible subsets of the shadow attributes and select the final key features by comparing their relative importance. During the feature selection, different class weights were assigned to the benign group and the malignant group to handle the imbalance issue.
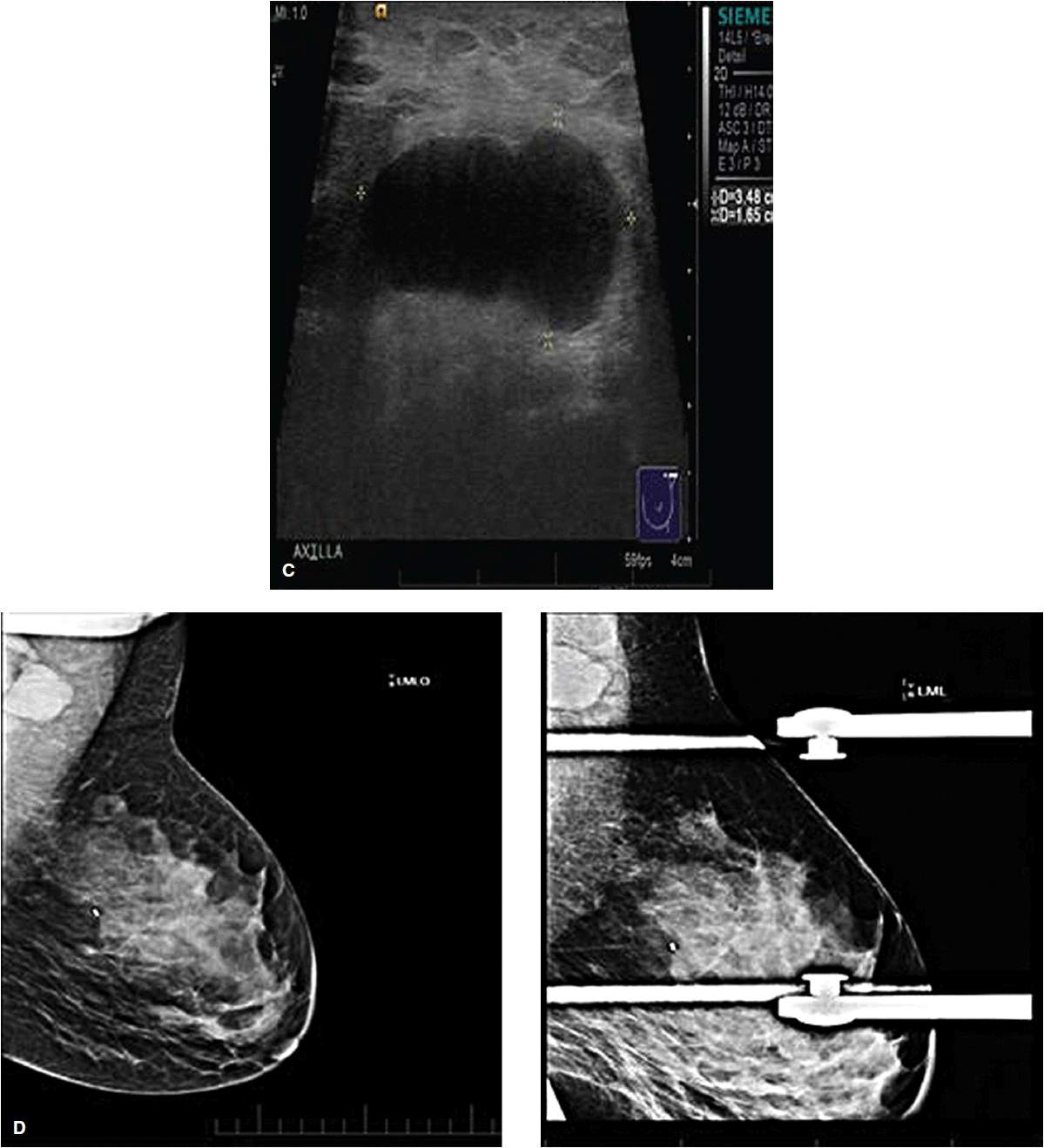
Infectious Mastitis And Breast Abscess
Breast abscess is a complication of infectious mastitis. Abscesses can be associated with lactation, in the case of puerperal abscesses, or independent of pregnancy, in the case of nonpuerperal abscesses . Puerperal abscesses tend to be peripheral in location and are often easily recognized clinically. Nonpuerperal abscesses can pose a diagnostic challenge and are more commonly seen in younger women. They are usually periareolar and typically have worse outcomes and a higher rate of recurrence than puerperal abscesses. The risk factors for nonpuerperal breast abscesses are thought to include smoking and diabetes .
Mammographically, mastitis and breast abscess present with skin thickening, asymmetry, a mass, or architectural distortion . Sonographic features of breast abscesses include one or more hypoechoic collections of variable shapes and sizes that are often continuous and multiloculated . Breast abscesses typically demonstrate a thick echogenic rim and increased vascularity, suggesting malignancy . Associated mastitis presents as an area of increased parenchymal echogenicity, representing inflamed glandular parenchyma. Skin thickening, distended lymphatic vessels, and inflammatory axillary adenopathy can also be seen. On MRI, breast abscesses will typically be T2-hyperintense, have progressive enhancement kinetics, and sometimes have the characteristic thin rim of peripheral enhancement .
Fig. 2
Also Check: Can Breast Cancer Cause Back Pain
What Does No Enhancement On Mri Mean
The differences between enhancing and nonenhancing lesions in MRI are obvious. Normally with T1 contrast agents at a usual dosage, the enhancing lesions appear hyperintense on MR images and nonenhancing lesions appear isointense or without signal changes in comparison to that on precontrast MR images.
What Does A Suspicious Breast Lump Mean
A severe injury to your breast tissue or nearby nerves can create a breast lump. Doctors describe this condition as fat necrosis. A collection of infected fluid in breast tissue also can cause a breast lump, one that’s often associated with localized breast pain and inflammation of the skin. Breast cancer.
Also Check: What Fruit Is Good For Breast Cancer
What Is A Histological Work
Determining your type of breast cancer begins with a histological workup, a summary prepared by the pathologist after you undergo a biopsy. Essentially, the histological evaluation is the microscopic analysis of the chemical and cellular properties associated with a suspicious breast tumor. The pathologists here at Providence Saint Johns will also confirm the size of the breast tumor where necessary for breast cancer staging purposes. The histological evaluation is essential to determine the most effective treatment recommendations following surgery.
Diagnosis Of Architectural Distortion On Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Using Radiomics And Deep Learning
- 1Department of Radiology, Key Laboratory of Intelligent Medical Imaging of Wenzhou, First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, China
- 2Department of Radiation Oncology, Rutgers-Cancer Institute of New Jersey, Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, NJ, United States
- 3Department of Radiological Sciences, University of California, Irvine, Irvine, CA, United States
- 4Department of Radiology, Yuyao Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Ningbo, China
- 5School of Laboratory Medicine and Life Sciences, Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, China
- 6Department of Medical Imaging and Radiological Sciences, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan
Purpose: To implement two Artificial Intelligence methods, radiomics and deep learning, to build diagnostic models for patients presenting with architectural distortion on Digital Breast Tomosynthesis images.
The radiomics model can achieve a satisfactory diagnostic accuracy, and the high specificity in the benign group can be used to avoid unnecessary biopsies. Deep learning can be used to localize the architectural distortion areas, which may provide an automatic method for ROI delineation to facilitate the development of a fully-automatic computer-aided diagnosis system using combined AI strategies.
You May Like: How Long Do You Have With Stage 4 Breast Cancer
What Is A Complex Sclerosing Lesion
Radial Scar or Complex Sclerosing Lesion is a pathological entity characterized by a fibroelastotic core with entrapped ducts. Radiologically it reveals radiolucent central core and radiating spicules, which is indistinguishable from invasive carcinoma mammographically as well as histopathologically. [
What Does Possible Architectural Distortion Mean
Architectural distortion, which refers to distortion of the breast parenchyma with no definite mass visible, can have a malignant or benign cause. A new study compares the risk of malignancy associated with architectural distortion detected on 2D digital mammography versus digital breast tomosynthesis .
Read Also: What To Buy For Breast Cancer Patient
Findings In Recent Mamogram
I just had my yearly mammogram, about 15 months apart. This is my 1st mamogram at Mayo, but I provided last years records and CD to compare. I was notified there were findings that require further testing. My current oncologist has also notified me with further results as, 2 asymmetries are seen in one breast. They suggest more tests. Anyone experience this finding? Doesn’t say anything about nodules, or calcification. I do have high density, so I opted for the 3D viewing. Basically for now, we’re looking at 2 asymmetries, which I think are pretty common, but this is all new to me. Appreciate any feedback if you’ve ever been diagnosed with asymmetries. Thanks!!
@dazlin Is this since breast surgery or radiation? My first mammogram following surgery and radiation was fine. The second one showed some activity and radiologist feels it may be fat necrosis from radiation. I am required now to have mammograms every 6 months. My PET scan also showed some activity and that is also every 6 months due to the neuroendocrine diagnosis from my second cancer lesion.