Risk Factors For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Age and gender are the two greatest risk factors for developing invasive ductal carcinoma. Women over the age of 55 are more likely to develop invasive breast cancer than any other group of people.
Some other risk factors that doctors have identified are:
- Weight weight gain and obesity in adulthood play a role due to changes in hormones.
- Breast tissue women with less fatty tissue in their breasts have an increased risk of the disease.
- Family history those with family members who also had breast cancer are more likely to develop the disease.
- No children women who have never had children are at increased risk. At the same time, women who breastfeed reduce their risk of developing breast cancer.
- Genetic mutations mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes are the most common causes of invasive breast cancer.
Less Common Invasive Breast Cancers
- Inflammatory breast cancer is an aggressive form of locally advanced breast cancer. Its called inflammatory breast cancer because the main warning signs are swelling and redness in the breast. With inflammatory breast cancer, warning signs tend to arise within weeks or months. With other breast cancers, warning signs may not occur for years.
- Paget disease of the breast is a carcinoma in situ in the skin of the nipple or in the skin closely surrounding the nipple. Its usually found with an underlying breast cancer.
- Metaplastic breast cancers tend to be larger and have a higher tumor grade than more common breast cancers. Metaplastic breast cancers can be hard to diagnose because the tumor cells can look very different from the tumor cells of more common breast cancers.
What Should A Person With Stage 3 Breast Cancer Expect From Treatment
Stage 3 treatment options vary widely and may consist of mastectomy and radiation for local treatment and hormone therapy or chemotherapy for systemic treatment. Nearly every person with a Stage 3 diagnosis will do best with a combination of two or more treatments.
Chemotherapy is always given first with the goal to shrink the breast cancer to be smaller within the breast and within the lymph nodes that are affected. This is known as neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
Other possible treatments include biologic targeted therapy and immunotherapy. There may be various clinical trial options for interested patients with Stage 3 breast cancer.
Recommended Reading: What Does Stage 3a Breast Cancer Mean
How Is Inflammatory Breast Cancer Treated
Inflammatory breast cancer is generally treated first with systemic chemotherapy to help shrink the tumor, then with surgery to remove the tumor, followed by radiation therapy. This approach to treatment is called a multimodal approach. Studies have found that women with inflammatory breast cancer who are treated with a multimodal approach have better responses to therapy and longer survival. Treatments used in a multimodal approach may include those described below.
How Is Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Diagnosed
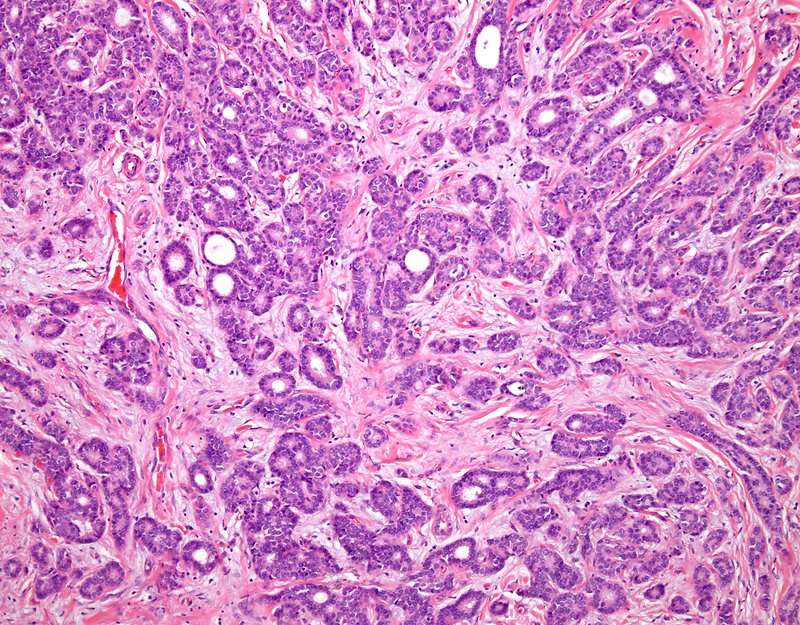
About 80% of cases are found by mammograms. On the mammogram, it appears as a shadowy area.
If your mammogram suggests that you may have DCIS, your doctor should order a biopsy to analyze the cells and confirm the diagnosis. Biopsies for DCIS are typically done using needles to remove tissue samples from the breast.
If you have DCIS, your doctor may do more tests to gather information about your cancer. These tests may include an ultrasound or MRI. Based on the results of various tests, your doctor will be able to tell the size of your tumor and how much of your breast is affected by the cancer.
Also Check: Is Male Breast Cancer Curable
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Treatment At Moffitt
In the Don & Erika Wallace Comprehensive Breast Program at Moffitt Cancer Center, our multispecialty tumor board reviews each thepatients breast cancer staging of many of our patients during a weekly meeting. This unique approach provides our patients with the benefit of highly individualized treatment based on multiple expert opinions in a single location, where we also offer comprehensive screening, diagnostic and supportive care services without the need for referrals.
If youd like to learn more about invasive ductal carcinoma stages and treatment options, call or complete a new patient registration form online. At Moffitt, we are providing every new patient with rapid access to a cancer expert within one day, a turnaround faster than that offered by any other cancer hospital across the country.
Inoperable Breast Cancer Is Often Still Treatable
Stage 3C breast cancer is divided into operable and inoperable stage 3C breast cancer. However, the term inoperable is not the same as untreatable.
If your physician uses the word inoperable, it may simply mean that a simple surgery at this time would not be enough to get rid of all the breast cancer that is within the breast and the tissue around the breast. There must be healthy tissue at all of the margins of the breast when it is removed. Keep in mind that the breast tissue goes beyond the breast mound it goes up to the clavicle and down to a few inches below the breast mound. There must also be tissue to close the chest wound after the surgery is performed.
Another treatment method may be used first to shrink the breast cancer as much as possible before surgery is considered.
Recommended Reading: Will I Die From Stage 1 Breast Cancer
Kinds Of Breast Cancer
The most common kinds of breast cancer are
- Invasive ductal carcinoma. The cancer cells begin in the ducts and then grow outside the ducts into other parts of the breast tissue. Invasive cancer cells can also spread, or metastasize, to other parts of the body.
- Invasive lobular carcinoma. Cancer cells begin in the lobules and then spread from the lobules to the breast tissues that are close by. These invasive cancer cells can also spread to other parts of the body.
More About Invasive Breast Cancer With Central Necrosis
Sometimes medics refer to an infiltrative breast carcinoma with central necrosis as a centrally necrotizing breast carcinoma, . Historically, centrally necrotizing breast carcinomas have an aggressive course.
Histologically, the composition of infiltrating ductal carcinoma with central necrosis is a well-circumscribed nodule with an extensive region of central necrosis. This area of necrosis is usually surrounded by a narrow rim of high-grade tumor cells. But these tumor cells usually show only minimal if any ductal differentiation, ie. they tend not to form into tubules.
The average age of development of an infiltrative ductal carcinoma with central necrosis is hard to estimate, but generally occurs in the mid 50s. Most infiltrative breast carcinomas with central necrosis are estrogen and progesterone receptor negative, making them more resistant to treatment.
Dont Miss: How Fast Does Squamous Cell Carcinoma Spread
Don’t Miss: Can Zantac Cause Breast Cancer
What Are The Symptoms Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Like other breast cancers, IDC may present as a lump that you or your doctor can feel on a breast exam. But in many cases, at first, there may be no symptoms, Wright says.
That is why it is important to have screening mammograms to detect breast cancers such as invasive ductal carcinoma. A mammogram may detect a lump that is too small for you to feel, or suspicious calcifications in the breast, either of which will lead to further testing.
According to Wright, the following are possible signs of invasive ductal carcinoma and other breast cancers. If you notice any of these, you should contact your doctor right away for further evaluation:
- Lump in the breast
- Nipple discharge, other than breast milk
- Scaly or flaky skin on the nipple or an ulceration on the skin of the breast or nipple. These can be signs of Pagets disease, a different kind of breast cancer that can occur along with IDC.
- Lumps in the underarm area
- Changes in the appearance of the nipple or breast that are different from your normal monthly changes
How Is Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Treated
No two patients are the same. Your doctor will customize your treatment plan based on your test results and medical history. Among other things, your doctor will consider:
- Tumor location
- Aggressiveness of the cancer cells
- Your family history of breast cancer
- Results of tests for a gene mutation that would increase the risk of breast cancer
Most women with DCIS don’t have the breast removed with a mastectomy. Instead, they have a lumpectomy.
Most common is a lumpectomy followed by radiation. The surgeon removes the cancer and a small area of healthy tissue around it. Lymph nodes under the arm donât need to be removed as they are with other types of breast cancer.
After a lumpectomy, radiation cuts the chances that the cancer will come back. If cancer does return, itâs called recurrence.
Some women may opt to have a lumpectomy only. Discuss the risks of not having radiation with your doctor before deciding against it.
You and your doctors may decide that a mastectomy to remove the breast is the best course of treatment if you have any of the following:
- A strong family history of breast cancer
- A gene mutation that makes having breast cancer more likely
- Very large areas of DCIS
- DCIS lesions in multiple areas throughout your breast
- Not being able tolerate radiation therapy
You and your treatment team may also consider the use of hormone therapy if the cancer tests positive for hormone receptors. It can cut the chance of getting another breast cancer.
Show Sources
Don’t Miss: How To Do Self Breast Examination For Cancer
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Treatment At Moffitt Cancer Center
As a National Cancer Institute-designated Comprehensive Cancer Center, Moffitt Cancer Center is a recognized leader in breast cancer research. Because our services are research-based, our patients have access to cutting-edge techniques and promising new medications that are available only through clinical trials. We continue to make great strides in understanding the causes of breast cancer and developing effective approaches to its prevention, diagnosis and treatment.
If youd like to discuss possible causes of invasive ductal carcinoma with the breast cancer experts at Moffitt, call or complete a new patient registration form online. No referrals are required.
- BROWSE
Request An Appointment At Moffitt Cancer Center
Please call for support from a Moffitt representative. New Patients and Healthcare Professionals can submit an online form by selecting the appropriate button below. Existing patients can call . for a current list of insurances accepted at Moffitt.
NEW PATIENTS To request a new patient appointment, please fill out the online form or call 1-888-663-3488.
REFERRING PHYSICIANS Providers and medical staff can refer patients by submitting our online referral form.
Moffit now offers Virtual Visits for patients. If you are eligible for a virtual appointment, our scheduling team will discuss this option further with you.
Moffitt Cancer Center is committed to the health and safety of our patients and their families. For more information on how were protecting our new and existing patients, visit our COVID-19 Info Hub
Recommended Reading: What Is Breast Cancer Month
Additional Grading Criteria: A Composite Total Of Tubular Nuclear And Mitotic Index Assesments
As a grade of low, intermediate or high is obtained through a composite sum by assigning a score based on the nuclear assessment, a mitotic index assessment, and a tubular assessment.
The nuclear assessment is based on the nuclear size within the invasive cells. They are described from small to medium to large in size, as well as by their uniformity in size and shape.
The tubular assessment refers to an approximate, quantitative account of the amount of cell groupings which remain in their normal tubular shape. The smaller the percentage of tubular structures in comparison to other shapes, the higher the score. Other structures to appear may include solid trabecula, vacuolated single cells, alveolar nests, and solid sheets of cells.
The mitotic index refers to evident patterns of cell division.Mitosis is a process by which a cell separates into two genetically identical daughter cells. . So, the mitotic index is assessment of the abundance of these pairs of daughter cells, measured in the count per square millimeter. Mitoses are only counted in the invasive area of the lesion .
| Histologic Grade | |
| 11-19 = 2 | > 20 = 3. |
Diagnosing Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Some women may feel a lump in their breast and seek evaluation, while others may learn they have breast cancer during their mammogram screening or breast X-ray. Other imaging tests and a biopsy may also be ordered to help the doctor assess the patients condition.
During a biopsy, the doctor removes some tissue or fluid from the breast for analysis under a microscope. The sample is sent off to a lab, where a pathologist checks for the presence of cancer cells, and it may take a few days to get the results.
If the diagnosis is breast cancer, the doctor then needs to determine its stage, including whether or not its started to spread inside or outside the breast. The specifics guide any treatment decisions.
Don’t Miss: Can Cancer Come Back In The Same Breast
How Is Invasive Breast Cancer Treated
Different things will determine the type of breast cancer treatment your doctor recommends, including:
- Size of the tumor
- Results of lab tests done on the cancer cells
- Stage of the cancer
- Your age and general health
- If youâve been through menopause
- Your own feelings about the treatment options
- Family history
- Results of tests for a gene mutation that would increase the risk of breast cancer
There are many treatments for invasive breast cancer. They include:
- Surgery. A lumpectomy is a surgical procedure in which a surgeon removes the cancer and a small area of healthy tissue around it. A mastectomy may be performed after chemotherapy. This procedure removes all of your breast.
- Chemotherapy. This drug treatment may be done before surgery to shrink the tumor and make the cancer operable. Itâs also sometimes given after surgery to try to prevent the cancer from coming back.
- Radiation. Often, radiation treatments are given after chemotherapy and surgery to prevent the cancer from coming back.
- Hormone therapy. Certain medications may be given if the cancer cells have hormone receptors.
- Targeted therapy. If the cancer cells have the gene HER2, you may be given drug treatments specifically for that.
The goal of your treatment is to give you the best possible outcome. Your doctor may use one or a combination of them.
Show Sources
Infiltrating Vs Invasive Breast Cancer: Depends Upon The Extent
Whether or not breast cancer is termed invasive or infiltrating will depend upon the extent of the malignant cells. There is a kind of informal progression from ductal carcinoma in situ in which the carcinoma is still well contained within the breast ducts and is not yet moving into the duct wall .
Infiltrating ductal carcinoma implies that the malignant cells are now inside the duct wall and threatening to grow into surrounding breast tissue or elsewhere in the body such as migration to the lymph nodes.
Invasive ductal carcinoma means that the breast carcinoma has moved beyond the breast duct walls altogether and is spreading into other body tissues.
Also Check: What Is Hormone Positive Breast Cancer
Clinical Trials Designed For Idc
Women with IDC may choose to enroll in a clinical trial to receive a new treatment thats not yet available to the general public.
Additionally, clinical trials help scientists determine if up-and-coming therapies are safe and effective.
Talk to your doctor about the benefits and risks of participating in a research study. You can also search for clinical trial near you at ClinicalTrials.gov, says Moffitt Cancer Center.
Rare Types Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Medullary ductal carcinoma accounts for only 3%5% of breast cancers. It may appear on a mammogram, and it does not always feel like a lump rather, it can feel like an abnormally spongy area in the breast tissue.
Mucinous ductal carcinoma is also called colloid breast cancer. It occurs when cancer cells within the milk duct of the breast produce mucous, which also contains breast cancer cells. The cells and mucous combine to form a tumor. Pure mucinous ductal carcinoma tends to grow slowly, and has a better prognosis than some other types of IDCs.
Papillary carcinoma forms finger-like projections that can be seen under a microscope. Many papillary tumors are benign, but even those that become cancerous are usually very treatable with a good prognosis. Papillary carcinoma most commonly occurs in people older than 60.
Tubular ductal carcinoma is a rare diagnosis of IDC, comprising only 2% of breast cancer diagnoses. The name comes from how the cancer looks under the microscope like hundreds of tiny tubes. Tubular breast cancer has an excellent prognosis.
Read Also: Can You See The Lump For Breast Cancer
In Thinking About Treatment Of Cancer Should I Consider Clinical Trials
For any type or stage of breast cancer, it is well worth researching clinical trials for treatment options. Indeed, due to breast cancer patients taking part in clinical trials advances in treatment have improved immensely.
There are many agencies that conduct trials and most in the US are funded by the National Cancer Institute which is part of the National Institute of Health . It may well be worth researching your own area and the trials available.
What Does It Mean To Have Stage 3 Breast Cancer
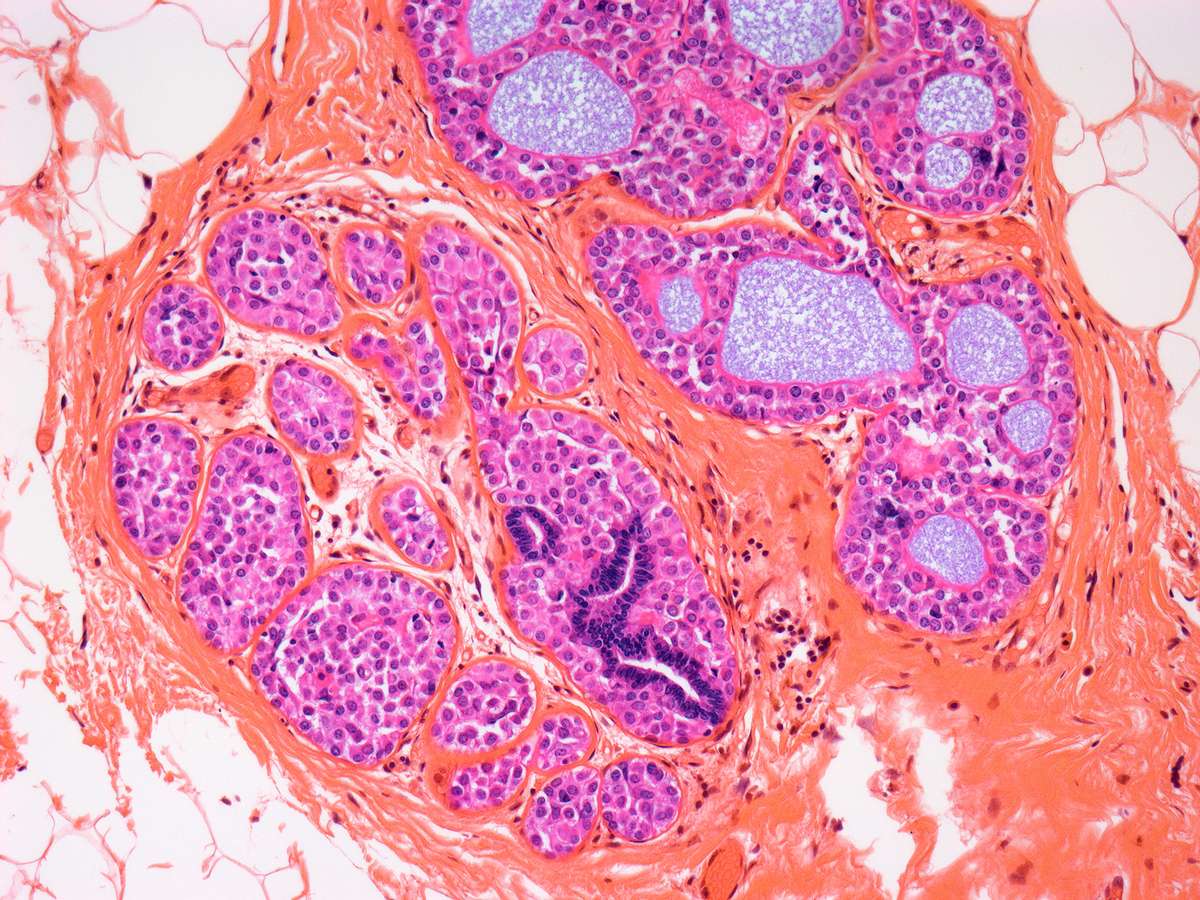
Stage 3 cancer means the breast cancer has extended to beyond the immediate region of the tumor and may have invaded nearby lymph nodes and muscles, but has not spread to distant organs. Although this stage is considered to be advanced, there are a growing number of effective treatment options.
This stage is divided into three groups: Stage 3A, Stage 3B, and Stage 3C. The difference is determined by the size of the tumor and whether cancer has spread to the lymph nodes and surrounding tissue.
Also Check: What Is The Medical Term For Breast Cancer