Triple Negative Breast Cancer
Triple negative breast cancer is 3 times negative: the tumor does not grow under the influence of the hormone estrogen the tumor does not grow under the influence of the hormone progesterone the tumor is not HER2-positive
About 15% of breast cancers are triple negative. This species is more common in women of reproductive age.Treatment often consists of chemotherapy, surgery and radiation.
Hormone therapy and most targeted therapies do not work in triple negative breast cancer.A triple negative tumor often grows rapidly and is aggressive.
It also spreads more often and faster than other types of breast cancer. The chance that this breast cancer will come back is also greater. Has the tumor not come back or metastasized after 7 years? Then there is a very good chance that it will not come back or metastasize.
You May Like: Stage 4 Breast Cancer Life Expectancy Without Treatment
Who Gets Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is the most common cancer among women other than skin cancer. Increasing age is the most common risk factor for developing breast cancer, with 66% of breast cancer patients being diagnosed after the age of 55.
In the US, breast cancer is the second-leading cause of cancer death in women after lung cancer, and its the leading cause of cancer death among women ages 35 to 54. Only 5 to 10% of breast cancers occur in women with a clearly defined genetic predisposition for the disease. The majority of breast cancer cases are sporadic, meaning there is no definitive gene mutation.
Dont Miss: Breast Cancer Symptom Checker
Breast Cancer Cell Lines
Part of the current knowledge on breast carcinomas is based on in vivo and in vitro studies performed with cell lines derived from breast cancers. These provide an unlimited source of homogenous self-replicating material, free of contaminating stromal cells, and often easily cultured in simple standard media. The first breast cancer cell line described, BT-20, was established in 1958. Since then, and despite sustained work in this area, the number of permanent lines obtained has been strikingly low . Indeed, attempts to culture breast cancer cell lines from primary tumors have been largely unsuccessful. This poor efficiency was often due to technical difficulties associated with the extraction of viable tumor cells from their surrounding stroma. Most of the available breast cancer cell lines issued from metastatic tumors, mainly from pleural effusions. Effusions provided generally large numbers of dissociated, viable tumor cells with little or no contamination by fibroblasts and other tumor stroma cells.Many of the currently used BCC lines were established in the late 1970s. A very few of them, namely MCF-7, T-47D, MDA-MB-231 and SK-BR-3, account for more than two-thirds of all abstracts reporting studies on mentioned breast cancer cell lines, as concluded from a Medline-based survey.
Metabolic markers
Recommended Reading: Symptoms Of Stage 2 Breast Cancer
Don’t Miss: What Is Invasive Breast Cancer
What Is Carcinoma In Situ
A carcinoma in situ is the very early stage of a cancer when the abnormal cancer cells are confined to their original site. At this stage no tumour has grown and no cancer cells have spread. It may be that many cancers remain at this dormant stage for months, or even years, before they start to grow and spread into a proper cancer. This may be because the cells of the carcinoma in situ do not have the ability to stimulate new blood vessels. If they cannot stimulate new blood vessels to grow then the cancer itself cannot grow or spread.
It is thought that one or more of the cells in a carcinoma in situ may then mutate after some time . This then gives them the ability to make chemicals to stimulate new blood vessels. The cancer then grows and spreads as described above.
A carcinoma in situ contains only a small number of cells and is usually too small to be detected by scans or X-rays. However, some screening tests may detect a carcinoma in situ. For example, some cells from an abnormal cervical screening test, looked at under the microscope, may show carcinoma in situ. These cells can then be destroyed by treatment which prevents cancer from developing. Sometimes a small sample taken from a part of the body may show a carcinoma in situ.
How Can Breast Cancer Cells Or Types React
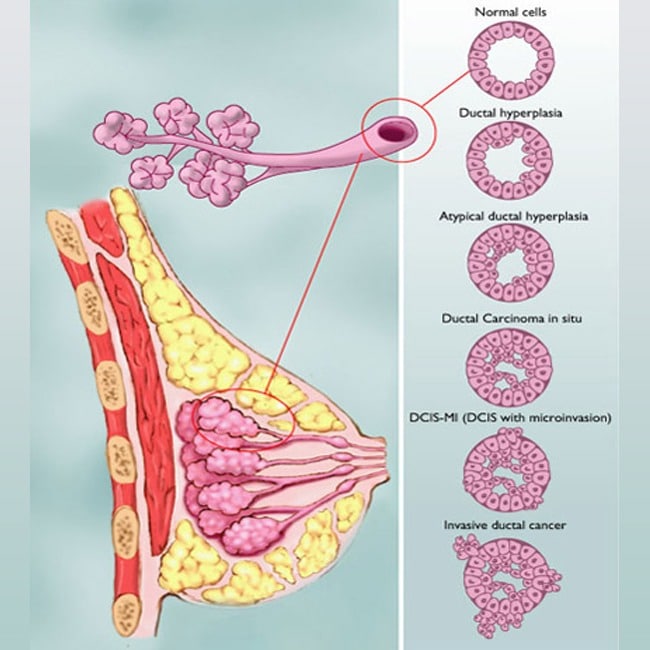
There are also other determinants of how a breast cancer cell or type may react and this is important to treatment options. If the cancer cell still has a reasonable detection for estrogen or progesterone, we call this Estrogen positive or Progesterone Positive breast cancer. This is usually a good thing because it means that the cell is not so altered that it still bears a resemblance to how a normal cell would act. It also means that we can use certain medicines such as anti-estrogen medicines like Tamoxifen or Aromatase inhibitors to block the bodys estrogen influence on the cells, in essence like stopping the fertilizer. Some cells express a particular protein on their surface Her2 Neu. We find if the tumor has this characteristic, then it will respond well to particular chemotherapy invented just for this type of expression called Herceptin which is a kind of chemotherapy. If a breast cancer cell is very abnormal and expresses none of these receptors or markers we call it Triple Negative meaning that it does not express ER or PR or Her2. These more aggressive cells typically require special chemotherapy to obliterate the cancer cells. Some types of breast cancer are very localized to like a particular area of the breast, like Pagets disease which is DCIS of the nipple. Other types of cancer cells are diffuse within the skin of the breast like inflammatory breast cancer.
Don’t Miss: Can Mri Detect Breast Cancer
First Class Stamp Cost
As of January 2020, the cost of a first class stamp is 55 cents.
The Royal Mail announced in a press release on April 4, 2022, that the price of first-class and second-class stamps will increase by 10p and 2p, respectively, beginning April 4, 2022. It is in line with an annual inflation rate of 2.5% in the past decade. In 2018, the cost of a First Class stamp was 95p, and the cost of a Second Class stamp was 68p.
What Is Invasive Breast Cancer Noninvasive Breast Cancer And Metastatic Breast Cancer
Noninvasive cancer is cancer that has not spread beyond the tissue where it started. Noninvasive breast cancer means the abnormal cells are only in the milk ducts of the breast. They cannot spread to nearby tissue or to other parts of the body.
Invasive breast cancer means the cancer has grown beyond the place where it started. Its in nearby normal breast tissue and can spread to other parts of the body.
Metastatic breast cancer is also called advanced breast cancer, or stage 4 breast cancer. Its invasive cancer that has spread from the breast. It can spread to the skin, lymph nodes, or to other areas, such as the liver, lungs, or bones.
Some people have metastatic cancer when theyre first diagnosed. More often, you get advanced breast cancer when the disease comes back somewhere else in the body, even after you had treatment.
Here are some other words you may hear to describe breast cancer.
- Carcinoma means cancer that starts in the cells that line the inner or outer surfaces of tissues, including breast ducts.
- In situ are words in Latin that mean in its original place.
- Ductal means cancer thats only in the milk ducts.
- Lobules are small round sacs that make breast milk.
You May Like: Where To Donate For Breast Cancer
What To Know About Breast Cancer Symptoms
The symptoms of breast cancer can vary widely and some types of breast cancer may not have any noticeable symptoms.
Sometimes a lump may be too small to be felt or to cause any changes to your breast or surrounding area. In these cases, cancerous cells are often first detected through screening techniques like a mammogram.
When there are symptoms, they can include:
- a lump or thickening of breast tissue that you can feel with your fingers
- breast swelling or changes to your breast size or shape
- changes to the skin on your breast, such as dimpling, redness, or skin irritation
- the nipple turning inward or nipple pain
- a lump in your underarm area
- nipple discharge other than breast milk
Its important to be familiar with how your breasts usually look and feel. This will help you notice any changes and to follow up with your healthcare professional promptly if anything looks or feels different.
Noninvasive breast cancer develops in the cells of a duct or lobule and remains in that location. Its also referred to as in situ which means in the original place.
There are two types of noninvasive breast cancer:
- ductal carcinoma in situ
Lets take a closer look at each type.
How Do Tamoxifen Raloxifene Anastrozole And Exemestane Reduce The Risk Of Breast Cancer
If you are at increased risk for developing breast cancer, four medications tamoxifen , raloxifene , anastrozole , and exemestane may help reduce your risk of developing this disease. These medications act only to reduce the risk of a specific type of breast cancer called estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. This type of breast cancer accounts for about two-thirds of all breast cancers.
Tamoxifen and raloxifene are in a class of drugs called selective estrogen receptor modulators . These drugs work by blocking the effects of estrogen in breast tissue by attaching to estrogen receptors in breast cells. Because SERMs bind to receptors, estrogen is blocked from binding. Estrogen is the fuel that makes most breast cancer cells grow. Blocking estrogen prevents estrogen from triggering the development of estrogen-receptor-positive breast cancer.
Anastrozole and exemestane are in a class of drugs called aromatase inhibitors . These drugs work by blocking the production of estrogen. Aromatase inhibitors do this by blocking the activity of an enzyme called aromatase, which is needed to make estrogen.
Recommended Reading: Early Symptoms Of Secondary Breast Cancer
You May Like: What Is Stage 3 Triple Negative Breast Cancer
What Is Lobular Carcinoma In Situ What Is Atypical Lobular Hyperplasia
Lobular neoplasia is when there are abnormal cells in the breasts lobules. It rarely becomes cancer. Types of lobular neoplasia include:
- Lobular carcinoma in situ , a condition that is not breast cancer or a precancer. Often, it does not become invasive cancer if its not treated.
- Atypical lobular hyperplasia , a condition that is not cancer. Its when there are more cells than usual in your breasts lobules. The extra cells are abnormal.
Both LCIS and ALH raise your risk of getting breast cancer in the future. If you have been diagnosed with either of them, talk with your doctor. Ask how often you should be screened for breast cancer and if you should have more screening tests.
Can Cancer Form In Other Parts Of The Breast
Cancers can also form in other parts of the breast, but these types of cancer are less common. These can include:
- Angiosarcomas. This type of cancer begins in the cells that make up the lining of blood or lymph vessels. These cancers can start in breast tissue or breast skin. They are rare.
- Inflammatory breast cancer. This type of cancer is rare and different from other types of breast cancer. It is caused by obstructive cancer cells in the skins lymph vessels.
- Paget disease of the breast, also known as Paget disease of the nipple. This cancer affects the skin of the nipple and areola .
- Phyllodes tumors. These are rare, and most of these masses are not cancer. However, some are cancerous. These tumors begin in the breasts connective tissue, which is called the stroma.
Also Check: What Stage Breast Cancer Do I Have
Nanotechnology In Breast Cancer
The field of nanotechnology has rapidly evolved as evidenced by the fact that there are more than 150 ongoing clinical trials investigating the efficacy of nanotechnology based drug delivery carriers targeting cancer. Various liposomal doxorubicin formulations were developed in an effort to improve the therapeutic index of the conventional doxorubicin chemotherapy while maintaining its anti-tumor activity. For example, the efficacy of three liposomal doxorubicins are currently being used: liposomal daunorubicin , liposomal doxorubicin , and pegylated liposomal doxorubicin . Generally, these agents exhibit efficacies comparable to those of conventional doxorubicin, except with better safety profiles and less cardio toxicity. In addition to liposomal doxorubicin, albumin-bound paclitaxel is another example of an E PR based nanovector application for breast cancer chemotherapy. Paclitaxel is highly hydrophobic and dissolved in cremophor to prevent paclitaxel precipitation. However, cremophor-associated toxicities are severe and challenge the application of paclitaxel. Albumin-bound paclitaxel was developed to improve the solubility of paclitaxel
Lobular Carcinoma In Situ
Lobular carcinoma in situ is also sometimes called lobular neoplasia. Though the name can be confusing, LCIS is actually not considered a cancer or a pre-cancer because it doesnt turn into invasive cancer if untreated. Rather, LCIS is an indication that a person is at a higher risk of getting breast cancer later on.
Don’t Miss: Where Is Breast Cancer Located
Surgery For Breast Cancer
Most women with breast cancer have some type of surgery as part of their treatment. There are different types of breast surgery, and they may be done for different reasons, depending on the situation. For example, surgery may be done to:
- Remove as much of the cancer as possible
- Find out whether the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes under the arm
- Restore the breasts shape after the cancer is removed
- Relieve symptoms of advanced cancer
Your doctor may recommend a certain operation based on your breast cancer features and your medical history, or you may have a choice about which type of surgery to have. Its important to know your options so you can talk about them with your doctor and make the choice that is right for you.
Breast Reconstruction After Surgery
Many woman having surgery for breast cancer might have the option of breast reconstruction. A woman having a mastectomy might want to consider having the breast mound rebuilt to restore the breasts appearance after surgery. In some breast-conserving surgeries, a woman may consider having fat grafted into the affected breast to correct any dimples left from the surgery. The options will depend on each womans situation.
There are several types of reconstructive surgery, but your options depend on your medical situation and personal preferences. You may have a choice between having breast reconstruction at the same time as the breast cancer surgery or at a later time .
If you are thinking about having reconstructive surgery, its a good idea to discuss it with your breast surgeon and a plastic surgeon before your mastectomy or BCS. This gives the surgical team time to plan out the treatment options that might be best for you, even if you wait and have the reconstructive surgery later.
To learn about different breast reconstruction options, see Breast Reconstruction Surgery.
Read Also: What Are The Symptoms To Breast Cancer
Types Of Invasive Breast Cancer
Most breast cancers are invasive, meaning the cancer has spread from the original site to other areas, like nearby breast tissue, lymph nodes or elsewhere in the body. Invasive breast cancer cells break through normal breast tissue barriers and spread to other parts of the body through the bloodstream and lymph nodes. The two most common types of invasive breast cancer are invasive ductal carcinoma and invasive lobular carcinoma.
Invasive ductal carcinoma
The most common type of breast canceraccounting for roughly 70 to 80 percent of all casesis called invasive ductal carcinoma . IDC is a cancer that starts in a milk duct and grows into other parts of the breast. With time, it may spread further, or metastasize, to other parts of the body.
Invasive lobular carcinoma
Invasive lobular carcinoma is the second most common type, accounting for roughly 5 to 10 percent of all breast cancers. ILC starts in lobules and then spreads into nearby breast tissue. Like IDC, it may metastasize. However, this cancer is harder to detect on mammograms and other exams than IDC. One in five women with ILC have both breasts affected.
Inflammatory breast cancer
Pagets disease of the breast
Angiosarcoma of the breast
Phyllodes tumors
Other, even more rare, types of invasive breast cancer include adenoid cystic carcinoma, low-grade adenosquamous carcinoma, medullary carcinoma, mucinous carcinoma, papillary carcinoma and tubular carcinoma.
Are You Under 40 You’re Not Alone
While most cases of breast cancer occur in women over 50, around 400 New Zealand women under the age of 44 are diagnosed with breast cancer every year. These days, breast cancer is much more treatable if detected early, and there are many women still thriving decades after experiencing breast cancer at a young age. Discover the specific concerns for young women with breast cancer.
Don’t Miss: Long-term Side Effects Of Chemotherapy For Breast Cancer
What Is Invasive Lobular Carcinoma
Invasive lobular carcinoma starts in the breasts lobules. This cancer spreads to nearby tissue. ILC is the second most common type of invasive breast cancer, after invasive ductal carcinoma. Out of every 100 cases of breast cancer, 10 to 15 are ILC.
People who have ILC may notice a thick or full area that does not feel like the rest of the breast. ILC doesnt always form a lump.
Tubular Carcinoma Of The Breast
Tubular carcinoma is a subtype of invasive ductal carcinoma . This type of breast cancer gets its name due to the tube-shaped structures, which can be seen under a microscope, that make up the tumor. The tumors are usually small and tend to grow slowly.
Tubular carcinoma is rare, accounting for up to 2 percent of invasive breast cancers.
Because these tumors are small, they are most often detected during a routine mammogram. They tend to be low grade with good prognosis.
Also Check: How Likely Is It To Die From Breast Cancer