A Constantly Evolving Field
When doctors began screening for breast cancer in the 1960s and 1970s, they used standard X-rays. Eventually, they developed more-specialized techniques and equipment for doing mammograms. In the early 2000s, digital mammography, in which images are stored on computers, replaced films. In the past several years, 3-D mammography has replaced 2-D mammography as the standard screening method for women with dense breasts. Digital 2-D mammography is the standard for those who dont have dense breasts.
More than 1,400 women, ages 40 to 75, participated in the JAMA study. All of them were found to have dense breasts on a prior mammogram, did not have any signs or symptoms of breast cancer, and were of average risk.
MSK recommends that women who are at high risk of developing breast cancer due to family history or mutations in the BRCA genes undergo screening every year, whether they have dense breasts or not..
The women in the trial were screened with both 3-D mammography and abbreviated breast MRI at 48 centers in the United States and Germany.
In the first year of the study, 23 women were diagnosed with breast cancer. The abbreviated MRI detected 22 out of the 23 breast cancers, while the 3-D mammogram detected only nine out of the 23 cancers. Only one cancer was discovered with 3-D mammography that was not found with abbreviated MRI.
Where Should Women Seek Counsel Regarding Risk Assessment For Breast And Ovarian Cancer
It can be very complex to put a patients family and personal health history together to determine what is relevant. Johns Hopkins Medicines Breast and Ovarian Surveillance Service, also known as the BOSS clinic, assists patients and referring physicians. BOSS clinic appointments are comprehensive single visits that provide patients with a care plan and help them understand their risk, whether they should be tested for BRCA1 or BRCA2 genes, and how they should most effectively screen for breast and ovarian cancer.
What Happens Before A Breast Mri
Before a breast MRI, personal items such as your watch, jewelry, and wallet — including any credit cards with magnetic strips — should be left at home or removed. Hearing aids should be removed before the test, because they can be damaged by the magnetic field. Secured lockers are typically available to store personal possessions.
Recommended Reading: Can Breast Cancer Affect Your Eyes
What Are The Most Common Uses For A Breast Mri
The most common use for breast MRI is high risk screening, which is indicated annually to supplement a mammogram for women who have a 20% or greater lifetime risk of breast cancer.
The 20% or greater lifetime risk is determined by one of multiple risk models. They are found online for example, on the National Cancer Institute website.
Recent literature supports the use of screening MRI for women with a personal history of breast cancer and dense breast tissue, as well as when a woman has a recent diagnosis of breast cancer.
Of the breast imaging modalities, MRIs have been shown to demonstrate the most accurate extent of disease of any of the breast imaging modalities. Our breast imaging specialists also look at the contralateral breast when there is a new breast cancer diagnosis. The data demonstrates that 3% to 5% of women will have asynchronous contralateral breast cancer, which is critical to diagnose at the time of breast cancer treatment.
The breast MRI can also identify the extent of the cancer that has been biopsied by determining if cancer is in more than one quadrant, and if the chest wall or the skin and nipple are involved. The MRI can help breast surgeons determine whether a lumpectomy or mastectomy should be planned.
Difficult imaging problem: Occasionally, when a definitive lesion cannot be identified by mammography or ultrasound, a breast MRI can help sort out the findings that are confusing on previous imaging.
Developing Indications For Breast Mri Screening

The ACS also defined patient categories where evidence was insufficient to recommend for or against screening. These include women with a lifetime risk of between 15% and 20% , women with biopsy results of an atypical epithelial proliferation , women with a personal history of breast cancer, and women with heterogeneously or extremely dense breasts on mammography. Based on expert opinion, screening of women at average risk with MRI was not advised by the ACS. Currently, however, evidence for the use of MRI screening in these subgroups is mounting.
You May Like: Can Breast Cancer Start In The Lymph Nodes
Is A Breast Mri Useful When It Is Suspected That Breast Implants Are Leaking
A breast MRI can be very useful in determining leakage. It is important to know what type of implant is in place. For example, saline implants don’t need an MRI for assessment of rupture or leakage because these implants simply collapse when they rupture, which can be diagnosed on physical examination or mammography.
Much of what is viewed in a breast MRI is the breast tissue parenchyma, and it requires contrast. Regarding implants, contrast material is not needed. Radiologists are looking to see where the silicone is located. The three options are that the silicone is in the implant, outside the implant but in the fibrous capsule that the body makes surrounding the implant, or free in the breast tissue or within a lymph node.
The ruptures are intracapsular or extracapsular . A breast MRI distinguishes these ruptures very clearly.
Why Is A Magnetic Resonance Imaging Of The Breast Performed
MRI is used to help detect breast cancer and other abnormalities in breast tissue. It is often used to provide more detail after a person has been diagnosed with breast cancer. A MRI exam helps doctors measure the extent of the cancer, look for other cancer or abnormal tissue in the breast, and monitor for breast cancer after treatment.
The American Cancer Society recommends that women with a high risk of breast cancer be screened with MRI and an annual mammogram to detect breast cancer. However, MRI is not recommended as a screening tool for women at average risk because it can miss some of the cancers found by a mammogram and because it can result in many false positive findings. In other words, the high sensitivity of the MRI can lead to many unnecessary tests, biopsies, and anxiety for average-risk patients for what turns out to be a non-cancerous lesion.
You May Like: What Stage Of Breast Cancer Is Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Mri For Breast Cancer Is Useful For A Second Look For Dense Breasts
The X-ray image below also shows an asymmetrical density, but it is very difficult to see due to the dense fibroglandular tissue in this particular patient.
A close up view shows an accentuated density with architectural distortion, and one can observe the tent sign given caused by the retractile desmoplastic reaction. Since the breast tissue is so dense, an MRI work up is a sensible approach in diagnosing and staging this particular patient.
The MR image of the lesion, shown below, confirms it to be multifocal breast cancer, very clearly delineating the different nodules. MRI also shows that the right breast is completely normal. Therefore, a mastectomy of the single affected breast would be a likely treatment approach.
What Are The Risks Of A Breast Mri
Because radiation is not used, there is no risk of exposure to radiation during an MRI procedure. Each patient must be screened before exposure to the MRI magnetic field.
Due to the use of the strong magnet, special precautions must be taken to perform an MRI on patients with certain implanted devices such as pacemakers or cochlear implants. The MRI technologist will need some information regarding the implanted device, such as the make and model number, to determine if it is safe for you to have an MRI. Patients who have internal metal objects, such as surgical clips, plates, screws or wire mesh, might not be eligible for an MRI exam.
If there is a possibility that you are claustrophobic then you must ask your physician to provide you with anti-anxiety medication that you can take prior to your MRI examination. You should plan to have someone drive you home afterwards.
If you are pregnant or suspect that you may be pregnant, you should notify your health care provider. To date there is no information indicating that MRI is harmful to an unborn child, however MRI testing during the first trimester is discouraged.
A doctor may order a contrast dye to be used during some MRI exams in order for the radiologist to better view internal tissues and blood vessels on the completed images. If contrast is used, there is a risk for allergic reaction. Patients who are allergic or sensitive to contrast dye or iodine should notify the radiologist or technologist.
Recommended Reading: Does Ovarian Cancer Cause Breast Pain
What Are The Risks And Potential Complications Of A Breast Mri
A breast MRI is generally a safe procedure with very few risks. An MRI does not expose you to radiation. There are no known harmful side effects of the brief exposure to the strong magnetic field it uses. However, allergic reactions to contrast agents or dyes can happen in rare instances. People with may also rarely have worsening kidney function with contrast agents.
With breast MRI, it is common for the test to find changes that turn out not to be . This is a false-positive result. When something shows up on an MRI, doctors must order additional testing to find out if it is cancerous. This means women may undergo more biopsies and other tests after breast MRI than other imaging exams. This is a main reason why breast MRI screening is not for women at average risk of breast cancer.
Mri For Breast Cancer: Post Lumpectomy
A follow-up MRI after lumpectomy or breast conservation surgery has the advantage of providing a bilateral view of the breasts. Usually, background enhancement and cystic alteration will decrease bilaterally on MRI after completion of surgery and radiation.
In addition, edema, skin thickening, seroma, and enhancement at the lumpectomy site will also decrease progressively. However, in some women these changes never actually resolve. Edema can still be present 6 or more years following lumpectomy in about 25% of women, and seroma remains in up to 4%.
Lumpectomy site enhancement in general is seen in around 35% of women in the first 12 months following lumpectomy, and in 15% of women even after 5 years. There is also some evidence to support the observation that women with high levels of fat necrosis in the lesion will be more likely to show lumpectomy site enhancement than those without.
Read Also: What Happens When Breast Cancer Comes Back
What Can I Expect After A Breast Mri
A breast MRI is usually an outpatient procedure. You can go home and resume your normal activities right away unless your doctor tells you otherwise.
The results of your breast MRI will determine your next steps. Benign results mean there is no cancer and no further treatment may be necessary. If the results indicate a problem, you may need more imaging exams, additional diagnostic tests , or treatment.
Current Indications For Mri Screening
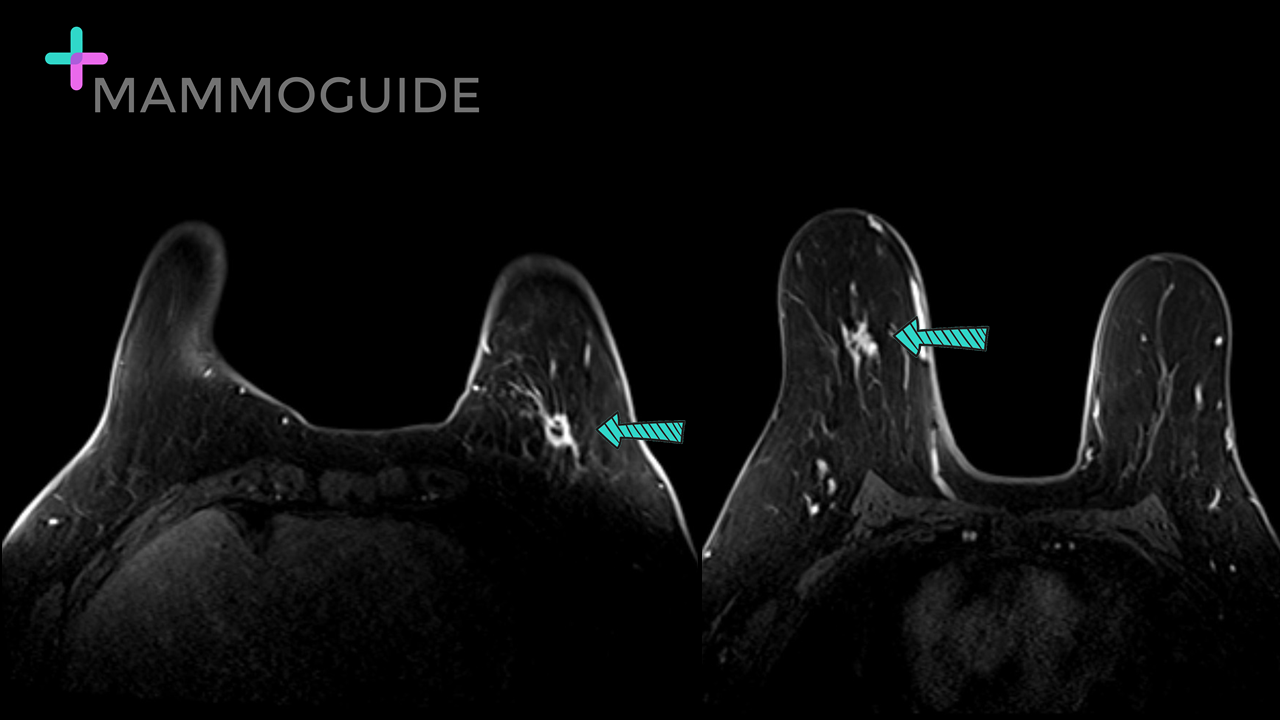
The largely improved detection of early breast cancer shown in the early studies is the basis for the widely adopted recommendations of the American Cancer Society . They advise MRI screening for all women with a lifetime risk for the development of breast cancer of 20â25% or higher based on family history or genetic predisposition. Based on expert opinion, these recommendations also include women with a history of radiation to the chest at a young age, and women with p53 and PTEN mutation, which were underrepresented in the original cohorts, but for whom the relative risk of developing breast cancer is likewise high .
These recommendations still form the basis for most national and international guidelines. Unfortunately, due to the fact that for many women the presence of genetic risk factors is unknown, and the fact that many facilities do not have breast MRI available, there is a large fraction of eligible women that is not screened according to these standards. In part, this may also be due to inadequate patient information about the benefits of MRI. Wernli et al reported that by 2009 29% of eligible women were screened with MRI. Miles et al showed that in 2012 43.9% of women with familial risk visited a clinic with MRI facilities for screening. However, only 6.6% were screened with MRI within 2 years from a mammogram. Stout et al reported that only 48.4% of women with known genetic mutations underwent MRI screening.
Read Also: Can Breast Cancer Cause Stomach Pain
Why Is A Breast Mri Performed
An MRI for a breast cancer evaluation is currently the most common reason to have a breast MRI. But there are also other reasons to have a breast MRI. Your doctor may recommend a breast MRI for the following:
-
Determining the extent of cancer after a new breast cancer diagnosis. This includes finding out whether the cancer has spread to the underlying muscles or if there are suspicious lymph nodes.
-
Evaluating a breast tumor when planning surgery to remove it. This includes looking for other areas of cancer in the same breast and in the opposite breast. It is also useful for women who have before surgery in a effort to shrink the tumor.
-
Evaluating an abnormality from another imaging exam, such as a mammogram or .
-
Evaluating an old site when something changes on a mammogram or ultrasound. An MRI can tell doctors if the change is due to normal scar aging or if it is a cancer recurrence.
-
Evaluating silicone breast implants to see if the implant has ruptured.
-
Screening women who are at high risk of breast cancer or have dense breast tissue. MRI screening is a supplemental exam that can complement mammography. MRI can find some cancers that a mammogram could miss. However, it can also miss certain cancers that would show up on a mammogram.
Breast Mri And Breast Cancer Screening For Women At Higher Risk
Compared to mammography alone, mammography plus breast MRI can increase detection of breast cancer in some women at higher than average risk of breast cancer .
The National Comprehensive Cancer Network recommends yearly screening with mammography plus breast MRI for some women at higher risk of breast cancer, including those with :
Both the NCCN and the American Cancer Society recommend women at higher risk of breast cancer begin screening at an earlier age than women at average risk . Figure 3.5 and Figure 3.6 outline their guidelines.
Talk with your health care provider about breast cancer screening. Together, you can make a screening plan thats right for you.
| For a summary of research studies on breast cancer screening with breast MRI plus mammography and mammography alone for women at higher than average risk of breast cancer, visit the Breast Cancer Research Studies section. |
You May Like: Can Breast Cancer Make Your Hair Fall Out
What Happens If Something Is Found On The Scan
If an abnormality is seen on the MRI, you will be asked to go back for more testing. This is a similar process to what happens if a problem is found on a screening mammogram. Usually an ultrasound is the next thing that is done. Even if you have recently had a breast ultrasound, you may be asked to have another one, which will focus on the area that looked abnormal on the MRI. Sometimes changes will be seen on the ultrasound that were not noticed, or not thought to be important, when the first one was done.
If an abnormal area is seen on the ultrasound, it may be recommended that you have an ultrasound-guided biopsy.
If no abnormality is seen on the ultrasound, you may not need to have anything else done. A follow-up MRI scan 6 or 12 months later may be all that is needed. However, if no abnormality is seen on the ultrasound, but there is still concern about the MRI abnormality, it may be recommended that you have an MRI-guided biopsy. This is a very specialised test that requires dedicated equipment that are not affected by the magnetic field.
Best Diagnostic Imaging Test For Cancer
If MRIs are less detailed than PET/CT scans, why are they still being used ?
- MRIs are cheaper than PET/CTs.
- There are far more MRI machines than PET/CT machines.
- MRIs are more detailed than ultrasounds and CT scans.
- More doctors are familiar with the older technology of MRIs than with the newer technology of PET/CT scans.
- MRIs do not expose people to radiation.
A PET/CT scan remains your best option for diagnostic imaging: PET/CTs can identify exactly where the cancer is in your body, its level of aggression, and if your treatment is working optimally. Please read more about why PET/CT scans are so effective and how you can get one immediately.
If you have any questions, please reach out to us today. Were standing by to help you access the best tests and treatments for your form of cancer.
Register for a Precision Second Opinion to discover how we can help you to reduce stress and dramatically increase treatment success.
Don’t Miss: How Do I Get Tested For Breast Cancer
Breast Magnetic Resonance Imaging And Dcis
DCIS on a mammogram is usually identified by the presence of microcalcifications. The tumour within the terminal ductal units and the ducts outgrows its blood supply, undergoes necrosis and calcifies. MRI does not pick up these calcifications. However, the non-mass enhancement that is seen in DCIS id probably because the gadolinium permeating into the ducts through the leaky basement due to protease activity produced by tumour cells. Thus MRI might actually detect the more clinically relevant high grade lesions. The low grade DCIS readily picked up by the x ray mammogram may be missed on MRI. On the other hand 10-15% of DCIS present as non-calcifying DCIS are missed X ray mammogram but detected on MRI.
Non-mass enhancement in a ductal or segmental distribution with clumped or stippled morphological appearance is the typical presentation of DCIS in about 70 -80% of cases. The remaining 20-30% of various enhancement patterns such as focus or a mass in a focal area or regional distribution is seen. The kinetic are variable and contribute less to the diagnosis of DCIS.