Outlook For People With Stage 3 Breast Cancer
Its natural to want to know your outlook, but statistics dont tell the whole story. Your breast cancer type, overall health, and many more factors beyond your control may affect treatment outcomes.
Establishing open communication with your treatment team can help you best assess where you are in your cancer journey.
Support groups can be a great source of comfort as you navigate your diagnosis through your treatment and beyond. Your doctors office or hospital can offer some suggestions and resources in your area.
What Is The Staging For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Staging refers to the extent of a cancer. A cancer is always referred to by the stage it was determined to be at diagnosis, even if it spreads.
Stages of invasive ductal carcinoma include:
- Stage I: Breast tumor is smaller than 2 centimeters in diameter and the cancer has not spread beyond the breast
- Stage II: Breast tumor measures 2 to 4 centimeters in diameter or cancerous cells have spread to the lymph nodes in the underarm area
- Stage III: Cancer is more extensive but it is confined to the breast, surrounding tissues, and lymph nodes
- Stage IV: Breast cancer has spread to lymph nodes beyond the underarm area or to distant sites, such as the lungs, liver, bones, or brain
Grading Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
In 1957, Bloom and Richardson first developed a histology grading system for invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast, based on the degree of tubule formation, cell nuclear pleomorphism and mitotic count. This system was replaced or modified in 1991 by the Nottingham grading system, which is still based on a points scoring system of the histologic features of the cancer mild, moderate or severe or Grade 1, 2 or 3 .
Recommended Reading: Is Triple Negative Breast Cancer Curable
Myoepithelial Cells As Regulators Of Tissue Polarity
Reversal of inside-out acini by addition of myoepithelial cells. Luminal cells make inside-out acini in collagen. Luminal epithelial cells were double-stained for MUC1 and ESA . In the presence of myoepithelial the acinar polarity is rescued as evidenced by apical expression of MUC1 and ESA . Bar, 25 μm. ).
How Is It Diagnosed
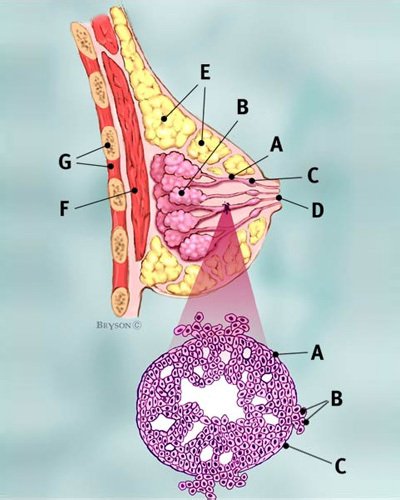
There are a variety of tests to diagnose invasive breast cancer. These include:
- Breast exam: During a breast exam, a healthcare professional will carefully feel your breasts for signs of lumps or other changes.
- Mammogram: During a mammogram, a device presses your breasts between two plates. X-ray images of the breast tissue are then taken and evaluated for signs of cancer.
- Imaging tests: A healthcare professional may order additional imaging tests to help them better visualize breast tissue. Some examples include ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging .
- Biopsy: During a biopsy, a sample of breast tissue is carefully removed and checked under a microscope for signs of cancer.
- Blood tests: Blood tests use a sample your blood to check for various markers of disease or illness.
If cancer is detected, additional tests can be used to help characterize the cancer and determine its stage. These tests can include things like:
- Receptor testing: Various tests can check for estrogen receptors, progesterone receptors, and HER2 status.
- Lymph node biopsy: A lymph node biopsy can determine if the cancer has spread to the nearby lymph nodes.
- Imaging tests: Imaging tests can look to see if cancer has spread to other areas. Some that may be used include bone scans, X-rays, CT scans, and positron emission tomography scans.
CE MM 4/8/2021: resolved
Treatment for invasive breast cancer depends on the stage of the cancer as well as other factors. Lets examine the most common treatment options.
Read Also: Is Stage Four Breast Cancer Terminal
What Does It Mean If My Carcinoma Is Well Differentiated Moderately Differentiated Or Poorly Differentiated
When looking at the cancer cells under the microscope, the pathologist looks for certain features that can help predict how likely the cancer is to grow and spread. These features include the arrangement of the cells in relation to each other, whether they form tubules , how closely they resemble normal breast cells , and how many of the cancer cells are in the process of dividing . These features taken together determine how differentiated the cancer is .
- Well-differentiated carcinomas have relatively normal-looking cells that do not appear to be growing rapidly and are arranged in small tubules for ductal cancer and cords for lobular cancer. These cancers tend to grow and spread slowly and have a better prognosis .
- Poorly differentiated carcinomas lack normal features, tend to grow and spread faster, and have a worse prognosis.
- Moderately differentiated carcinomas have features and a prognosis in between these two.
What Does Stage 3 Mean
Because stage 3 breast cancer has spread outside the breast, it can be harder to treat than earlier stage breast cancer, though that depends on a few factors.
With aggressive treatment, stage 3 breast cancer is curable however, the risk that the cancer will grow back after treatment is high.
Doctors further divide stage 3 cancer into the following stages:
Recommended Reading: How Does Breast Cancer Look Like
What Causes Lobular Breast Cancer
The life cycle of normal cells is to grow, divide and die. Cancer cells do not follow this normal life cycle. Technically, the definition of cancer is uncontrollable cell growth. The cause of this uncontrollable cell growth is a mutation in the DNA of cells. The cause of the DNA mutation is not always clear to scientists.
The growth of breast cancer cells is fueled by estrogen and/or progesterone, which are female hormones produced in the body. Most types of breast cancers are usually estrogen positive, which mean they grow in response to estrogen. Your doctor may prescribe medications to block the effects of estrogen to help prevent the return of cancer after your initial treatment.
Who Is More Likely To Develop Lobular Breast Cancer
Risk factors for developing lobular breast cancer are the same as those for developing breast cancer in general. These include:
- Older age. The risk of breast cancer increases with age. Most breast cancers are diagnosed after age 50.
- Being diagnosed with lobular carcinoma in situ. This means you have abnormal cells confined within the lobules of your breast. Although this is not considered cancer, it does increase your risk of developing breast cancer.
- Family history of breast cancer. Having a mother, sister, or daughter who has had breast cancer.
- Early puberty/late menopause. Starting your period at an early age or experiencing late menopause .
- Not having children/later childbirth. Not having children or having your first child after the age of 35.
- Postmenopausal hormone use. Using the female hormones estrogen and progesterone for more than 5 years to manage menopause symptoms.
- Exposure to radiation. Receiving radiation to the breast or chest to treat cancer before the age of 30.
- Having genetic mutations for certain types of breast cancer. Being a carrier of the familial breast cancer genes, BRCA1 and BRCA2.
- Being overweight.
- Drinking alcohol. Compared with nondrinkers, women who consume one alcoholic drink a day have a 10% increase in risk. The risk increases the more you drink.
You May Like: What To Say To Breast Cancer Patient
Additional Types Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma:
There are four types of invasive ductal carcinoma that are less common:
- Medullary Ductal Carcinoma This type of cancer is rare and only three to five percent of breast cancers are diagnosed as medullary ductal carcinoma. The tumor usually shows up on a mammogram and it does not always feel like a lump rather it can feel like a spongy change of breast tissue.
- Mucinous Ductal Carcinoma This occurs when cancer cells within the breast produce mucous, which also contains breast cancer cells. The cells and mucous combine to form a tumor. Pure mucinous ductal carcinoma carries a better prognosis than more common types of IDCs.
- Papillary Carcinoma This is a very good prognosis breast cancer that primarily occur in women over the age of 60.
- Tubular Ductal Carcinoma This is a rare diagnosis of IDC, making up only two percent of diagnoses of breast cancer. The name comes from how the cancer looks under the microscope like hundreds of tiny tubes. Tubular breast cancer has an excellent prognosis.
Show me more…
Invasive Breast Cancer And Staging
Whether or not invasive cancer cells are present can influence how breast cancer is staged after a diagnosis.
Breast cancer that remains isolated to the area in which it started and has not spread into healthy breast tissue is called cancer in situ. You may also see this referred to as non-invasive breast cancer or Stage 0 breast cancer.
When invasive cancer is detected, it can be staged as stage 1 through 4. Many of these stages also have subcategories.
Several factors are taken into consideration with the TNM staging system thats used for invasive breast cancer. This includes:
Other factors that can impact staging are:
There are different types of invasive breast cancer. Lets examine some of the most common ones in more detail.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Root Cause Of Breast Cancer
The Overall Prognosis For Her
Many studies demonstrate that breast cancers with an over-expression of HER-2 have a poorer prognosis. It is difficult however to isolate just the HER-2 aspect of the tumor as the specific cause of this poorer outlook.
In addition, it is difficult, in general, to find practical indications of just what a negative prognosis actually means.
The HER-2 status is part of the picture, but so are:-
- tumor size
- grade
- lymph node status
- Other hormonal indicators
- the type of cancer
However, it is clear that a positive HER-2 over-expression does correspond to an increase in the likelihood for lymph node metastasis.
HER-2 over-expression can also predict a poorer response to Taximophen , though researchers are working on ways to combat this.
What If My Report Mentions Lymph Nodes
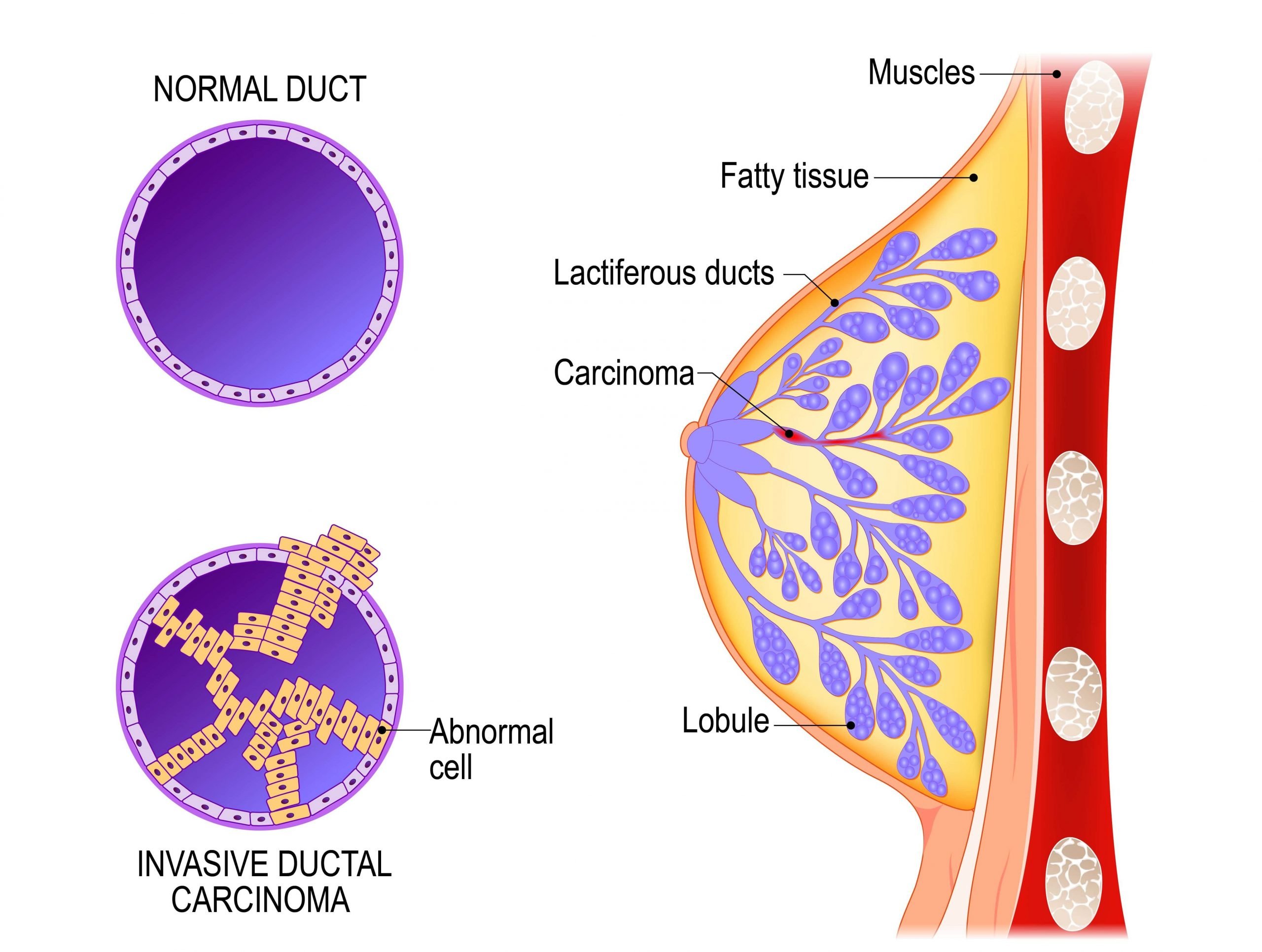
If breast cancer spreads, it often goes first to the nearby lymph nodes under the arm . If any of your underarm lymph nodes were enlarged , they may be biopsied at the same time as your breast tumor. One way to do this is by using a needle to get a sample of cells from the lymph node. The cells will be checked to see if they contain cancer and if so, whether the cancer is ductal or lobular carcinoma.
In surgery meant to treat breast cancer, lymph nodes under the arm may be removed. These lymph nodes will be examined under the microscope to see if they contain cancer cells. The results might be reported as the number of lymph nodes removed and how many of them contained cancer .
Lymph node spread affects staging and prognosis . Your doctor can talk to you about what these results mean to you.
Don’t Miss: What Is Genetic Counseling For Breast Cancer
Symptoms Of Invasive Breast Cancer
Make an appointment to see your doctor if you notice anything different or unusual about the look and feel of your breasts.
The symptoms of breast cancer include:
- a new lump or thickening in your breast or armpit
- a change in size, shape or feel of your breast
- skin changes in the breast such as puckering, dimpling, a rash or redness of the skin
- fluid leaking from the nipple in a woman who isnt pregnant or breast feeding
- changes in the position of nipple
The Decision To Proceed With Exploratory Lymph Node Dissection Is A Subject Of Debate With Microinvasive Breast Tumors
With microinvasive breast cancer, we find a curious situation where physicians can look at the same set of statistics, and yet come to different conclusions some say that axillary lymph node dissection is warranted, other feel that it is completely unnecessary, also pointing to the cost, discomfort and stress involved. They are many grey area decisions in breast cancer treatment, and an experienced physician will tend to have a feel for the subtleties in all of the diagnostic presentations and risk factors associated with the patient, and make an appropriate decision.
Don’t Miss: Why Does Dense Breast Tissue Increase Cancer Risk
What Is Tumor Grading
After surgery to remove the tumor, a doctor will check it and assign a grade to it. The grade depends on how closely the cancer cells resemble normal cells when viewed under a microscope. Low-grade cancer cells are similar to normal breast cells. Higher grade breast cancer cells look more different. They show the cancer is more aggressive.
The doctor will also test for estrogen receptors and progesterone receptors. This test will show whether the female hormones — estrogen and progesterone — influence the cancer cells. If the test is positive, it means hormones cause the cancer cells to grow. In that case, therapies to suppress or block hormones may help treat the cancer.
The cancer will also be tested for a gene called HER2. If itâs found, additional drugs like trastuzumab can be used.
Other tests will see if the cancer has spread from the breast to other areas of the body.
Nuclear Assessment Images For Infiltrating Ductal Carcinoma
Essentially uniform in size and shape, the malignant nuclei in the image below would suggest a grade I nuclear assessment, adding 1 point to the cumulative total. Microcalcification does not figure in a nuclear grade assessment of infiltrating ductal carcinoma, being more of a screening indicator rather than a staging parameter.
In the lesion below the malignant nuclei show moderate varation of size and shape. This would likely correspond to a nuclear grade assessment of grade II, adding 2 points to the cumulative total.
Size and shape of nuclei in the image below are highly variable, suggesting a grade III nuclear assessment. This would add 3 points to the cumulative score for arriving at an overall grade of infiltrating ductal breast cancer.
Also Check: How Is Radiation Done For Breast Cancer
Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
DCIS is the most common type of noninvasive breast cancer, with about 60,000 new cases diagnosed in the United States each year. About one in every five new breast cancer cases is ductal carcinoma in situ.
Also called intraductal carcinoma or stage 0 breast cancer, its considered a noninvasive breast cancer. With DCIS, abnormal and cancerous cells havent spread from the ducts into nearby breast tissue nor anywhere else, such as the lymph nodes.
DCIS is divided into several subtypes, mainly according to the appearance of the tumor. These subtypes include micropapillary, papillary, solid, cribriform and comedo.
Patients with ductal carcinoma in situ are typically at higher risk for seeing their cancer return after treatment, although the chance of a recurrence is less than 30 percent. Most recurrences occur within five to 10 years after the initial diagnosis and may be invasive or noninvasive. DCIS also carries a heightened risk for developing a new breast cancer in the other breast. A recurrence of ductal carcinoma in situ would require additional treatment.
The type of therapy selected may affect the likelihood of recurrence. Treating DCIS with a lumpectomy , and without radiation therapy, carries a 25 percent to 35 percent chance of recurrence. Adding radiation therapy to the treatment decreases this risk to about 15 percent. Currently, the long-term survival rate for women with ductal carcinoma in situ is nearly 100 percent.
Receptor Status And Triple Negative Breast Cancer
Your pathology report and your healthcare providers may describe your breast cancer as estrogen receptor , progesterone receptor or human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 positive or negative. Or, they may say that your breast cancer is triple negative or triple positive.
Estrogen and progesterone receptors are proteins found in some cancer cells that allow a hormone to attach and feed the cancer cells. Hormone receptor status is reported as positive or negative and sometimes a percent is also provided. For example, 90% estrogen receptor positive. ER/PR+ breast cancers will, at a minimum, receive some form of hormone therapy such as Tamoxifen.
HER2 is a protein involved in normal cell growth, which may also be present on breast cancer cells. If too much of the HER2 protein is produced, the tumor is considered HER2+ . Breast cancers that are HER2+ will receive HER2 directed therapy such as Herceptin.
Triple positive breast cancer is positive for HER2, ER and PR. You will receive HER2 directed therapies as well as hormone therapy.
Triple negative breast cancer is negative for HER2, ER and PR. Therefore, HER2 directed therapy and hormone therapy are not utilized. Typical treatment is chemotherapy.
Related Topics
Read Also: What Are The Early Warning Signs Of Breast Cancer
How Is Lobular Breast Cancer Diagnosed
Your doctor will likely order a mammogram and ultrasound to look for abnormal breast tissue. A breast MRI scan is a more sensitive test for detecting breast cancer. Your doctor may order this test if you are at higher risk of breast cancer or if mammogram or ultrasound findings raise concerns that should be investigated further.
If abnormal breast tissue is seen on breast imaging, a small sample of tissue is taken from the area of concern using a needle and examined under a microscope. The results of the biopsy either confirm or rule out a diagnosis of breast cancer.
Concluding Remarks And Future Directions

In this review, we have cited evidence that myoepithelial cells in both mice and human mammary glands originate from a suprabasal cell type within the luminal epithelial compartment within the adult breast. Furthermore, we discuss observations that normal myoepithelial cells are critical for correct polarity of luminal epithelial cells, most likely via production of laminin-1. On the other hand, the myoepithelial cells present in tumors have many traits in common with normal myoepithelial cells, but show either complete absence or reduced expression of laminin-1 and are thus unable to induce the polarization of luminal epithelial cells.
In summary, although much remains to be learned, the role of myoepithelial cells as possible tumor suppressors may include their function as a guardian of ânormalcy,â being a paracrine inhibitor of invasion in early breast cancer as well as a target for differentiation therapy by inducing malignant cancer cells to differentiate along the myoepithelial pathway to a less devastating cell type.
You May Like: Is Triple Positive Breast Cancer Curable