Stage 2 Breast Cancer
What is Stage 2 breast cancer?
Stage 2 breast cancer cells or tumors are larger than Stage 1 cancers, and may have spread to nearby lymph nodes. There are two types of Stage 2 breast cancer:
- Stage 2A breast cancer Generally speaking, Stage 2A breast cancer can indicate one of the following:
- No tumor can be found in your breast, but cancer larger than 2 millimeters can be found in one to three underarm lymph nodes or near the breastbone.
- The tumor measures 2 centimeters or smaller, and has spread the nearby axillary lymph nodes.
- The breast cancer has not spread to area lymph nodes, however, the tumor measures between 2 and 5 centimeters.
What are the options for Stage 2 breast cancer treatment?
What is the Stage 2 breast cancer treatment timeline?
Again, it depends on what treatments or follow-up therapies are needed. Generally, the treatment timeline for Stage 2 breast cancer can last three to six months. Again, certain treatments like hormone therapies designed to stop the cancer from coming back can last for one to 10 years.
What Are The Different Grades Of Breast Cancer
There are three grades of invasive breast cancer:
- Grade 1 looks most like normal breast cells and is usually slow growing
- Grade 2 looks less like normal cells and is growing faster
- Grade 3 looks different to normal breast cells and is usually fast growing
Sometimes the grade given to a cancer after a biopsy can change after surgery. This is because after surgery theres more tissue for the pathologist to look at, which can give them more detailed information about the cancer.
Breast Cancer Is A Disease In Which Malignant Cells Form In The Tissues Of The Breast
The breast is made up of lobes and ducts. Each breast has 15 to 20 sections called lobes. Each lobe has many smaller sections called lobules. Lobules end in dozens of tiny bulbs that can make milk. The lobes, lobules, and bulbs are linked by thin tubes called ducts.
Each breast also has blood vessels and lymph vessels. The lymph vessels carry an almost colorless, watery fluid called lymph. Lymph vessels carry lymph between lymph nodes. Lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped structures found throughout the body. They filter lymph and store white blood cells that help fightinfection and disease. Groups of lymph nodes are found near the breast in theaxilla , above thecollarbone, and in the chest.
The most common type of breast cancer is ductal carcinoma, which begins in the cells of the ducts. Cancer that begins in the lobes or lobules is called lobular carcinoma and is more often found in both breasts than are other types of breast cancer. Inflammatory breast cancer is an uncommon type of breast cancer in which the breast is warm, red, and swollen.
For more information about breast cancer, see:
Recommended Reading: Clinical Trial For Breast Cancer
Checking The Lymph Nodes
The usual treatment is surgery to remove the cancer. Before your surgery you have an ultrasound scan to check the lymph nodes in the armpit close to the breast. This is to see if they contain cancer cells. If breast cancer spreads, it usually first spreads to the lymph nodes close to the breast.
Depending on the results of your scan you might have:
- a sentinel lymph node biopsy during your breast cancer operation
- surgery to remove your lymph nodes
You may have other treatments after surgery.
How The Breast Cancer Staging Process Starts
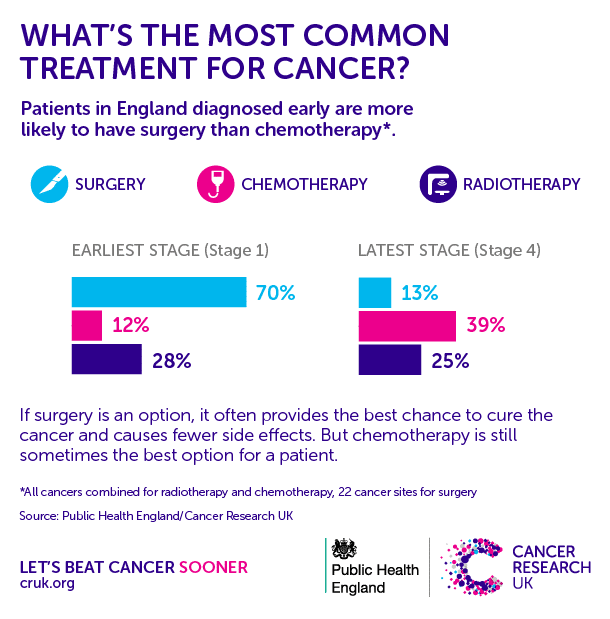
The breast cancer staging process begins with diagnostic testing. Depending on previous screening results, if any breast cancer symptoms are present, and other factors, your doctor may recommend one of the following tests:
- Diagnostic mammogram A mammogram involves using an X-ray to take photos of your breast tissue at different angles. To do this, your breasts are gently compressed between two plates so the X-ray can be taken.
- Ultrasound An ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging test that bounces soundwaves of your breast tissue to create a picture of the inside of your breast.
- MRI An MRI is another non-invasive imaging test that uses radio waves and a magnetic field to create an image of your breast tissue. This can help doctors determine the size and placement of tumors.
- Biopsy A biopsy removes small masses and growths from your breast so they can be examined under a microscope by a pathologist and determine if theyre cancerous.
If cancer is detected, a CT scan may be ordered to look for any distant metastasis or local invasion to other organs. And youll likely be connected with a breast surgeon right away, either through a nurse navigator or your doctor.
Don’t Miss: Can Estroven Cause Breast Cancer
Aromatase Inhibitors Cut Breast Cancer Risk In Postmenopausal Women
2011-2014
A large Phase III trial shows for the first time that exemestane part of a group of drugs called aromatase inhibitors greatly lowers the chance of developing invasive breast cancer in postmenopausal women who are at a high risk for breast cancer. This includes women with BRCA gene mutations, as well as other risk factors. In 2014, another aromatase inhibitor, anastrozole , was shown to lower the risk of breast cancer by nearly 50% over five years.
Two other drugs, tamoxifen and raloxifene , are also FDA-approved for breast cancer prevention in women at high risk for the disease Aromatase inhibitors work differently, however, and tend to carry milder side effects.
What Is The Life Expectancy For Stage 3 Breast Cancer
The life expectancy for people with breast cancer is improving, according to the American Cancer Society. It points out that current survival rates are based on people who were diagnosed and treated at least 5 years ago and treatments have advanced over that time.
Your life expectancy with stage 3 breast cancer depends on several factors, such as:
- the size of the tumors
You should talk with your doctor about how these factors may apply to you.
Also Check: How To Cure Breast Cancer With Baking Soda
Recommended Reading: Do You Get Pain With Breast Cancer
Finding Your Breast Cancer
- Most small breast cancers are found on screening mammography and possibly by ultrasound or maybe a breast MRI. You may have detected your own breast lump and sought further help from your physician. The time to schedule a mammogram, have it performed, return for further breast imaging and then get the results can take days to weeks. Always ask to have your tests and appointments scheduled as soon as possible.
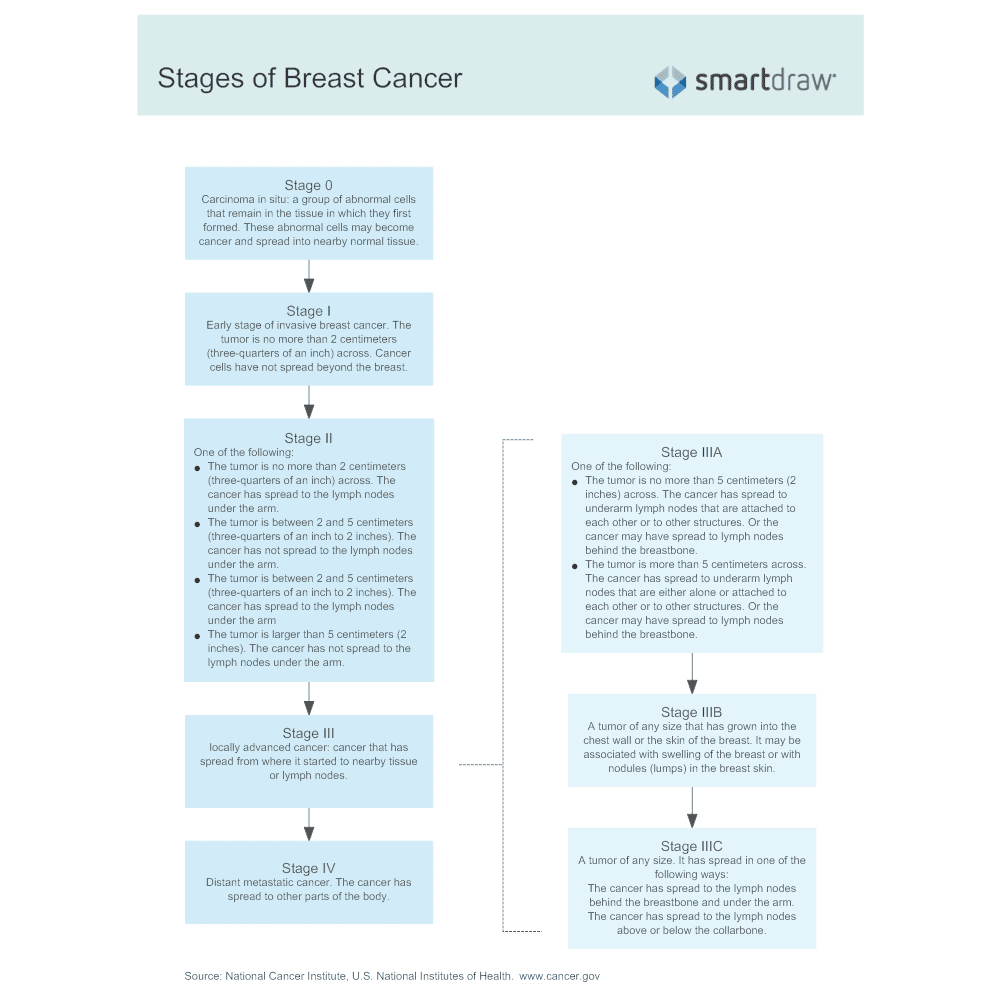
What Is Stage 1 Breast Cancer
Invasive breast cancer occurs when cancer cells have started to move from their original location usually in the milk ducts into the surrounding breast tissue. Stage 1 breast cancer is the earliest form of invasive breast cancer. It may further be classified into substages: stage 1a and stage 1b.
Read Also: High Risk Breast Cancer Screening Guidelines
Complete Loss Of Consciousness
At the end of life, the chemical balance of the body becomes completely upset. The dying person then slips into unconsciousness. This is usually right towards the end, maybe only a few hours or days before death.
The persons breathing becomes irregular and may become noisy. You wont be able to wake them at all. Their breathing will stay irregular for some time and will stop at some point.
Patients Can Enter Clinical Trials Before During Or After Starting Their Cancer Treatment
Some clinical trials only include patients who have not yet received treatment. Other trials test treatments for patients whose cancer has not gotten better. There are also clinical trials that test new ways to stop cancer from recurring or reduce the side effects of cancer treatment.
Clinical trials are taking place in many parts of the country. Information about clinical trials supported by NCI can be found on NCIs clinical trials search webpage. Clinical trials supported by other organizations can be found on the ClinicalTrials.gov website.
Also Check: What Does An Oncologist Do For Breast Cancer
Stage 1b Breast Cancer Means One Of The Following Descriptions Applies:
Lymph nodes have cancer evidence with small clusters of cells between the approximate size of a pinprick to the approximate width of a grain of rice .
AND EITHER No actual tumor is found in the breast.
OR The tumor is smaller than the approximate size of a peanut .
Similar to stage 0, breast cancer at this stage is very treatable and survivable. When breast cancer is detected early, and is in the localized stage , the 5-year relative survival rate is 100%.
Treatment For Stage 1 Breast Cancer
Doctors can offer a variety of for stage 1 breast cancer, although surgery is the primary treatment.
Surgery
A lumpectomy or mastectomy are both viable surgical options for people with stage 1 breast cancer. A doctor will decide what surgery is most appropriate depending on the location of the primary tumor, how large it is, the size of the breast, family history, genetics, and the persons preference.
The doctor may also carry out a biopsy on one or more lymph nodes.
After removing the tissue, they will send it to a laboratory for further tests. The results will help inform decisions on the next stage of treatment.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy is a standard treatment for stage 1 breast cancer. However, the decision will depend on factors such the age of the person, the type of cancer, the size of the tumor, and whether there are cancer cells in the lymph nodes.
Hormone therapy
If the breast cancer is ER+ or PR+, hormone therapy may be effective. Hormone therapy works by preventing the growth of estrogen, which helps cancer grow, by blocking estrogen from attaching to tissue and fuelling cancer growth, or both.
Hormone therapy can reach cancer cells in the breast, as well as other areas of the body, and it can reduce the risk of cancer returning.
Chemotherapy
However, the
Stage 2 breast cancer also has subcategories known as 2A and 2B.
Also Check: How Do You Get Breast Cancer
Clinical Manifestations Of Stage 4
The main classification signs of breast cancer stage 4 are its spread to remote organs or lymph nodes. The size of the tumor at this stage is no longer important moreover, it may no longer be detected at the primary site.
It is the metastases that most often develop in the liver, lungs, and bones that give information about the development of the oncological process. They are painful and cause vivid symptoms. Metastases in the liver give jaundice and increase abdominal size. Metastases in the lungs give shortness of breath, and in the bones severe pain and frequent fractures.
- severe intoxication
You May Like: Harrington Breast Cancer Center Amarillo Tx
In The Last Days Of Life Patients And Family Members Are Faced With Making Decisions About Treatments To Keep The Patient Alive
Decisions about whether to use life-sustaining treatments that may extend life in the final weeks or days cause a great deal of confusion and anxiety. Some of these treatments are ventilator use, parenteral nutrition, and dialysis.
Patients may be guided by their oncologist, but have the right to make their own choices about life-sustaining treatments. The following are some of the questions to discuss:
- What are the patients goals of care?
- How would the possible benefits of life-sustaining treatments help reach the patients goals of care, and how likely would this be?
- How would the possible harms of life-sustaining treatments affect the patients goals of care? Is the possible benefit worth the possible harm?
- Besides possible benefits and harms of life-sustaining treatments, what else can affect the decision?
- Are there other resources, such as palliative care, a chaplain, or a medical ethicist, that could help the patient or family decide about life-sustaining treatments?
Read Also: What Is The Strongest Chemotherapy Drug For Breast Cancer
Recommended Reading: Do Wired Bras Cause Breast Cancer
What Should A Person With Stage 0 Or Stage 1 Breast Cancer Expect Regarding Treatment
Even though Stage 0 breast cancer is considered non-invasive, it does require treatment, typically surgery or radiation, or a combination of the two. Chemotherapy is usually not part of the treatment regimen for earlier stages of cancer.
Stage 1 is highly treatable, however, it does require treatment, typically surgery and often radiation, or a combination of the two. Additionally, you may consider hormone therapy, depending on the type of cancer cells found and your additional risk factors. Like stage 0, Chemotherapy is often not necessary for earlier stages of cancer.
Material on this page courtesy of National Cancer Institute
Medically Reviewed on April 15, 2020
M Categories For Breast Cancer
M followed by a 0 or 1 indicates whether the cancer has spread to distant organs — for example, the lungs, liver, or bones.
M0: No distant spread is found on x-rays or by physical exam.
cM0: Small numbers of cancer cells are found in blood or bone marrow , or tiny areas of cancer spread are found in lymph nodes away from the underarm, collarbone, or internal mammary areas.
M1: Cancer has spread to distant organs as seen on imaging tests or by physical exam, and/or a biopsy of one of these areas proves cancer has spread and is larger than 0.2mm.
Read Also: Where To Check For Breast Cancer Lumps
Targeted Drug Denosumumab Helps Prevent Common Bone
About 80 percent of women with metastatic breast cancer experience cancer spread to the bone, a complication that causes pain, bone weakening and other side effects that affect quality of life. In 2010, a large study shows that the targeted drug called denosumumab can prevent or significantly delay bone metastases. Other drugs, such as zoledronic acid , have previously been used to prevent and treat these bone-related complications, but this study suggests denosumumab may be more effective.
How Long Does It Take For Stage 1 Breast Cancer To Develop Into Stage 2
It is not possible to determine exactly how long it will take for newly diagnosed breast cancer to progress from stage 1 to stage 2. It can happen within months if it is an aggressive high-grade tumor, or it can take longer. Its important to know that stage 1 breast cancer could have already been present for a while before being detected, so it may progress quickly.
Read Also: What Happens If You Have Stage 4 Breast Cancer
First Immunotherapy Approved For Metastatic Triple
Atezolizumab in combination with chemotherapy is not only the first immunotherapy approved for breast cancer, but also an important advance for patients with advanced triple-negative breast cancer, which has an extremely poor prognosis. The FDA approval of the immunotherapy combination PD-L1 targeted therapy atezolizumab with nanoparticle albumin-bound paclitaxel was largely based on the results of the IMpassion130 trial. Progression-free survival was improved among patients with tumors that expressed PD-L1 who received atezolizumab in combination with nab paclitaxel.
Staging And Grading Of Breast Cancer

Knowing the stage and grade of the cancer helps your doctors plan the best treatment for you.
On this page
Your specialist doctor needs certain information about the cancer to advise you on the best treatment for you. This includes:
- the stage of the cancer
- the grade of the cancer
- whether the cancer has receptors for hormones or a protein called HER2.
This information comes from the results of all the tests you have had, including:
- the biopsy, when the tissue was examined
- other tests that were done on the cells.
Your specialist doctor and nurse will talk to you about this. They will explain how it helps you and your doctor decide on your treatment plan.
We understand that waiting to know the stage and grade of your cancer can be a worrying time. We’re here if you need someone to talk to. You can:
Read Also: What Is Localized Breast Cancer
Is There A Breast Cancer Cure
There is currently no cure for metastatic breast cancer, or breast cancer that has spread to distant parts of the body. However, early stages of breast cancer that remain localized are highly treatable 99 percent of people who receive treatment in the earliest stages of breast cancer live for 5 years or longer after diagnosis, according to the
Targeted Therapy For Breast Cancer
Targeted therapy refers to a variety of drugs that enter the bloodstream and treat cancer throughout the body. Targeted therapy drugs aim to attack cancer cells without harming healthy cells, and tend to have fewer side effects than chemotherapy drugs.
Targeted therapies are often used to treat HER2-positive breast cancers. These are cancers that have an excess of a protein called HER2 that promotes the growth of cancer cells.
Common targeted therapy drugs for HER2-positive breast cancers include:
- Monoclonal antibodies like trastuzumab are synthetic antibodies designed to attach to HER2 proteins and stop cells from growing.
- Antibody-drug conjugates like ado-trastuzumab emtansine attach to HER2 proteins on cancer cells and help chemotherapy reach them.
- Kinase inhibitors like Lapatinib block HER2 proteins.
Targeted therapies are also used to treat hormone receptor-positive breast cancer along with hormone therapy.
Common targeted therapy drugs for people with hormone receptor-positive cancers include:
- CDK4/6 inhibitors, which block CDK proteins in cancer cells to stop them from dividing and slow cancer growth.
- mTOR inhibitors, which block mTOR proteins in cancer cells to stop them from dividing and growing. This treatment is believed to help hormone therapy drugs work more efficiently.
- PI3K inhibitors, which block the PI3K proteins in cancer cells and helps prevent them from growing.
Common targeted therapy drugs for people with TNBC include:
Recommended Reading: Why Do I Have Breast Cancer