What Is Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the breast tissues. Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers that affect women and is the second leading cause of cancer deaths in women. Men can also develop breast cancer, however, less than 1% of breast cancers are diagnosed in men.
Cancers are a unique group of diseases caused by genetic mutations, which make certain types of cells turn abnormal and grow out of control. Most types of cancers grow into masses of tissue known as tumors. Cancer spreads when tumor cells break off from the primary tumor, migrate to other parts of the body and start growing.
Also Check: What Does Breast Cancer Do To The Body
Hormone Receptor Status And Prognosis
Hormone receptor status is related to the risk of breast cancer recurrence.
Hormone receptor-positive tumors have a slightly lower risk of breast cancer recurrence than hormone receptor-negative tumors in the first 5 years after diagnosis .
After 5 years, this difference begins to decrease and over time, goes away .
|
For a summary of research studies on hormone receptor status and survival, visit the Breast Cancer Research Studies section. |
Hormone Receptor Positive Testing: Er And Pr
The estrogen receptor was first identified in the 1960s and with the progesterone receptor became recognized as a predictive marker for which women with breast cancer would respond to hormone treatment.
Ligand binding assays using frozen breast tumor tissues were an early detection method for assessing hormone receptor positive cancers.
In the last three decades, the mammographic screening program has led to a decrease in the size of detected breast cancers and an increase in the use of tumor sampling by core needle biopsy .
The availability of specific antibodies that recognize ER in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue is the basis for the development of immunohistochemical assays to detect ER retrospectively in small specimens.
According to clinical studies, IHC can determine ER status and is also predictive of patient response to endocrine therapy. The ability of ER status as determined by IHC to predict hormonal therapy response is superior to that of ER status as determined by biochemical methods.
The use of IHC to assess the ER and PR status of breast cancers in FFPE tissue sections is now a routine part of pathology practice worldwide. So, the caveat for these visual, IHC methods is that optimal fixation and a high standard of method quality assurance are necessary.
HER2 over-expression is more common in high-grade invasive breast cancers of Grade 2 or Grade 3. Unlike ER, IHC staining should not be present in normal breast.
Recommended Reading: When Is Chemo Necessary For Breast Cancer
More Aggressive Breast Cancers Are Often Her
Breast cancer tumors with a positive HER-2 status are usually fast-growing and aggressive. There tends to be a higher level of HER-2 expression in higher-grade tumors than in lower grade tumors.
HER-2 receptors and also epidermal growth factor receptors are stimulants to cancer cell growth. Other hormonal factors of a tumor can also make cancer more aggressive.
Some breast cancer tumors will have a decrease in the level of tumor-suppressor genes, such as p53, which make invasion beyond the breast ducts more likely. A decrease in the levels of metastasis-suppressor genes such as nm23 also make spread to the lymph nodes and other areas of the body more likely.
HER-2 positive breast cancers do appear to be more likely to spread early in the cancer course to major visceral sites such as the:-
- axillary lymph nodes
- adrenal glands
Receptors For Breast Cancer
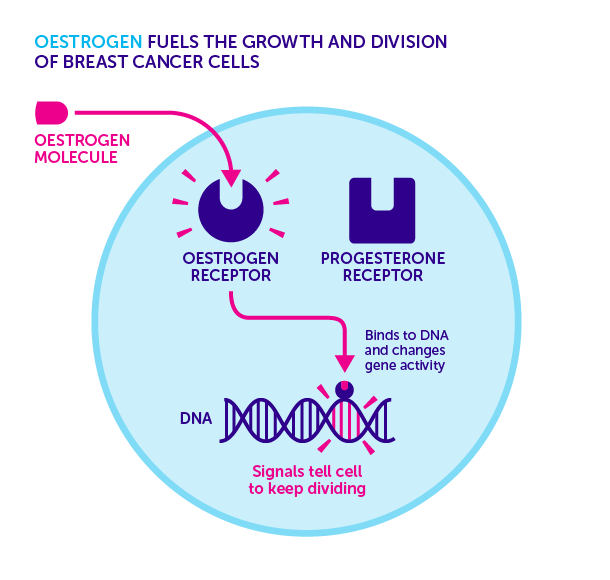
Some breast cancer cells have hormone or protein receptors that affect how the cancer grows.
On this page
Breast cancer cells may have receptors that hormones or a protein called HER2 can attach to and encourage the cells to grow. A pathologist tests the cancer cells that were taken during the biopsy or surgery for these receptors.
The results help you and your doctor decide on the most effective treatment for you.
Also Check: How You Know You Have Breast Cancer
Palpation Of Benign Breast Masses
In contrast to breast cancer tumors, benign lumps are often squishy or feel like a soft rubber ball with well-defined margins. Theyre often easy to move around and may be tender.
Breast infections can cause redness and swelling. Sometimes it can be difficult to tell the difference between mastitis and inflammatory breast cancer, but mastitis often causes symptoms of fever, chills, and body aches, and those symptoms arent associated with cancer.
Palpation Of Cancerous Masses
Cancerous masses in the breast are often very firm, like a rock or a carrot, and have an irregular shape and size. They are often fixedthey feel like they are attached to the skin or nearby tissue so that you cant move them around by pushing on thembut can be mobile. Theyre also not likely to be painful, though they can be in some cases.
On exam, other changes may be present as well, such as dimpling of the skin or an orange-peel appearance, nipple retraction, or enlarged lymph nodes in the armpit.
One type of breast cancer, inflammatory breast cancer, does not usually cause a lump but instead involves redness, swelling, and sometimes a rash on the skin of the breast.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Recurrence Rate Of Triple Negative Breast Cancer
Management And Treatment Options For Inflammatory Cancer Of The Breast
For some women with IBC, the initial investigations to find a diagnosis may not confirm a benign or a malignant condition.
So, a patient may be given conservative treatments such as anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics. Monitoring of the response to antibiotic therapy is very important if symptoms do not improve further investigations will be necessary.
Sometimes, a large excisional breast biopsy is needed to really figure out what is going on.
Inflammatory breast cancer cells tend to grow widely through the tissues of the breast, rather than as a single tumour. For this reason, chemotherapy drugs or radiation therapy are often given before surgery.
The Following Statistics Are A Little Old Now They Are Much Better
There are of course many factors that contribute to the survival of breast cancer. However, some older studies show that only about 60%of patients with HER-2 positive status invasive breast cancer are disease free after 10 years.
In addition, about 65% survive overall .
And, a greater number of HER-2 positive patients succumb to the illness during the first five years than those who are negative for HER-2 overexpression.
At the same time, all other factors assumed to be equal, patients with negative HER-2 status tumors tend to be disease free at a rate of 75% over 10 years and have a slightly higher overall survival rate.
From this, we can informally estimate that women with breast cancer which overexpresses HER-2 are about 10% more likely to have significant difficulties and ultimately succumb to the disease within the first five years, than those who do not.
Because some of the Incidence and Prognosis rates are a little old now check out our brand new Index of Posts on Survival Rates.
Read Also: How To Cure Breast Cancer With Baking Soda
What Are The Stages Of Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is staged by the size of the tumor and extent of spread. Breast cancers are also graded from one to three, based on how abnormal the cancer cells look and how fast they grow. One is low grade cancer and three is high grade cancer that grows and spreads rapidly.
The four stages of breast cancer are:
- Stage I: The tumor is relatively small and localized to the original site, with possible spread to the sentinel lymph nodes, which are the first lymph nodes the cancer is likely to spread to.
- Stage II: The tumor has grown and spread to a few nearby lymph nodes.
- Stage III: The tumor has grown into many lymph nodes and other tissue in the breast.
- Stage IV: The cancer has spread to distant parts of the body.
Another highly detailed classification system is the TNM classification system based on tumor size, lymph node involvement and metastatic spread.
How Is The Stage Determined
The staging system most often used for breast cancer is the American Joint Committee on Cancer TNM system. The most recent AJCC system, effective January 2018, has both clinical and pathologic staging systems for breast cancer:
- The pathologic stage is determined by examining tissue removed during an operation.
- Sometimes, if surgery is not possible right away or at all, the cancer will be given a clinical stage instead. This is based on the results of a physical exam, biopsy, and imaging tests. The clinical stage is used to help plan treatment. Sometimes, though, the cancer has spread further than the clinical stage estimates, and may not predict the patients outlook as accurately as a pathologic stage.
In both staging systems, 7 key pieces of information are used:
- The extent of the tumor : How large is the cancer? Has it grown into nearby areas?
- The spread to nearby lymph nodes : Has the cancer spread to nearby lymph nodes? If so, how many?
- The spread to distant sites : Has the cancer spread to distant organs such as the lungs or liver?
- Estrogen Receptor status: Does the cancer have the protein called an estrogen receptor?
- Progesterone Receptor status: Does the cancer have the protein called a progesterone receptor?
- Her2 status: Does the cancer make too much of a protein called Her2?
- Grade of the cancer : How much do the cancer cells look like normal cells?
In addition, Oncotype Dx® Recurrence Score results may also be considered in the stage in certain circumstances.
Recommended Reading: How To Donate To Breast Cancer Charity
Optimizing Breast Cancer Therapy
As advances in breast cancer surgery and other modalities occur, we will continue to reevaluate whether we can de-escalate treatment approaches to lessen the burden of treatment for patients.
At MSK, we adopted the no ink on tumor consensus guideline early and conducted a study to confirm the benefits for our patients. We also pioneered the de-escalation of axillary dissection in women with invasive breast cancer and sentinel node metastasis following evidence that found no difference in overall survival or nodal recurrence between sentinel lymph node biopsy and complete axillary lymph node dissection.
The diagnosis and treatment of invasive breast cancer requires a collaborative, multidisciplinary approach. At MSK, the breast cancer team evaluates more than 4,500 new breast cancer cases and sees 3,300 surgical inpatients and outpatients annually. Our objective is to create the most effective individualized treatment plan for each patient to optimize outcomes, reduce the burden of treatment, and improve quality of life.
Monica Morrow, MD, FACS, Chief, Breast Service, Department of Surgery, and Anne Burnett Windfohr, Chair, Clinical Oncology, discuss MSKs evidence-based, leading-edge breast cancer surgical program.
Disclosure: Dr. Morrow has received honoraria from Genomic Health and Roche.
Dont Miss: What Not To Eat With Breast Cancer
Finding The Type Of Cancer
A pathologist looks at the cancer cells under a microscope to see which type of breast cancer it is. They can tell this by the shape of the cells and the pattern of the cells in the breast tissue.
Pathologists also sometimes use particular dyes to stain the cells and show up certain proteins or features of the cells.
Recommended Reading: Does Dense Breast Tissue Increase Cancer Risk
What Is Invasive Breast Cancer Versus Noninvasive Breast Cancer
Noninvasive cancer means the abnormal cells are contained in the milk ducts of the breast and lack the ability to spread to surrounding tissue or elsewhere in the body. Invasive breast cancer means the cancer has grown beyond its original location into surrounding normal breast tissue and has the potential to spread to other parts of the body.
Crole Of 1252d3 In Regulation Of Angiogenesis Invasion And Metastasis
Metastasis, the process by which tumor cells invade secondary sites, requires degradation of the extracellular matrix and is facilitated by angiogenesis, the growth of new blood vessels into developing tumors. Effects of vitamin D signaling on late stage breast cancer have been studied in ER negative breast cancer cell lines, such as MDA-MB-231 and SUM159PT cells, which are invasive in vitro and metastatic in vivo. In these cell lines, 1,252D3 and EB1089 inhibit invasion as measured by the in vitro Boyden chamber assay . Inhibition of invasion by vitamin D compounds can be dissociated from effects on proliferation, and may be linked to regulation of extracellular proteases such as MMP-9, urokinase-type plasminogen activator , and tissue type plasminogen activator . In MDA-MB-231 cells, these effects may result from vitamin Dmediated up-regulation of protease inhibitors PA inhibitor 1 and MMP inhibitor 1 .
Sudhakar Jinka, Rajkumar Banerjee, in, 2017
Don’t Miss: How Can I Know If I Have Breast Cancer
Types Of Breast Cancer
There are several types of breast cancer, and any of them can metastasize. Most breast cancers start in the ducts or lobules and are called ductal carcinomas or lobular carcinomas:
- Ductal carcinoma. These cancers start in the cells lining the milk ducts and make up the majority of breast cancers.
- Lobular carcinoma. This is cancer that starts in the lobules, which are the small, tube-like structures that contain milk glands.
Less common types of breast cancer include:
-
Medullary
-
Metaplastic
-
Papillary
-
Inflammatory breast cancer is a faster-growing type of cancer that accounts for about 1% to 5% of all breast cancers.
-
Pagets disease is a type of cancer that begins in the ducts of the nipple.
Breast cancer can develop in women and men. However, breast cancer in men is rare. Less than 1% of all breast cancers develop in men.
Read Also: When Is Chemo Necessary For Breast Cancer
All About Er Positive Her2 Negative Breast Cancer
About one in eight women in the United States will develop breast cancer, according to commonly used statistics.
But other reports indicate that breast cancer rates are on the decline, likely because of improved recognition, prevention, and treatment. One advancement is the ability to identify different breast cancer types based on specific molecules found in tumors. The distinction greatly aids in breast cancer treatment selection and helps doctors predict how aggressive cancers will advance.
A crucial step in the process of beast cancer evaluation is testing tumor tissue removed during a biopsy or surgery to determine if it has estrogen and progesterone receptors molecules that the hormones bind to.
Cancerous cells may have none, one, or both receptors. Breast cancers that have estrogen receptors are called ER-positive . Those with progesterone receptors are referred to as PR-positive .
In addition to hormone receptors, some breast cancers have high levels of a growth-promoting protein called HER2/neu. If a tumor has this property, it is called HER2-positive. HER2 positive cancers are more aggressive than HER2 negative cancer.
Knowing breast cancer type, leads doctors to determining best treatments.
HER2 negative cancers will not respond to treatment with drugs that target HER2, such as trastuzumab and lapatinib .
Overall, estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer is treatable, especially when diagnosed early.
Don’t Miss: Is Breast Cancer Caused By Smoking
What Is Inflammatory Breast Cancer
As its name suggests, inflammatory breast cancer often causes the breast to become red, swollen, and inflamed. Some women with IBC also notice thickened or discolored breast skin with tiny dimples, puckers, or ridges that make it look like an orange peel. While the symptoms may sound like an infection, the real culprit is cancer that is blocking lymphatic vessels in the skin and breast tissue, causing a buildup of fluid and, in some cases, pain, discoloration, and sudden swelling of the breast. Also called inflammatory breast carcinoma or locally advanced breast cancer, IBC can spread quickly, making prompt diagnosis and treatment essential.
How Worried Should Women Be
Inflammatory breast cancer is a rare disease, so the chances of your getting it are quite small. Awareness of what symptoms to look for and of how to go about having those symptoms evaluated is the most important defense against this and any disease.
Additional information about IBC can be found at:
Don’t Miss: Does Stress Cause Breast Cancer
Risk Of Recurrence: Early And Late
Research has shown the HER2-positive early breast cancers are two to five times more likely to recur than HER2-negative tumors. Even very small HER2-positive tumors with negative lymph nodes have a much higher risk of recurrence relative to tumors that are HER2-negative. Treatment with Herceptin can cut this risk by half.
The pattern of breast cancer recurrence may also differ. Small tumors are also more likely to have a metastatic recurrence if they are HER2-positive.
Despite the fact that HER2-positive and estrogen receptor-negative tuors are more likely to recur early on than estrogen receptor-positive and HER2-negative cancers, late recurrences are much less common.
With estrogen receptor positive breast cancers, the cancer is more likely to recur after 5 years than in the first 5 years, and the risk of recurrence remains steady each year for at least 20 years following the diagnosis. In contrast, those who have HER2 positive tumors and reach their 5 year mark are much more likely to be “in the clear” and remain recurrence free.
Breast Cancer : Much Progress But Work Remains
Mention that statistic, and many women in the U.S. immediately know it refers to their lifetime risk of getting breast cancer.
Although the statistic may stir up anxiety, those diagnosed with breast cancer today have a more positive prognosis than ever, experts say. Thats due to better understanding of the disease, wider choices of treatments, and more individualized treatment designed to reduce the risk of recurrence and lessen side effects.
While breast cancer incidence has risen by 0.5% per year in recent years, and it remains the second leading cause of cancer death in women, outpaced only by lung cancer, there are now more than 3.8 million breast cancer survivors in the U.S.
If the disease is caught early, women with breast cancer have a survival rate of an astounding 99%, though that may dip to 28% if the cancer has spread.
But despite the progress, much work remains. Read on to see how far weve come in the fight against breast cancer and what experts say needs to happen next.
Breast Cancer: Not a Single Disease
Breast cancer is increasingly viewed as multiple different diseases, says Harold J. Burstein, MD, a breast oncologist at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston.
That discovery, in turn, has helped to individualize treatment and predict exactly how much treatment is needed for a specific patient, he and other experts say.
Molecular Diagnostics and ER-Positive Cancers
New Hope for HER2-Positive Cancers
Expanded Genetic Testing
Don’t Miss: What Chemo Drugs Are Used For Triple Negative Breast Cancer