How Early Can Ibc Be Diagnosed
Because of IBCs quick-growing and aggressive nature, combined with its tendency to be misdiagnosed, its commonly diagnosed at an advanced stage.
- IBC tends to grow in layers, which is why it can be missed during exams.
- On imaging, these sheets of tissue can resemble nests.
- Your doctor may be able to feel these areas of thickening on your skin, as well as possibly see areas of higher density on a mammogram.
- Routine blood tests may not pick up abnormalities related to inflammatory breast cancer.
How To Determine If Breast Cancer Has Spread
This information may be obtained through a combination of clinical examinations, imaging studies, blood tests, lymph node removal and tissue samples . If, based on the initial test results, a physician believes that the cancer may have spread to other parts of the body, further testing may be ordered, such as a bone scan, positron emission tomography scan or liver function test.
Chemotherapy Hormone Therapy And Her2
Treatments after surgery and radiation therapy depend on treatments given before surgery and tumor characteristics, such as hormone receptor status and HER2 status :
- If chemotherapy was not completed before surgery, the remaining chemotherapy is given after surgery.
- HER2-positive IBC is treated with HER2-targeted therapy before and/or after surgery.
- Hormone receptor-positive IBC is treated with hormone therapy.
Don’t Miss: What Is Non Palpable Breast Cancer
Heres What You Need To Know About Inflammatory Breast Cancer
Inflammatory breast cancer is a rare and aggressive form of the disease that doesnt get a lot of attention. Its tough to diagnose because of its unusual symptoms, and its more common in young women which makes it particularly tricky since the symptoms mimic that of mastitis, a common breast infection in new moms who breastfeed. Heres what you need to know:
Symptoms
The symptoms for IBC dont appear like regular breast cancers. First off, you dont often find a lump. Instead, your breast may appear red, itchy, swollen, warm and tender. This happens because of the way the cancer cells have formed in the breast. They block the lymph vessels in your skin causing infection-like symptoms instead of one solid lump.
Treatment
When IBC is initially diagnosed it is always considered locally advanced. This is because it has already spread to surrounding tissue in the skin and/or lymph nodes. Further tests are done to confirm if it has spread beyond local tissue to distant organs, known as stage IV or metastatic. It can be a very aggressive, fast-growing cancer so treatment can also be aggressive.
Statistics
What Causes Inflammatory Breast Cancer
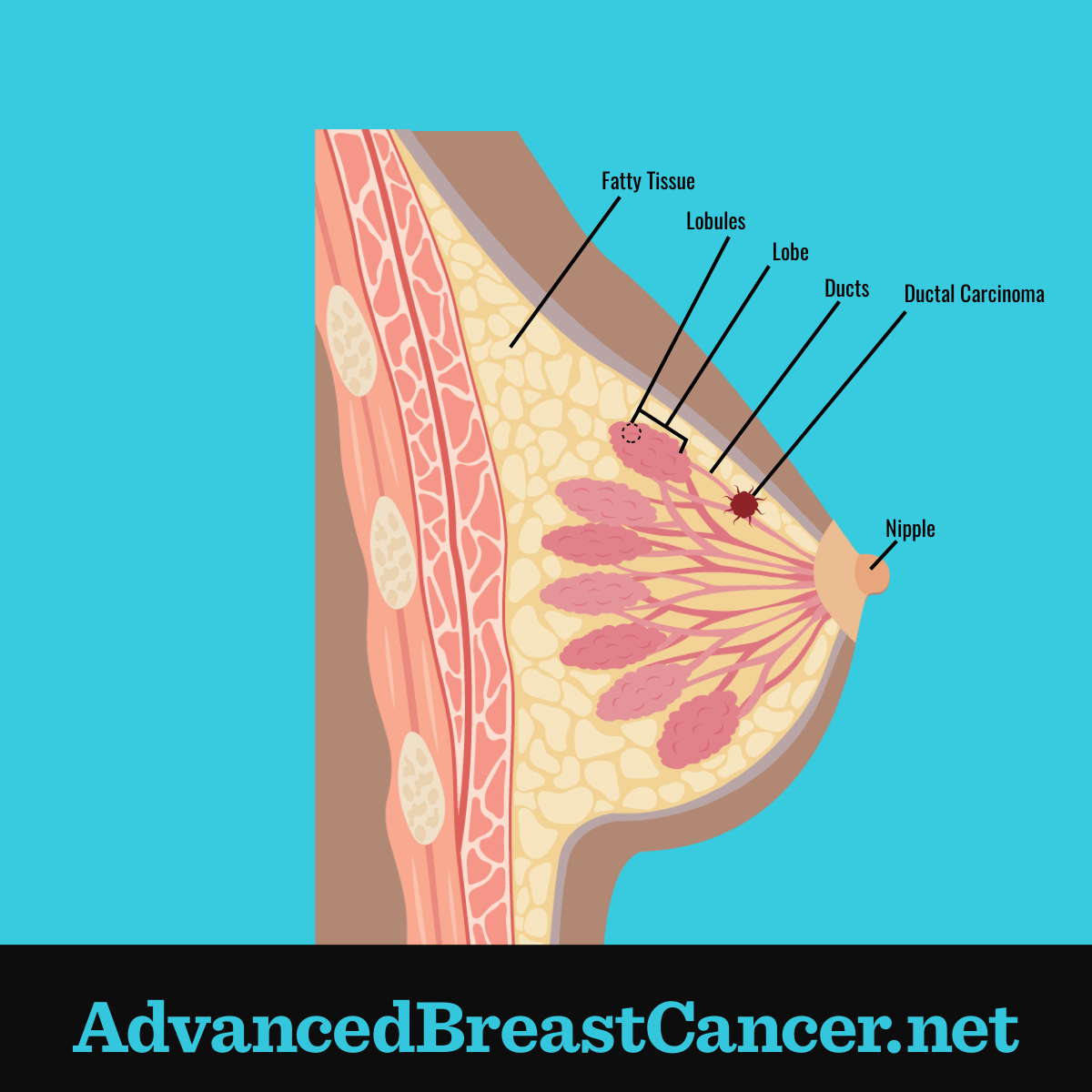
Most inflammatory breast cancer is considered invasive ductal carcinoma. Ductal carcinoma is cancer that forms from cells lining your milk ducts. An invasive ductal carcinoma is cancer that spreads beyond your milk ducts, invading healthy tissue. Researchers dont know what causes these cells to become malignant .
Inflammatory breast cancer develops when cancer cells block lymph vessels. Lymph vessels are hollow tubes in your lymphatic system that allow lymph fluid to drain out of your breast. The blockage causes your breast to become red, swollen and inflamed. In most cases of IBC, cancer cells spread outward from your lymph vessels. Cancer that has metastasized affects your other organs and is harder to treat.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Most Accurate Test For Breast Cancer
Treating Stage Iv Inflammatory Breast Cancer
Patients with metastatic IBC are treated with systemic therapy. This may include:
- Hormonal therapy
- Targeted therapy with a drug that targets HER2
- Immunotherapy if the cancer makes a protein called PD-L1
- Targeted drug therapy with a PARP inhibitor called olaparib if the woman has a BRCA mutation
One or more of these treatments might be used. Many times, a targeted drug is given along with chemotherapy or with hormone therapy. Surgery and radiation may also be options in certain situations. See Treatment of Stage IV Breast Cancer for more information.
Clinical Trials For Ibc
Research is ongoing to improve treatment for IBC.
New therapies are being studied in clinical trials. The results of these trials will decide whether these therapies will become part of the standard of care.
After discussing the benefits and risks with your health care provider, we encourage you to consider joining a clinical trial.
Don’t Miss: Does Bottled Water Cause Breast Cancer
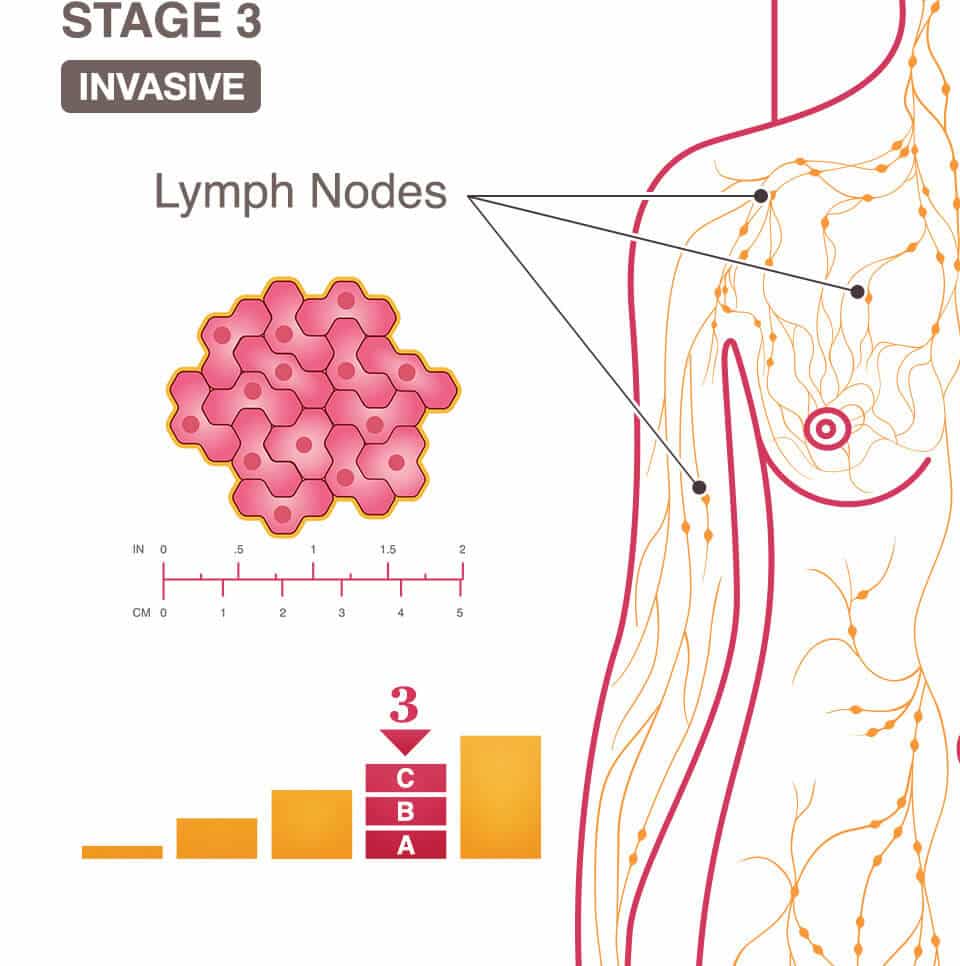
Types Of Stage 3 Breast Cancer
These days, people with breast cancer can know more about the tumor than ever before.
In addition to staging, oncologists can now determine a tumors grade and subtype. This information helps the doctor describe the tumor and cancer stage in a more detailed way so that other members of the care team can understand the cancer better.
The tumor grade and subtype of breast cancer can vary between people. Most doctors will test tumors to determine which genes they express, so that treatment options can adapt to the results.
Doctors define different types of stage 3 breast cancer by:
- Tumor grade: This is a measurement of how much the cancer cells differ from healthy cells under a microscope. This also provides a measure of how quickly the cancer cells are likely to grow.
- ER status: This describes whether the cancer cells have receptors for the hormone estrogen.
- PR status: This indicates whether the cancer cells have receptors for the hormone progesterone.
- HER2 status: This describes whether the cancer cells are making the HER2 protein.
What Is Stage 1 Breast Cancer
This breast cancer is the earliest stage of invasive breast cancer. In stage 1, the tumor measures up to 2 cm and no lymph nodes are involved. At this stage, the cancer cells have spread beyond the original location and into the surrounding breast tissue.
Because a stage 1 tumor is small, it may be difficult to detect. However, breast self-exams and routine screening are always important and can often lead to early diagnosis, when the cancer is most treatable.Stage 1 breast cancer is divided into two categories:
Stage 1A: The tumor measures 2 cm or smaller and has not spread outside the breast.
Stage 1B: Small clusters of cancer cells measuring no more than 2 mm, are found in the lymph nodes, and either there is no tumor inside the breast, or the tumor is small, measuring 2 cm or less.
At stage 1, TNM designations help describe the extent of the disease. For example, there may or may not be cancer cells in the lymph nodes, and the size of the tumor may range from 1 cm to 2 cm. Most commonly, stage 1 breast cancer is described as:
- T: T1, T2, T3 or T4, depending on the size and/or extent of the primary tumor
- N0: Usually, cancer has not spread to the lymph nodes.
- M0: The disease has not spread to other sites in the body.
Stage 1 breast cancer survival rate
The survival rate for stage 1A breast cancer may be slightly higher than for stage 1B. However, all women with stage 1 breast cancer are considered to have a good prognosis.
Don’t Miss: When Does Breast Cancer Develop
How Is Ibc Different From Other Types Of Breast Cancer
Unlike with other types of breast cancers, only 15 percent of people diagnosed with IBC have a lump. Thats why it can be mistaken for breast infections or injuries because of the redness and swelling it causes. While its possible to detect IBC on a mammogram, the imaging device may not recognize evidence of disease because the cancer forms in layers.
More women than men are affected by IBC, and it tends to be seen in younger women than other breast cancers. Black women are also at a slightly higher risk of the disease than white women, and being overweight or obese is also known risk factor for IBC.
What Are Symptoms Of Triple Negative Breast Cancer
TNBC symptoms are the same as other common breast cancers. And many breast cancer symptoms are similar to other less serious conditions. That means having certain symptom doesnt mean you have breast cancer. Possible breast cancer symptoms include:
- A new lump or mass.
- Swelling in all or part of a breast.
Also Check: 3 Cm Tumor In Breast
You May Like: Stage 1 Her2 Positive Breast Cancer
T Categories For Breast Cancer
T followed by a number from 0 to 4 describes the main tumor’s size and if it has spread to the skin or to the chest wall under the breast. Higher T numbers mean a larger tumor and/or wider spread to tissues near the breast.
TX: Primary tumor cannot be assessed.
T0: No evidence of primary tumor.
Tis: Carcinoma in situ
T1 : Tumor is 2 cm or less across.
T2: Tumor is more than 2 cm but not more than 5 cm across.
T3: Tumor is more than 5 cm across.
T4 : Tumor of any size growing into the chest wall or skin. This includes inflammatory breast cancer.
Staging Inflammatory Breast Cancer

By the time a doctor diagnoses inflammatory breast cancer, the breast cancer cells have usually grown into the skin. This local advancement means the cancer is at least stage III. In some cases, the breast cancer cells have already spread to parts of the body away from the breast which means the cancer is metastatic or stage IV.
After diagnosing inflammatory breast cancer, doctors order more tests to collect information about the cancers characteristics. These tests, as well as the results of your biopsy and any imaging tests, make up the various parts of your pathology report.
Doctors also collect the following information on inflammatory breast cancer:
-
targeted therapy at the same time as chemotherapy if the cancer is HER2-positive
- Advertisement
mastectomy and lymph node removal if the cancer responded positively to treatment, meaning the breast skin shows little to no signs of inflammatory breast cancer symptoms
- Advertisement
a different chemotherapy regimen or radiation therapy if the cancer has not responded well to treatment, meaning the breast skin is still showing signs of inflammatory breast cancer symptoms
After mastectomy, doctors recommend radiation therapy to destroy any remaining cancer cells. Still, in some cases, doctors may recommend more chemotherapy after mastectomy but before radiation therapy. Doctors do not offer radiation therapy after surgery to anyone who has radiation therapy before surgery because the cancer did not respond to chemotherapy.
Also Check: What Is The Her2 Gene In Breast Cancer
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Healthcare providers, including primary care clinicians, radiation, surgical and medical oncologists, and pathologists should form a dynamic team in the management of this complicated and challenging cancer. An individual patient-centered approach should be developed to address the patient’s ethical and social needs. All available community resources should be provided to the patient at the time of obtaining medical care. At the institutional level, conducting mobile screening mammograms for communities, tumor boards, and continuation of medical education conferences for clinicians play a vital role in understanding and improving the awareness of diagnosis and treatment for providers.
What Makes Ibc Different
Inflammatory breast cancer accounts for only a tiny fraction of breast cancers, so its symptoms are less well known and the disease has received less attention from researchers. It also has different physical signs than other types of breast cancer instead of a lump, IBC causes swelling and visible changes in the skin around the breast including redness and a dimpling of the skin called peau d’orange, which is French for the skin of an orange.
IBC also tends to show up in women at a younger age and spread more quickly than other types of cancer. And because the cancer cells have already grown into the skin by the time symptoms appear, its typically diagnosed at stage 3 or stage 4.
Unlike strides made against other types of breast cancer, there arent yet any targeted therapies against IBC.
You May Like: How Many Women Are Diagnosed With Breast Cancer
Diagnosing Inflammatory Breast Cancer
It can be difficult to diagnose inflammatory breast cancer because there is usually no lump to feel during a physical exam or to see in a mammogram. Doctors have to examine any changes to the breast and order a biopsy if they suspect inflammatory breast cancer.
Doctors also may recommend additional imaging tests, such as an ultrasound or breast MRI.
Who Is Likely To Have Inflammatory Breast Cancer
Anyone can develop inflammatory breast cancer, but certain factors may raise your risk.
- Gender: IBC can affect people of all genders, but its more common in women and people assigned female at birth .
- Age: People with IBC tend to be younger than people with other forms of breast cancer. Inflammatory breast cancer is most commonly diagnosed in women and people AFAB who are younger than 40. The median age of diagnosis is 57.
- Race: People who are Black are more likely to get diagnosed with IBC than people who are white.
- Weight: People with obesity or overweight are more likely to get diagnosed than people with a BMI that falls within the normal range.
Read Also: What Are The Chances Of Surviving Triple Negative Breast Cancer
What Are The Survival Rates For Ibc
IBC is a fast-growing and aggressive cancer. However, many factors may influence your outcome from IBC:
- The location, stage and whether or not the cancer has spread all can affect how you respond to treatment.
- Age and overall health also play a role.
While its true that this type of cancer has a lower survival rate than other forms of breast cancer, its important to remember that your situation is unique, and statistics are generated from previous patients and past treatments.
With localized IBC, meaning it hasnt spread to other organs, the five-year survival rate is about 39 percent. However, statistics on survival depend on several factors, including the cancers stage and the type of treatment you have. For instance, if cancer has spread to other organs in the body, the survival rate is about 18 percent. But if the cancer has spread to only nearby lymph nodes, the survival rate averages about 52 percent.
Expert cancer care
What Are The Treatment Options For Stage 3 Breast Cancer
Another way a doctor may describe stage 3 breast cancer is if its operable or inoperable. This will determine further treatments.
If a cancer is operable, this means a doctor believes most or all of the cancer can be removed with surgery.
Inoperable cancer is still treatable with systemic therapy, but surgery isnt the right option because doctors feel they cant remove enough cancerous cells.
Treatment options for stage 3 breast cancer may include:
- Surgery: known as a mastectomy, to remove cancerous tissue and also to remove lymph nodes
- Hormone therapy: to slow or stop the growth of cancerous cells, if hormones are driving their growth
- Chemotherapy: involves taking medications to kill fast-growing cancer cells
- Targeted therapy: uses your genes to attack cancer cells without harming healthy cells
Your doctor may also recommend a combination of two or more treatments.
Recommended Reading: What Is Adjuvant Endocrine Therapy For Breast Cancer
Why Is Inflammatory Breast Cancer More Aggressive
Inflammatory breast cancer is not just in the skin. It may be scattered throughout the breast parenchyma . The migratory/invasive nature of IBC allows it to invade the skin and produce the visual symptoms of IBC. The reasons why IBC is more aggressive than non-IBC are not well understood. Molecular studies on just tumor cells has failed to identify reproducible gene expression differences, leading to the hypothesis that IBC may be more aggressive because of the role of the tumor microenvironment . These are being actively studied, so that in the future these factors may be targeted or used as early diagnostic markers.
Are there any genetic markers for inflammatory breast cancer?
What Are The Symptoms Of Inflammatory Breast Cancer
IBC symptoms can develop quickly over several weeks. They are a result of lymph vessels becoming blocked and white blood cells building up. Inflammatory breast cancer symptoms include:
- Large patches of redness
- Generalized pain
These blockages may also cause the lymph nodes under the arm or around the collarbone to become swollen. If youre pregnant or breastfeeding, some of these symptoms might be mistaken for a common breast infection called mastitis. This is caused by breast tissue inflammation that usually affects people who are lactating, and they may or may not have an infection. You may initially be diagnosed with this condition and sent home with antibiotics. Its important to talk to your doctor if your symptoms dont go away in seven to 10 days. Unlike an infection, inflammatory breast cancer symptoms do not tend to come and go.
Breast cancer treatment: The care you need is one call away
Your multidisciplinary team will work with you to develop a personalized plan to treat your breast cancer in a way that fits your individual needs and goals.
Don’t Miss: Can Breast Cancer Cause Fatigue
What Clinical Trials Are Available For Women With Inflammatory Breast Cancer
NCI sponsors clinical trials of new treatments for all types of cancer, as well as trials that test better ways to use existing treatments. Participation in clinical trials is an option for many patients with inflammatory breast cancer, and all patients with this disease are encouraged to consider treatment in a clinical trial.
Descriptions of ongoing clinical trials for individuals with inflammatory breast cancer can be accessed by searching NCIs list of cancer clinical trials. NCIs list of cancer clinical trials includes all NCI-supported clinical trials that are taking place across the United States and Canada, including the NIH Clinical Center in Bethesda, MD. For information about how to search the list, see Help Finding NCI-Supported Clinical Trials.
People interested in taking part in a clinical trial should talk with their doctor. Information about clinical trials is available from NCIs Cancer Information Service at 18004CANCER and in the NCI booklet Taking Part in Cancer Treatment Research Studies. Additional information about clinical trials is available online.
Selected References
Anderson WF, Schairer C, Chen BE, Hance KW, Levine PH. Epidemiology of inflammatory breast cancer . Breast Diseases 2005 22:9-23.